![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
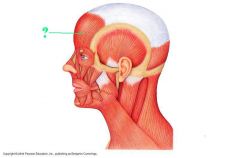
raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead
|
Frontalis
|
|
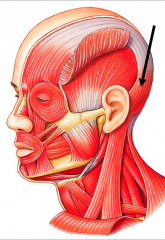
pulls scalp posteriorly
|
Occipitalis
|
|
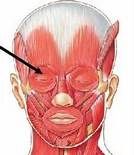
closes eye; produces winking, blinking, squinting ("blink" muscle)
|
Orbicularis Oculi
|
|
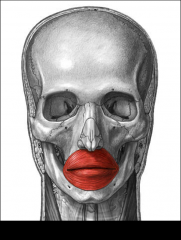
Closes and protrudes lips; used in whistling and forming many letters during speech; the "kissing muscle"
|
Orbicularis oris
|
|
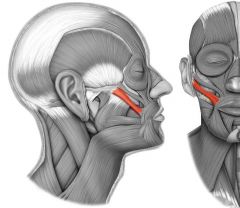
elevates corner of mouth; "smiling" muscle
|
Zygomaticus
|
|
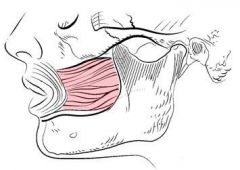
compresses cheek as in blowing sucking whistling; holds food between teeth during chewing
|
Buccinator
|
|
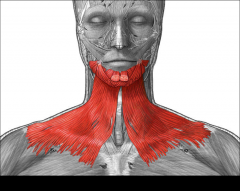
Draws down the lower lip and angles of the mouth; tenses skin of the neck; helps depress mandible
|
Platysma
|
|
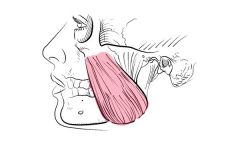
chewing muscle; closes mouth
|
Masseter
|
|
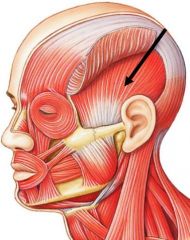
closes jaw, elevates and retracts mandible
|
Temporalis
|
|
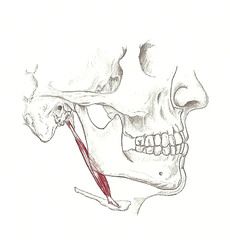
Elevates and retracts hyoid bone"swallow"
|
Stylohyoid
|
|
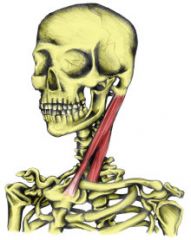
flexes neck; rotates head
|
Sternocleidomastoid
|
|
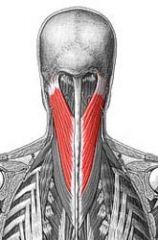
Extends head
|
Splenius capitus
|
|
|
The function of the muscular system is to:
|
Provide movement and change in body position relative to environment
|
|
|
What are the 4 characteristics of muscle fibers?
|
Elastic Excitable Extensible Contractable
|
|
|
Name the 3 types of muscle tissues.
|
Smooth Skeletal Cardiac
|
|
|
Fibrous connective tissue that surrounds the entire muscle
|
Epimysium
|
|
|
Connective tissue that surrounds individual muscle fibers
|
Endomysium
|
|
|
Individual bundles of muscle fibers
|
Fasicluli(pl.) Fasicle(s.)
|
|
|
Connective tissue that surrounds individual fasciculi
|
Perimysium
|
|
|
Fibrous connective tissue, continuous with mysium that connects muscle to bone
|
Tendon
|
|
|
Connective tissue that extends as a flat, broad layer
|
Aponeurosis
|
|
|
Name the 8 arrangement types of fasciculi
|
Parallel Quadrilateral Fusiform Convergent Pennate Unipennate Bipennate Circular
|
|
|
What are the major characteristics of parallel muscles?
|
Long, strap-like and run parallel to longitudinal axis. EX. Sartorius and rectus abdominus
|
|
|
Give an example of a quadrilateral muscle.
|
Stylohyoid muscle
|
|
|
What are the major characteristics of fusiform muscles?
|
Nearly parallel to longitudinal axis and terminate at either end in flat tendons. EX. Biceps brachii
|
|
|
What are the major characteristics of convergent muscles?
|
Broad fascicle origin with narrow insertions and are triangle or fan shaped. EX. Deltoid and Pectoralis major
|
|
|
What are the main characteristics of pennate muscles?
|
Short, obliquely directed fasciculi with tendons that extend nearly the entire muscle and tire quickly.
|
|
|
Pennate muscles with fasciculi only on 1 side of a tendon are called:
|
Unipennate muscles EX. Extensor digitorum longus
|
|
|
Pennate muscles with fasciculi on both sides of a centrally located tendon are called:
|
Bipennate muscles EX. Rectus femoris
|
|
|
Circular muscles:
|
Enclose an orfice and act as a sphincter with fasciculi arranged in a circular pattern EX. Orbicularis oris
|
|
|
Muscle origins are attached to more_______bones, while insertions attach to more______structures.
|
Stationary, Moveable
|
|
|
Flexors
|
Decrease the angle between joints
|
|
|
Extensors
|
Increase the angle between joints
|
|
|
Abductors
|
Move a body part away from the midline
|
|
|
Adductors
|
Move a body part closer to the midline
|
|
|
Levators
|
Produce upward movement
|
|
|
Depressors
|
Produce downward movement
|
|
|
Pronators
|
Rotate forearm and turn palm posteriorly
|
|
|
Supinators
|
Rotate forearm and turn palm anteriorly
|
|
|
Sphincter
|
Circular muscle that constricts a body opening
|
|
|
Tensor
|
Makes a body part more rigid
|
|
|
Rotator
|
Moves a bone around its own longitudinal axis
|
|
|
Name the 4 muscles that comprise the rotator cuff tendon.
|
Subscapularis Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor
|
|
|
Name the 3 muscles that make up the hamstring.
|
Biceps femoris
Semitendinosus Semimembranosus |
|
|
Name the 7 criteria used when naming muscles.
|
Direction of fibers Shape
Location Origin and Insertion point Size Actions of movement Number of origins |

