![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the number one risk factor for low back pain (LBP)?
|
Genetics
|
|
|
ankylosing spondylitis has a relationship with what disease?
|
inflammatory bowel disease
|
|
|
What injury has an increased risk with osteoporosis ?
*****TEST |
vertebral compression fractures
because the bone quality is not as good |
|
|
must know ligamentous attachments of sacrum
|
sucks.
|
|
|
iliolumbar ligament attachments
|
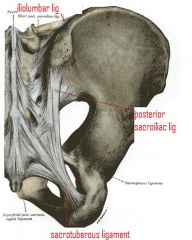
origin-transverse process of L5
attaches to medial aspect of the posterior corner of the iliac crest |
|
|
posterior sacroiliac ligament attachements?
|
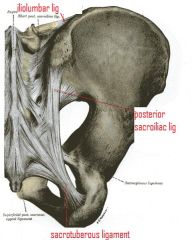
1st, second, and 3rd transverse tubricle of the sacrum
to the posterior superior iliac spine |
|
|
sacrotuberous ligament attachment
|
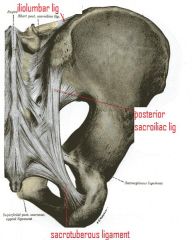
From sacrum
To tuberosity of the ischium |
|
|
gluteus maximus attachments?
|
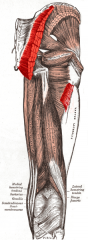
P: Ilium and sacrum, D: Iliotibial tract and gluteal tuberosity
|
|
|
gluteus medius attachment
|
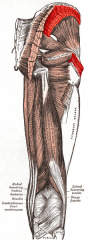
P: Ilium, D: Greater trochanter
|
|
|
gluteus minimus attachment
|
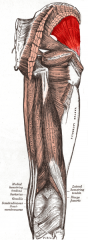
P: Ilium, D: Greater trochanter
|
|
|
this pain is only in the back and/or buttock area without radiation into the legs
|
Axial
|
|
|
this pain is Caused by non-nerve injuries such as muscle, tendon, ligament or disc damage, arthritis or fractures
|
axial
|
|
|
pain usually in the legs > back, often with leg numbness, tingling or weakness
type of pain? |
Radicular
|
|
|
Caused by nerve irritation/injury such as nerve root impingement by herniated disc or arthritis
type of pain? |
Radicular
|
|
|
pain usually in the back > legs, with normal neurologic exam
type of pain? |
Pseudoradicular
|
|
|
Caused by referred pain from injured non-nerve structures such as muscles, tendons, ligaments or joints
type of pain? |
Pseudoradicular
|
|
|
a patient has pain that is on the iliac crest, and has pain that shoots down the back of the leg. You ask if the pain is found behind the knee, specifically at the joint. The patient says that the pain skips the knee. What kind of back pain is it?
|
pseudoradicular b/c it skips the joint
|
|
|
posterior sacroiliac ligament
please list referred areas of pain |
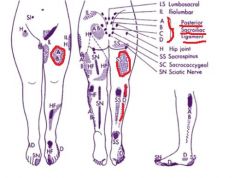
Posterior thigh and calf pain
anterior thigh pain |
|
|
iliolumbar ligament
please list referred areas of pain |
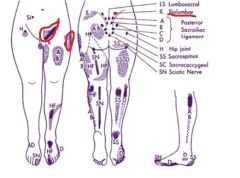
posterior on iliac crest
lateral hip inguinal |
|
|
patient says taht they have leg pain that is worse than their back pain (what kind of pain is this?) and says they have some numbness/weakness.
what is this likely? Emergency or seek attention? |
radicular pain
nerve damage seek attention |
|
|
if pain wakes a patient in the middle of the night
Emergency or seek attention? |
seek attention
|
|
|
person has pain with balance or bowel/bladder problems... what is this likely?
Emergency or seek attention? |
spinal cord damage
seek attention |
|
|
Pain after a significant injury (car accident, bad fall, bad sports/recreational injury) what could this be
Emergency or seek attention? |
tissue damage such as fracture, disc damage, or severe strain or sprain
seek attention |
|
|
Progressively worsening pain despite relative rest, ice/heat, and over-the-counter medicines
Emergency or seek attention? |
seek attention
|
|
|
Significant or worsening weakness in the legs with or without pain
what could this be? Emergency or seek attention? |
severe nerve or spinal cord damage
emergency |
|
|
Acute changes in bowel or bladder function with or without pain
what could this be? Emergency or seek attention? |
conus medullaris syndrome.
