![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
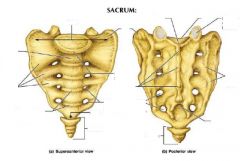
|
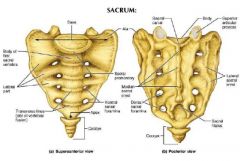
|
|

|
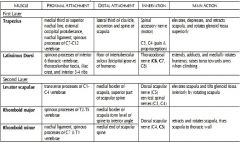
|
|
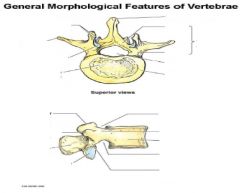
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Identify the components of a typical synovial joint (3)....
|
1. Capsule that enclose joint cavity
2. Bursae 3. Articular discs (meniscus, menisci) |
|
|
What are components of the joint capsule?
|
1. Fibrous Capsule- made of dense connective tissue
2. Accessory ligament- "intrinsic ligament" 3. Synovial lining- has fluid |
|
|
What are the (6) types of synovial joints?
|
1. Plane
2. Hinge 3. Saddle 4. Condyloid (bicondylar) 5. Ball and socket 6. Pivot |
|
|
What type of joint is the following...
a. elbow b. carpal bones, acrmioclavicular c. knee joint |
a. hinge
b. plane c. condyloid |
|
|
What type of joint is the following...
a. uniaxial b. flexion and extension only c. "gliding joints" d. flexion/extension and adduction and abduction (only) |
a. plane, hinge, or pivot
b. hinge c. plane d. saddle and condyloid (bicondylar) |
|
|
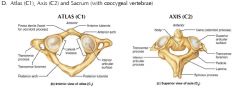
What type of joint is the following...
a. pivot around axis b. Atlantoaxial joint (C1-C2) c. hip and shoulder d.Concave in one direction and convex in the other |
a. Pivot
b. pivot c. ball and socket d. saddle |
|
|
What type of joint is the following...
a. multiaxial b. flexion/extension, AB/ADduction, and rotation c. interphalangeal joints d. carpal bones |
a. ball and socket
b. ball and socket c. Condyloid (bicondylar) d. plane |
|
|
What type of joint is the following...
a. proximal radioulna joint |
a. pivot
|
|
|
Define and give characteristics of typical fibrous joint and example...
What is a syndesmosis and how does it relate to fibrous joints? |
-Held together by fibrous tissue (sutures of skull) and have little movement
- Syndesmosis- a fibrous joint held together by a sheet of fibrous tissue which is somewhat moveable |
|
|
Give examples and explain differences in fribrous joints...
|
a. sutures in skull
b. interosseous membranes- (radius/ulna, tibia/fibula) (syndesmosis) |
|
|
What is a typical Cartilaginous joint and what are two main types?
|
-Joint held together by fibrocartilage or by hyaline cartilage
a. Primary (synchondrosis)- united by hyaline cartilage b. Secondary (symphysis)- held together by fibrocartilage |
|
|
Explain primary cartilaginous joints and give examples
Explain secondary cartilaginous joints and give examples |
AKA synchondrosis- united by cartilage
a. temporary in growth ex. epiphysis of long bone AKA symphasis- held together by fibrocartilage a. somewhat movable, variable ex. intervetebral disks, pubic symphysis |
|
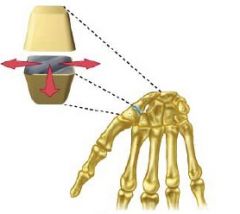
What type of joint?
|
synovial- plane joint
|
|
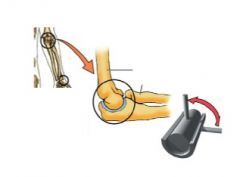
What type of joint?
|
synovial- hinge joint
|
|
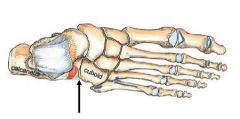
What type of joint is this?
