![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
128 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
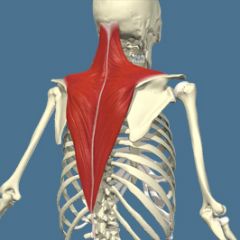
Trapezius Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Back of the skull C7, all of thoracic vertebrae,
Insertion: Spine of Scapula and lateral edge of clavicle. |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Trapezius 4 movements |
Upper fibres Elevate the shoulder girdle and extend the neck
Middle Fibres retract the shoulder girdle
Lower fibres depress the shoulder girdle
the whole muscle upwardly rotates the scapula and works as a synergist with serratus anterior |
|
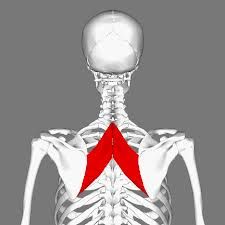
Rhomboids Name the Origin and insertion points |
Origin Spinous Processes of the Cervical and Thoracic vertebrae (C7 and T1-T5)
Insertion: Medial Border of the Scapula |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Rhomboids 2 movements |
Retracts the Scapula Downwardly rotates the scapula (works as a synergist with Pectorialis Minor) |
|
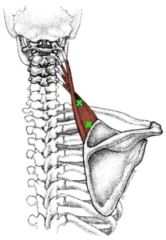
Name the Muscle |
Levator Scapulae |
|
|
Levator Scapulae Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Transverse processes of the Cervical Vertebrae (C1-C4)
Insertion: Medial Border of the Scapulae, between superior angle and the root of the spine of the scapula |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Levator Scapulae 3 movements |
Elevates the scapula Assists in downward rotation of the scapula Laterally flexes the neck (insertion fixed) |
|
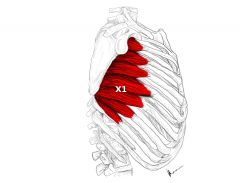
Name the muscle |
Serratus anterior |
|
|
Serratus anterior Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Front of the Ribs 1-8
Insertion: Anterior surface of the medial border of the scapula |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Serratus anterior 2 movements |
Protract the Scapula
Upwardly rotates the scapula |
|
|
What Muscle works as a synergist with the trapezius |
Serratus Anterior |
|
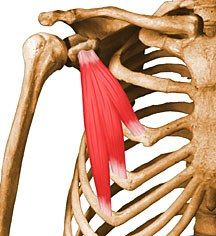
Name the muscle |
Pectoralis Minor |
|
|
Pectoralis Minor Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Front of the Ribs 3-5
Insertion: Coracoid process of the Scapula |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Pectoralis Minor 3 movements |
Protracts the Scapula Downwardly rotates the Scapula Elevates the rib cage during breathing |
|
|
What works as a synegist with the Rhomboids |
Pectoralis Minor |
|
|
Deltoids Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Clavicle (anterior Head) Acromion (medial head) and spine of the scapula (posterior head)
Insertion: Lateral surface of the humorous (nearly half way down) |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Deltoids 3 movements |
Anterior Fibres Flex the shoulder and assist in horizontal flexion
All Fibres Abduct the shoulder
Posterior Fibres extend the shoulder and assist in horizontal extension |
|
|
Pectoralis Major Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Clavicle, Sternum and cartilages of ribs 1-6
Insertion: Top of humerus |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Pectoralis Major 3 movements |
Horizontal Flexion Adduction Medial Rotation |
|
|
Latissimus Dorsi Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Via thoracolumbar fascia (TLF) from spinous processes of T6-T12, Lumber and sacral vertebrae and Illiac crest, lower 3-4 ribs and bottom (inferior) edge of Scapula
Insertion: Top of the Humerus (anterior) |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Latissimus Dorsi 4 movements |
Adducts and extends the arm Assists in medial rotation of the arm Depresses the shoulder girdle via the insertion of the humerus |
|
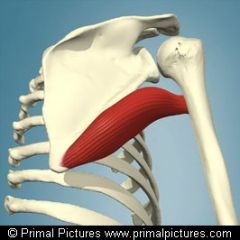
Name the Muscle |
Teres Major |
|
|
Teres Major Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Lateral Border of the scapula near the inferior angle
Insertion: Humerus (proximal, anterior) |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Teres Major 3 movements |
Medial Rotation
adduction and extension of the shoulder joint |
|
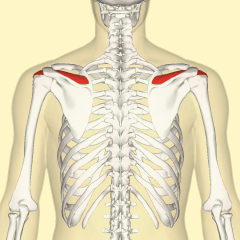
