![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Muscles |
Produce movement by Contracting in response to nerve stimulation. |
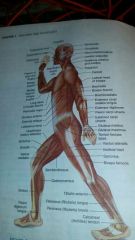
|
|
|
Muscle contractions |
Sliding together of actin and myosin filaments within the muscle cell or Fiber |
|
|
|
What does muscle cells consist of? |
Myofibrils which in turn are made up of still smaller units called sacromeres |
|
|
|
What should be present in order for a muscle cell to contract? |
Calcium and ATP |
|
|
|
What causes the release of calcium ions the sarcoplasmic reticulum? |
Nervous stimulation from motor neurons |
|
|
|
How do muscles contract? |
Calcium ions attach to inhibitory proteins on the actin filaments within the cell, moving them aside so that cross-bridges can form between actin and myosin filaments. Using energy supplied by ATP the filaments slide together to produce contraction. |
|
|
|
What skeletal muscles make up the muscular system? |
Voluntary muscles |
|
|
|
Voluntary muscles |
Under conscious control |
|
|
|
Involuntary muscles |
your heart, which keeps beating all day and night. Other involuntary muscles help digest food and are found in your stomach and intestines. It takes guts to be an involuntary muscle! |
|
|
|
How does skeletal muscles work? |
They work in pairs |
|
|
|
Prime mover |
The muscles that executes the given movement |
|
|
|
Antagonist |
The muscle that produces the opposite movement |
|
|
|
Synergists |
May work in cooperation with the prime mover |
|
|
|
Flexor |
Reduce angle at joint |
|
|
|
Extensor |
Increase the angle |
|
|
|
Abductors |
Draw a limb away from the midline |
|
|
|
Adductors |
Return the limb back toward the body |
|

