![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does Calcium affect the release of Acetylcholine release? |
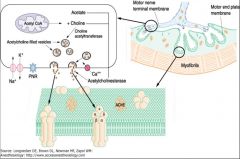
Is utilized in the fusion of a vessicle and the release of the Acetylcholine. |
|
|
What are the four groups of muscle relaxants (based on duration) and what are the drugs in each class? |
Ultrashort Duration-Succinylcholine (metabolized by cholinesterase) Short Duration- Non current Intermediate Duration- Vecuronium, Atracurium, Cisatracurium, Rocuronium (onium-no histamine release)(Hepatic metabolism or biliary excretion) Long Duration-Pancuronium (urinary excretion) |
|
|
Three factors affecting duration of action? |
How the drug is metabolized and excreted Total dose administered Patient sensitivity |
|
|
Muscle relaxants that end in urium are what type of drug, and release what? |
Benzylisoquinoline and release histamine. |
|
|
Muscle relaxants that end in onium are what type of drug, and have what effect?
|
Steroidal and have a possible vagolytic effect. |
|
|
What are 4 physical monitoring techniques to evalute muscle relaxation? |
Head lift for 5 secs, Hand Grip, Vital capacity and tidal volume, and Twitch monitoring |
|
|
What is the threshold for patient perception of electrical sensation? |
1 mA |
|
|
What is the frequency of a single twitch, TOF, Tetnus, and Posttetanic Count? |
Twitch 0.1 Hz to 1 Hz and 0.2 msec TOF 4 Twitches at 2 Hz every 1/2 sec Tetanus 50-100 Hz for 5 sec Posttetanic 50 Hz for 5 sec, 3 sec pause 1 twitch at 1 Hz |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a Phase 1 Muscle Relaxation (Depolarizing Agents)? |
Single Twitch height reduced No Fade No post-tetanic Potentiation Preceded by fasciculation (usually) |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a Phase 2 Muscle Relaxation (Non-Depolarizing Agents)?
|
Single Twitch height reduced Fade Post-tetanic Potentiation |
|
|
What percentage of receptors are blocked with a muscle relaxant when you have a TOF of: 1 Twitch 2 Twitches 3 Twitches 4 Twitches |
No Twitches-100% 1 Twitch-90% 2 Twitches-80% 3 Twitches-75% 4 Twitches<70% |
|
|
What is the TOF ratio considered adequate relaxation, and safe to extubate? |
TOF 0.15-0.25 is adequate relaxation TOF > 0.9 is safe to extubate |
|
|
What does an ED95 mean for muscle relaxants? |
The dose required to produce 95% suppression of an evoked response or twitch. ED95 is like a MAC, the dose that half the patients will reach 95% twitch depression and half the patients will not. |
|
|
What are the intubating doses for common muscle relaxing medications? |
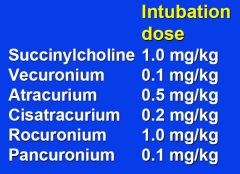
|
|
|
What medications are given to antagonize muscle relaxants, and what medications need to be given with them? |
Anticholinesterase agents and must be given with an anticholinergic agent (Atropine or glycopyrrolate) to prevent the parasypathetic response. Edrophonium 0.5-1.0 mg.kg (use with atropine) Neostigmine 50-70 ug/kg (max 5 mg) Pyridostigmine 0.45 mg/kg |
|
|
What drugs can potentiate the action of muscle relaxants? |
Volatile Anesthetics and Magnesium Sulfate |