Name the muscle |
Supraspinatus |
|
|
Supraspinatus Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Superior to the spine of the scapula
Insertion: Superiorly on the head of the humerus |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Supraspinatus 2movements |
Assists Deltoid an abduction of the arm
Stabilises the shoulder joint, helping to prevent downward dislocation |
|
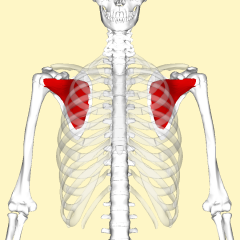
Name the muscle |
Subscapularis |
|
|
Subscapularis Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Anterior Surface of the scapula
Insertion: Anteriorly on the head of the humerus |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Subscapularis 2movements |
rotates the arm medially Stabilises the joint |
|
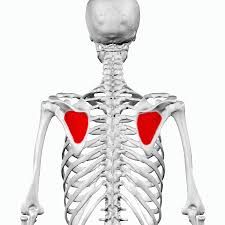
Name The muscle |
Infraspinatus |
|
|
Infraspinatus Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Inferior to spine of the scapula Insertion: Laterally on the head of the humerus
|
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Infraspinatus 2movements |
Rotates the arm laterally Stabilises the joint |
|
|
Teres Minor Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Lateral border of the scapula near the inferior angle
Insertion: Laterally on the head of the humerus |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Teres Minor 2movements |
Rotates the arm laterally Stabilises the joint. |
|
|
which of the following is not a rotator cuff muscle A: Supraspinatus B: Teres major C:Subscapularis D: Teres Minor |
B: Teres Major |
|
|
Biceps brachii Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Scapula Insertion Top of the radius and bicipital aponurosis to medial part of the forearm |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Biceps brachia 3 movements |
Flexes the elbow Supinates the forearm Assists in flexion of the forearm |
|
|
Brachialis Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Humerus Insertion: Ulna |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Brachialis 1 movements |
Flexes the elbow |
|
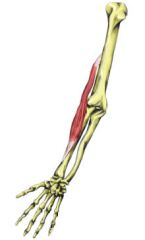
Name the muscle |
Brachioradialis |
|
|
Brachioradialis Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Laterally at the distal end of the humerus Insertion: Laterally at the distal end of the radius |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Brachioradialis 2 movements |
Flexion when the forearm is semi-pronated (drinking action) Assists other flexors |
|
|
Triceps Brachii Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Long head of the Scapula just above the shoulder joint, other two heads on the posterior of the humerus
Insertion: Olecranon of the Ulna |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Tricep Brachii 2 movements |
Extension of the elbow Assists in shoulder extension and adduction (long head only) |
|
|
Lliocostalis group Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Ribs and illiac crest Insertion: Transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae and ribs superior to origin |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Lliocostalis group 1 movements |
Extends the spine |
|
|
Longuissimus group Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Transverse processes of cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae
Insertion: Transverse processes of superior vertebrae of origin |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Longuissimus group 2 movements |
Extends the head and rotates it to the same side Extends the spine |
|
|
Spinalis Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Iliac Crest and Iliolumbar Fascia Insertion: Upper 4 lumbar vertebrae and lower margin of the 12th rib |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Spinalis 1 movements |
Extends the spine |
|
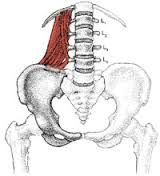
Name the muscle |
Quadratus Lumborum |
|
|
Quadratus Lumborum Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Iliac crest & Iliolumbar Fascia Insertion: Upper 4 lumbar bertebrae and lower margin of the 12th Rib |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Quadratus Lumborum 3 movements |