|
Synovial- saddle joint
|
|

What type of joint?
|
synovial- condyloid (bicondylar) joint
|
|

What type of joint?
|
synovial- ball and socket joint
|
|
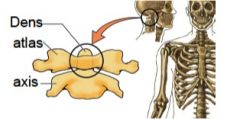
what type of joint?
|
synovial- pivotjoint
|
|
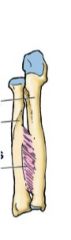
What type of joint?
|
Fibrous- syndesmosis
|
|
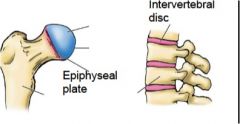
what type of joints?
|
primary and secondary Cartilaginous
|
|
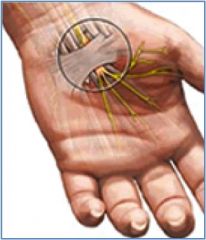
What are the two arrows pointing to?
|
Transverse carpal ligament and median nerver
|
|
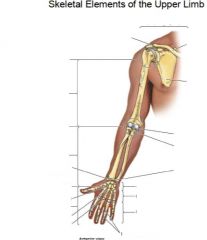
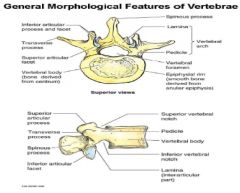
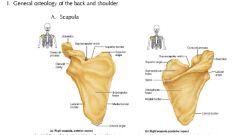
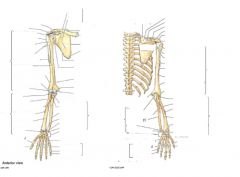
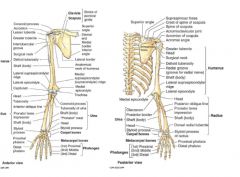
What are the landmarks?
|
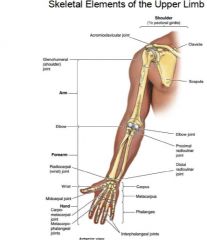
|
|
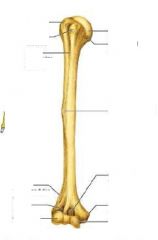
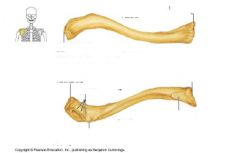
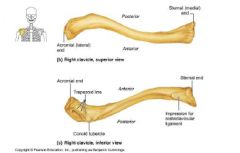
What are labels on arm bone?
|
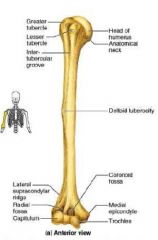
|
|
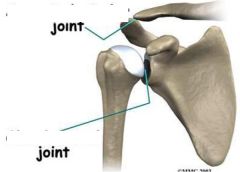
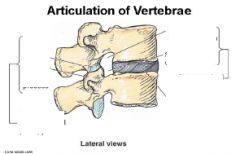
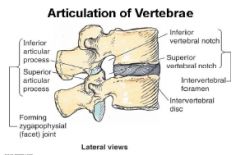
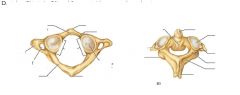
What joints are shown?
