![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What does a group of functionally related muscles form?
|
They form compartments that are separated from others by connective tissue fascia.
|
|
|
|
The origin of a muscle...
|
Attaches to bone at the stationary end.
|
|
|
|
The insertion attaches...
|
To the bone at the mobile end.
|
|
|
|
Muscles and portions of muscle...
|
Are wrapped by connective tissue in multiple ways.
|
|
|
|
What does fascia cover?
|
It covers the entire muscle or a portion of a muscle.
|
|
|
|
What does epimysium do?
|
It is deep to the fascia and invaginates to wrap many muscle fibers into structures called fascicles.
|
|
|
|
What is a perimysium?
|
It is the connective tissue that is wrapped around the fascicles.
|
|
|
|
What does perimysium form?
|
It inviginates to form endomysium, and they wrap around individual muscle cells.
|
|
|
|
What do muscles do?
|
They cooperate with each other to provide proper movements.
|
|
|
|
What is agonist mean?
|
The agonist is the "prime mover" in the muscle that produces most of the force for a specific movement.
|
|
|
|
What is agonist mean?
|
The agonist is the "prime mover" in the muscle that produces most of the force for a specific movement.
|
|
|
|
A synergist is...
|
A muscle that assists the prime mover.
|
|
|
|
What is agonist mean?
|
The agonist is the "prime mover" in the muscle that produces most of the force for a specific movement.
|
|
|
|
A synergist is...
|
A muscle that assists the prime mover.
|
|
|
|
The antagonist is...
|
Is a muscle that opposes the prime mover. To help the muscle relax or maintain some tension.
|
|
|
|
What is agonist mean?
|
The agonist is the "prime mover" in the muscle that produces most of the force for a specific movement.
|
|
|
|
A synergist is...
|
A muscle that assists the prime mover.
|
|
|
|
The antagonist is...
|
Is a muscle that opposes the prime mover. To help the muscle relax or maintain some tension.
|
|
|
|
What is a fixator?
|
It is a muscle which holds a bone steady to prevent its movement which would otherwise affect attempted movements elsewhere.
|
|
|
|
What is agonist mean?
|
The agonist is the "prime mover" in the muscle that produces most of the force for a specific movement.
|
|
|
|
A synergist is...
|
A muscle that assists the prime mover.
|
|
|
|
The antagonist is...
|
Is a muscle that opposes the prime mover. To help the muscle relax or maintain some tension.
|
|
|
|
What is a fixator?
|
It is a muscle which holds a bone steady to prevent its movement which would otherwise affect attempted movements elsewhere.
|
|
|
|
What is the other name of skeletal muscle cells?
|
Muscle fibers because they are so long.
|
|
|
|
What is agonist mean?
|
The agonist is the "prime mover" in the muscle that produces most of the force for a specific movement.
|
|
|
|
A synergist is...
|
A muscle that assists the prime mover.
|
|
|
|
The antagonist is...
|
Is a muscle that opposes the prime mover. To help the muscle relax or maintain some tension.
|
|
|
|
What is a fixator?
|
It is a muscle which holds a bone steady to prevent its movement which would otherwise affect attempted movements elsewhere.
|
|
|
|
What is the other name of skeletal muscle cells?
|
Muscle fibers because they are so long.
|
|
|
|
What is the plasma membrane of a muscle fiber?
|
Sarcolemma
|
|
|
|
The cytoplasm of the in the muscle fibers is...
|
Sarcoplasm
|
|
|
|
Myofibrils a.k.a myofilaments is...
|
Large number of contractile elements that are in the muscle fibers.
|
|
|
|
Myofilaments exists as...
|
Myosin, actin, or elastic filaments
|
|
|
|
Myosin...
|
Thick filaments
|
|
|
|
Actin...
|
Thin filaments
|
|
|
|
What does mycrofilaments help?
|
Help form the functional unit of muscle fibers called sarcomere.
|
|
|
|
The sacomeres are attached...
|
To each other length wise.
|
|
|
|
What causes the entire muscle to contract?
|
The sarcomere length gets shorten upon contraction.
|
|
|
|
What is the striations of sarcomeres?
|
It is a repeating pattern of dark A bands and light I bands.
|
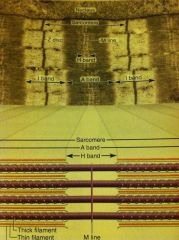
|
|
|
What are the striations from?
|
The pattern of myosin a and actin.
|
|
|
|
The impulse for a contraction in a muscle
|
1.impulse of a motor neuron at is terminal.