Unilateral concentric contraction: Lateral flexion of lumbar spine
Unilateral isometric contraction: prevents lateral flexion of lumbar spine
Bilateral eccentric contraction: assists in preventing hyper flexion of the lumbar spine |
|
|
Multifidus Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Sacrum and Transverse processes of the vertebrae Insertion: Spinous processes 2-4 vertebrae superior to the origin |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Multifidus 3 movements |
Extension of the vertebrae (bilaterally) Assists in rotation of the vertebral column (unilaterally) Assists in lateral flexion of the spine (unilaterally) |
|
|
What is the Multifidus important for? A: Thoracic Stability B: Lumber spine Stabillity C: Pelvis Stability |
B Lumber stability - local muscle, controls the fine positioning of adjacent vertebrae
|
|
|
Rectus Abdominis Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Pubis and Pubis symphasis Insertion: Cartilages of ribs 5-7 and the base of the sternum |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Rectus Abdominis 2 movements |
Flexion of the vertebral column Tilts the pelvis backwards |
|
|
External Obliques Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Outer surface of the bottom eight ribs Insertion: Mainly Linea alba, also iliac crest |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the External Obliques 2 movements |
Unilaterally: Rotation and lateral flexion (in combination with internal obliques)
Bilaterally: Flexion of the vertebral column |
|
|
Internal Obliques Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Thoracolumbar Fascia, Iliac crest Insertion: Linea Alba, bottom three ribs |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Internal Obliques 2 movements |
Unilaterally: rotation and lateral flexion ( with external obliques)
Bilaterally: flexion of the vertebral column |
|
|
Transverse Abdominis Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Thoracolumbar fascia, cartilage of the lower 6 ribs and Iliac crest
Insertion: Linea alba |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Transverse Abdominis 2 movements |
Compression of abdominal cavity, and increasing intra-abdominal pressure
Support of abdominal contents |
|
|
Which way do broad muscle fibres run in the anterior abdominal wall? |
Different angles to each other |
|
|
What muscles are the most superficial layer of the abdominals
A: rectus abdominis & transverse abdominals B: Rectus abdominis & internal obliques C: Rectus abdominis & External obliques D: Rectus abdominis & Psoas major |
C: Rectus abdominis & External obliques |
|
|
What muscles are the deepest layer of the abdominals A External Obliques B: Rectus abdominis C: internal obliques D: transverse abdominals |
D: transverse abdominals |
|
|
The tendons of abdominal muscles converge in a broad, fibrous sheet this is also known as? |
Aponeurosis |
|
|
What abdominal muscle is the top layer and can be seen in trained individuals known as a six pack? |
Rectus Abdominis |
|
|
What is not an important role of the abdominal muscles A: prevent hyperextension of the spine B: protect and support the abdominal organs C: contraction brings about intra abdominal pressure that facilitates actions such as sneezing D: acts as a sheath of connective tissue, which functions like a strong support stocking and encloses all the abdominal muscles |
D: acts as a sheath of connective tissue, which functions like a strong support stocking and encloses all the abdominal muscles |
|
|
Iliacus Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Inside surface of the Ilium
Insertion: top of the femur |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Iliacus 1movements |
Flexes the hip |
|
|
What muscle shares a tendon with Psoas major? |
Iliacus |
|
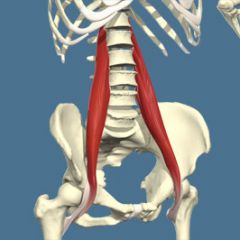
Name the muscle |
Psoas Major |
|
|
Psoas Major Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Transverse processes and intervertebral disc of all lumbar vertebrae and T 12
Insertion: Top of the femur |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Psoas Major 4 movements |