|
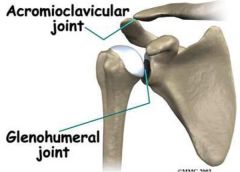
|
|

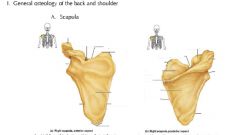
Label points
|
|
|
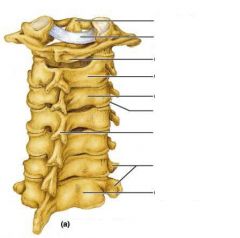
label
|
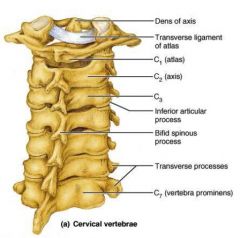
|
|
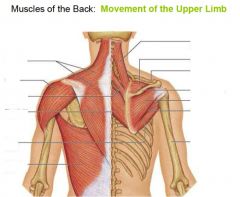
label
|
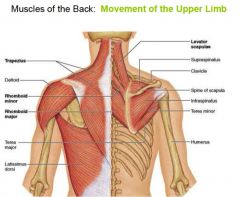
|
|
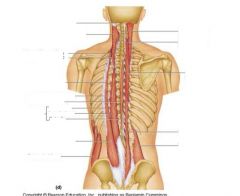
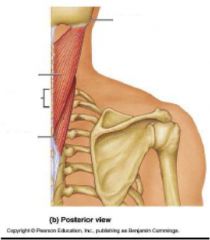
What is role of these muscles?
|
maintain posture
|
|
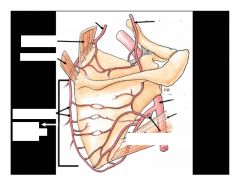
Identify blanks...
|
|
|
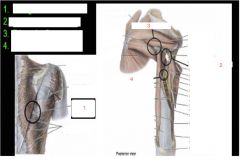
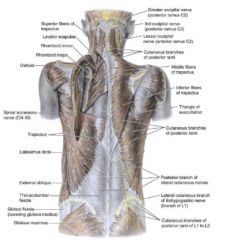
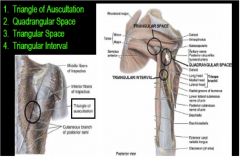
Identify the spaces of the back and the rest of the muscles
|
|
|
Label the spots
|
|
|
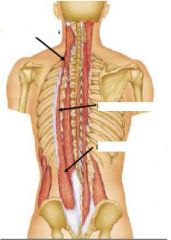
Label parts
|
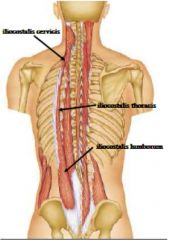
|
|
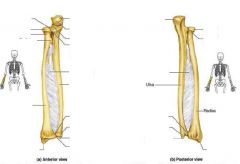
Name the lines
|
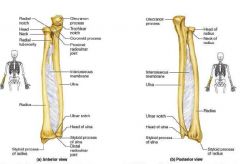
here are them answers!
|
|
|
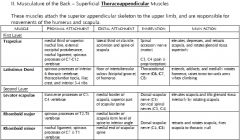
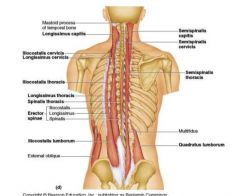
What back muscles make up the hypaxial groups and what are innervations?
|
All are expaxial
1. Trapezoid- motor- Spinal accessory C11 sensory C3, C4 2. Latissimus Dorsi- Thoracodorsal nerve C6, 7 and 8 3. Levator Scapulae- Cervical spinal nerves C3, C4 and dorsal scapular C5 4. Rhomboid Major/ Minor- Dorsal scapular C4, C5 |
|
|
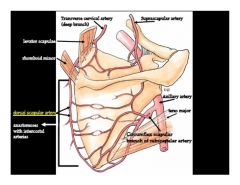
Where does the following back muscles receive blood from?
a. latissimus dorsi b. trapezius c. rhomboid major |
a. thoracodorsal artery
b. superficial branch of transverse cervical artery c. deep branch of transverse certical artery d. |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and innervations of the following...