emergency |
|
|
Numbness along the insides of both thighs (“saddle anesthesia”)
what could this be? Emergency or seek attention? |
cauda equina syndrome.
emergency |
|
|
Acute back pain with fever, chills, and/or night sweats
what could this be? Emergency or seek attention? |
infection of the spine.
emergency |
|
|
Acute back pain with a tearing sensation and bounding pulse in the stomach area
what could this be? Emergency or seek attention? |
dissecting or ruptured aortic aneurysm
emergency |
|
|
a patient with pain with a structural origin (e.g. arthritis, myofascial, ligamentous or tendinous dysfunction) and/or functional deficits (e.g. decreased strength, flexibility, activity tolerance, work capacity) should see what type of physician
|
Musculoskeletal physiatrist
|
|
|
if a patient has well-localized pain generators without profound neurologic deficits (e.g. painful radiculopathy, facet arthropathy, discogenic pain), unresponsive to other conservative treatments such as physical therapy, OMT, or medications what type of physician should they see?
|
Interventional pain specialist (spinal injections under fluoroscopic guidance)
|
|
|
patient has Localized pain with/without pain in other joint areas, particularly the hands, and associated findings such as rash (e.g. lupus, psoriatic arthritis, dermatomyositis) or lab abnormalities (e.g. elevated ESR, ANA or rheumatoid factor).
who should they see ? |
Rheumatologist
|
|
|
patient has peripheral neurologic deficits without an identifiable structural cause (low motor neuron lesions, e.g. peripheral neuropathy, ALS), or central nervous system deficits (upper motor neuron lesions, e.g. multiple slerosis, stroke, ALS
who should they see |
Neurologist
|
|
|
person has profound and/or emergent neurologic deficits from structural causes (e.g. large disc herniation causing severe radiculopathy, spondylosis causing severe spinal stenosis), unresponsive to other treatments such as medications or spinal injections
who should they see? |
Neurosurgeon
|
|
|
most important! Often this is all that is needed to make the diagnosis.
what diagnostic test? |
History & Physical exam
|
|
|
good for bones (e.g. fractures, arthritis, alignment and dynamic stability with flexion/extension views).
what diagnostic test? |
Plain radiograph (X-ray):
|
|
|
excellent for bones, discs, joints, nerves, soft tissue.
what diagnostic test? |
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging):
|
|
|
excellent for bony anatomy (e.g. complex fractures, arthritis, alignment)
what diagnostic test? |
CT (computed tomography):
|
|
|
pt comes in with history of prostate cancer and some back pain. Should he use an MRI or Nuclear Bone Scan?
|
Nuclear Bone Scan
|
|
|
excellent for bone metabolism (e.g. fractures, tumors). (gets whole spine)
what diagnostic test? |
Nuclear bone scan (nuclear scintigraphy
|
|
|
excellent for vascular problems (aneurysms, aortic dissection, and arterial stenosis
what diagnostic test? |
Angiogram
|
|
|
burns the nerves that transmit pain signals from the facet joints, long-lasting
what treatment is this? |
Radiofrequency ablation
|
|
|
minimally invasive, cements and stabilizes compression fractures
what treatment is this? 2 |
Vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty
|
|
|
spondylosis
spondylolysis spondylolisthesis NEED TO KNOW**** |
spondylosis:arthritis of the spine
spondylolysis: fracture at the pars spondylolisthesis: decapitation of the pars, entire lumbar segment slides forward |
|
|
a patient is having problems with sensation of their inner thigh closet to the pubic bone, what spinal root is this most likely due to?
|
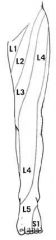
L1
|
|
|
a patient is having sensation problems starting from the outer hip down the middle of the thigh, extending down the shin to the medial ankle. What is the problem?
|
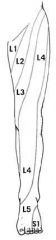
problem with L4 spinal root
|
|
|
patient is having problems with sensation on the top of their foot including their big toe.. what is the problem?
|
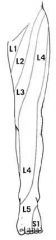
L5 spinal root
|
|
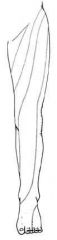
fill in the associated dermatomes
|
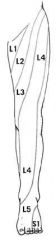
|
|
|
patient is a gymnast who has pain worse with flexion or extension. You see a step-off sign at spinous process, paraspinal spasm, and foraminal narrowing causing rediculopathy. What does this patient have?
|
spondylolistheis
|
|
|
patient has a radiograph with"Scottie dog" neck broken. What does this patient have?
|
spondylolisthesis
|