Flexes the hip (fixed origin) Pulls the trunk towards the leg (sit up action, insertion fixed)
Unilaterally: assists in lateral flexion of the trunk Stabilises lumbar spine |
|
|
Sartorius Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: anteriorly and laterally on the Iliac Crest Insertion (medially) |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Sartorius 2 movements |
Flexion and lateral rotation of the hip Flexion of the knee |
|
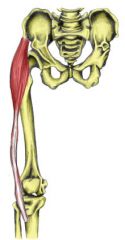
Name the muscle |
Tensor Fascia Latae |
|
|
Tensor Fascia Latae Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Crest of Ilium
Insertion: Iliotibial tract/band |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Tensor Fascia Latae 3 movements |
Flexes the hip Abducts the hip Medially rotates the hip |
|
|
Gluteus Maximus Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Base of the spine (sacrum and coccyx) and back of the ilium
Insertion: Iliotibial tract/ band and femur |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Gluteus Maximus 1 movements |
Extends and laterally rotates hip |
|
|
Gluteus Minimus Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Outer surface of the Illium Insertion: Laterally on top of the femur |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Gluteus Minimus 3 movements |
Abducts the hip Assists in turning the thigh inwards (medial rotation) Posterior fibres laterally rotates the hip when hip is flexed |
|
|
the gluteus Minimus is important in hip stabilisation during the support phase in walking/running, it prevents the pelvis dipping and the ………... |
Knees rolling in |
|
|
Gluteus Medius Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Outer Surface of the Ilium Insertion: Laterally on top of the femur |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Gluteus Medius 3 movements |
Abducts the hip Assists in turning the thigh inwards (medial rotation) Posterior fibres laterally rotates the hip when hip is flexed |
|
|
The Gluteus Medius important in hip stabilisation during the support phase in walking/running. True/ False |
True |
|
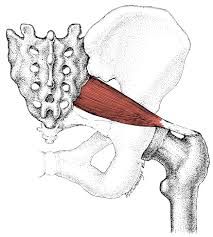
Name the muscle |
Piriformis |
|
|
Piriformis Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Anterior surface of Sacrum Insertion: Top of the Femur (greater trochanter) |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Piriformis 2 movements |
Abducts the hip Assists in lateral rotation of the hip. |
|
|
Adductor group Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Pubis Insertion Medial/posterior surface of the femur |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Adductor Group 1 movements |
Adducts the hip |
|
|
Pectineus Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Pubis Insertion: Femur |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Pectineus 2 movements |
Adducts and flexes the hip Assists in turning the thigh inwards (medial rotation) |
|
|
Gracilis Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Pubis Insertion: Top of the tibia (just below the knee) |
|
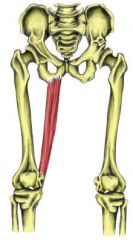
Name the muscle |
Gracilis |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Gracilis 2 movements |
Adducts the Hip Assists in knee flexion (helps the hamstring) |
|
|
What muscle is not in the hamstring group? A:Bicep Femoris B: Semmimembranosus C: Semitendinosus D: Biceps brachii |
Biceps brachii |
|
|
Hamstring group Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Ischium Short head of Bicep femoris: half way down femur
Insertion: Semimembranosus and semitendinosus - Tibia Bicep femoris - head of fibula |
|
|
Where does the Short head of Bicep femurs originate? |
half way down posterior surface of femur |
|
|
Quadricep group Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Rectus femoris: Iliac spine and top of acetabulum Vastus muscles- Femur
Insertion: front of tibia via patella tendon |
|
|
Name the muscle in the Quadricep group |
Rectus Femoris Vastus Medialis Vastus Intermedius Vastus Laterals |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Hamstring group 2 movements |