2. Release of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine into a synaptic cleft. 3.acetylcholine binds to their receptors in the muscle fibers sarcolemma that opens ion channels. 4.Na enters the muscle cell through ion channels and causes depolarization. (Impulse) 5.impulse goes through the sarcolemma and T tubules and causes release Ca into sarcoplasm. 6.Ca binds troponin on the actin filaments moves tropomycin away from actins binding site for myosin. 7.myosin is able to bind to actin and reaches forward causing thin filaments to move towards the center of the sarcomere shortening the sarcomere |
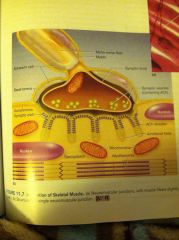
|
|
|
Muscle twitch is...
|
A quick contraction and relaxation due to single, brief stimulus. (Nerve impulse)
|
|
|
|
Twitches happen because...
|
Very in strength depending in stimulus frequency.
|
|
|
|
What is a treppe (staircase) twitch?
|
An increase if strength from more frequent stimulus but the muscle still recovers fully b/w twitches.
|
|
|
|
Why does a treppe twitch happen?
|
Greater Ca2 in the sarcoplasm because the SR does not have time b/w stimuli to completely reabsorb all the Ca2.
|
|
|
|
Why does a treppe twitch happen?
|
Greater Ca2 in the sarcoplasm because the SR does not have time b/w stimuli to completely reabsorb all the Ca2.
|
|
|
|
Incomplete tetanus show...
|
Increasing strength from more frequent stimulation but the muscle does not recover b/w twitches. Each twitch happens before the previous twitch is over with "rides piggy back" which creates higher tension.
|
|
|
|
Why does a treppe twitch happen?
|
Greater Ca2 in the sarcoplasm because the SR does not have time b/w stimuli to completely reabsorb all the Ca2.
|
|
|
|
Incomplete tetanus show...
|
Increasing strength from more frequent stimulation but the muscle does not recover b/w twitches. Each twitch happens before the previous twitch is over with "rides piggy back" which creates higher tension.
|
|
|
|
Complete tetanus...
|
Twitches fuse into a smooth prolonged contraction that has no time to relax b/w stimuli and produces 4x the tension as a single twitch.
|
|
|
|
Why does a treppe twitch happen?
|
Greater Ca2 in the sarcoplasm because the SR does not have time b/w stimuli to completely reabsorb all the Ca2.
|
|
|
|
Incomplete tetanus show...
|
Increasing strength from more frequent stimulation but the muscle does not recover b/w twitches. Each twitch happens before the previous twitch is over with "rides piggy back" which creates higher tension.
|
|
|
|
Complete tetanus...
|
Twitches fuse into a smooth prolonged contraction that has no time to relax b/w stimuli and produces 4x the tension as a single twitch.
|
|
|
|
Isotonic concentration occurs when...
|
1.Muscle changes in length but not in tension.
2.Muscle changes in tension but not in length. |
|
|
|
What do all muscle contractions depend on?
|
ATP
|
|
|
|
What do all muscle contractions depend on?
|
ATP
|
|
|
|
ATP supply depends on what?
|
Availability of oxygen and food molecules (glucose & fatty acid)
|
|
|
|
What do all muscle contractions depend on?
|
ATP
|
|
|
|
ATP supply depends on what?
|
Availability of oxygen and food molecules (glucose & fatty acid)
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 pathways for ATP synthesis?
|
1.Anaerobic fermentation: enables cells to produce ATP in absence of oxygen.
2.Aerobic respiration: requires a continual supply of oxygen. |
|
|
|
What do all muscle contractions depend on?
|
ATP
|
|
|
|
ATP supply depends on what?
|
Availability of oxygen and food molecules (glucose & fatty acid)
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 pathways for ATP synthesis?
|
1.Anaerobic fermentation: enables cells to produce ATP in absence of oxygen.
2.Aerobic respiration: requires a continual supply of oxygen. |
|
|
|
What does anaerobic fermentation produce?
|
Lactic acid;major factor in muscle fatigue
|
|
|
|
What do all muscle contractions depend on?
|
ATP
|
|
|
|
ATP supply depends on what?
|
Availability of oxygen and food molecules (glucose & fatty acid)
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 pathways for ATP synthesis?
|
1.Anaerobic fermentation: enables cells to produce ATP in absence of oxygen.
2.Aerobic respiration: requires a continual supply of oxygen. |
|
|
|
What does anaerobic fermentation produce?
|
Lactic acid;major factor in muscle fatigue
|
|
|
|
Aerobic respiration produces...
|
CO2 and water
|
|
|
|
What happens during strenuous exercise?
|
Oxygen debt develops.
|
|
|
|
What happens during strenuous exercise?
|
Oxygen debt develops.
|
|
|
|
What happens after excessive exercise?
|
Heavy breathing continues to replace the used up oxygen.
|
|