a. rhomboid major b. rhomboid minor c. levator scapula |
a. Origin- T2-5 spinous process,Insertion- medial border of scapula from level of spine to inferior angel, Nerve- Dorsal scapular C4,5
b. Origin C7-T1 spinous process, Insert- medial end of spine on scapula Nerve- Dorsal scapular C4-5 c. Origin- posterior turbercles of transverse process of C1-4 Insert- medial border scapula and superior spine of scapula, Nerve- Cervical spinal nerves- C3,4, Dorsal scapular C5 |
|
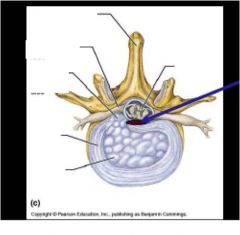
Label this, what does the blue arrow show? In a traumatic injury to the lumbar region what part of this section goes out?
|
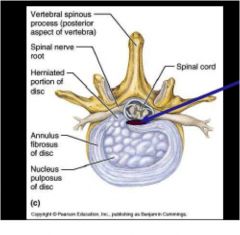
blue arrow- posterior longitudinal ligament
|
|

what does picture show?
|
normal cervical spine nerve root and cord
|
|

what does this show?
|
central stenosis
|
|
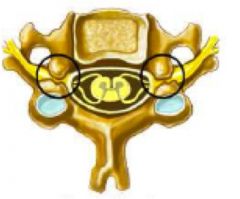
what does spinal nerve root cross section show?
|
foraminal stenosis
|
|
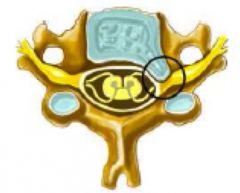
what does this spinal nerve root cross section show?
|
herniated disc
|
|
|
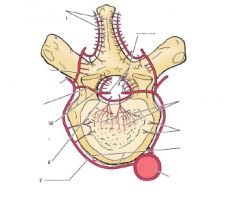
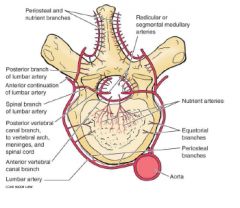
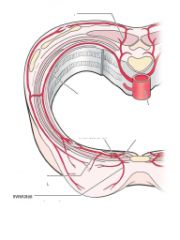
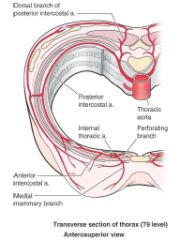
What are the arteries to these parts of vertebrae...
a. cervical region b. thoracic |
a. vertebral and cervical arteries
b. posterior intercostal arteries |
|
|
What are the arteries to these parts of vertebrae...
a. lumbar region b. sacral region |
a. subcostal and lumbar arteries
b. iliolumbar arteries, and medial and lateral sacral arteries |
|
|
What provides the venous drainage for the vertebra? (4 veins)
|
1. internal vertebral venous plexus
2. external vertebral venous plexus 3. basivertebral veins 4. intervertebral veins |
|
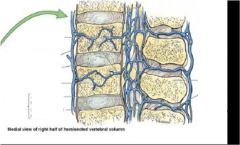
Label the above medial view of right half of hemisected vertebral column
|
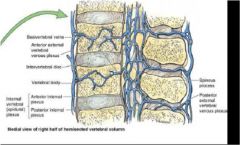
|
|
|
Label 1 through 4
|
1. arachnoid mater
2. dura mater 3. pia mater 4. denticulate ligament |
|
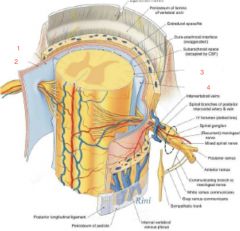
Label 1 through 4
|
1. arachnoid mater
2. dura mater 3. pia mater 4. denticulate ligament |
|
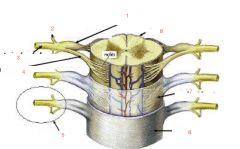
Label one through eight
|
1. dorsal root & ganglion
2. dorsal ramus 3. ventral ramus 4. ventral ramus 5. spinal nerve 6. dura mater 7. arachnoid mater 8. pia mater |