Knee Flexion Hip extension |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Quadricep group 2 movements |
all extend the knee Rectus Femoris Flexes the hip |
|
|
The Vasti muscles have a majour function of stabilising the knee joint and ensuring correct tracking of the patella during ………. and …….. |
Flexion Extension |
|
|
What muscle in the quadricep group works in the last 15 degrees of extension to keep the patella moving smoothly in the patella fossa A: Rectus Femoris B: Vastus intermedius C: Vastus Medialis D" Vastus Laterals |
C: Vastus Medialis |
|
|
Tibialis Anterior Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Lateral Condyle of tibia, Upper half of the lateral surface of the tibia and interosseous membrane
Insertion: Underside of Medial cuneiform and first metatarsal |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Tibialis Anterior 2 movements |
Ankle Dorsi flexion Sub talar joint inversion (turns the sole of the foot inwards |
|
|
Gastrocnemius Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Condyles of the femur, just above the knee
Insertion: Calcaneous via calcaneal (archilies) tendon |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Gastrocnemius 2 movements |
Ankle Planter Flexion Assists in knee flexion |
|
|
Soleus Name Insertion point and origin |
Origin: Tibia, Fibula and interosseous membrane Insertion: Calcaneus via calcaneal |
|
|
Name the joint actions of the Soleus 1 movements |
Ankle Planter flexion |
|
|
When performing a supine leg raise, what muscle is the prime mover? (1 mark) A; Psoas major B; Vastus medialis C; Rectus abdominis D; Gluteus maximus
|
A; Psoas major |
|
|
What actions are performed by the Tensor fascia latae shown in the picture?
A- Adduction and external (lateral) rotation of the hip B- Flexion and internal (medial) rotation of the hip C- Extension and internal (medial) rotation of the hip D- Elevation and external (lateral) rotation of the hip
|
B- Flexion and internal (medial) rotation of the hip |
|
|
What is the function of muscle spindle cells?
A- They respond to excessive lengthening of the muscle B- They respond to excessive contraction of the muscle C- They respond to excessive heat within the muscle D- They respond to excessive lactic acid within the muscle |
A- They respond to excessive lengthening of the muscle |
|
|
Which of the following muscles attaches to the femur and calcaneus?
a. Rectus femoris
b. Tibialis anterior
c. Gastrocnemius
d. Soleus |
c. Gastrocnemius hatW |
|
|
What attaches to the M line? A-Actin B-Myosin C-Mitochondria D-Myoglobin |
B - Myosin |
|
|
What attaches to Z Discs A- Myosin B- Sacromere C-Actin D- myoglobin |
C-Actin |
|
|
Which is charertersitic of type 1 slow twitch fibres? A- fast oxidative Fibres B- High Firing threshold C- Slow oxidative Fibres D- Anerobic glycolytic pathway |
C- Slow oxidative Fibres |
|
|
Which is charactersitic of type2a fast oxidative glycolytic fibres?
A- Contract quickly generating greater force B- Contract smoothly and gradually C- Reach maximum contraction quickly D- resistance to fatigue |
A- Contract quickly generating greater force |
|
|
Which is charactersitic of type2B fast glycolytic fibres
A- contain a large amount of Myoglobin B- Good network of Capillaries C- contain the most Actin & myosin D- contain large number of mitochondria |
C- contain the most Actin & myosin |
|
|
which of the muscle fibre types depends on glucose stored in muscle, generating ATP aerobically? A- Fast Glycolytic fibres (type 2B) B- Slow oxidative fibres (type1) C- Fast oxidative glycolic fibres (type 2A) D- Slow Glycolytic fibres (type 1)
|
A- Fast Glycolytic fibres (type 2B) |
|
|
What binds the outside of the muscle? A- Perimysium B- Endomysium C- Epimysium D- Periostieum |
C- Epimysium |
|
|
What wraps around a single muscle fibre/cell A- Perimysium B- Endomysium C- Epimysium D- Periostieum |
B- Endomysium |
|
|
What does the Sacromere do? A- lengthens for muscle contraction B- divide along a length of muscle C- Shortens for muscle contraction D- withstands forces in different directions? |
C- Shortens for muscle contraction |

