![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Flexation
|
Bending a Joint
|
|
|
Extension
|
Straightening a joint
|
|
|
Abduction
|
Moving a body part (usually a limb) away from the mid line of the body.
|
|
|
Adduction
|
Moving a body part (usually a limb) towards the mid line of the body
|
|
|
Elevation
|
Raising a body part
|
|
|
Depression
|
Lowering a body part
|
|
|
Rotation
|
Moving a body part around its axis
|
|
|
Protraction
|
Moving a body part anteriorly
|
|
|
Retraction
|
Moving a body part posteriorly
|
|
|
Pronation
|
Turning the palm posteriorly; ventral side of torso facing down
|
|
|
Supination
|
Turning the palm anteriorly; ventral side of torso facing up
|
|
|
Circumduction
|
circular (more accurately, conical) movement such as the shoulder joint.
|
|
|
Opposition
|
opposable thumb. tool use
|
|
|
Inversion
|
turning the sole of the foot inward
|
|
|
Eversion
|
turning the sole of the foot outward
|
|
|
Dorsiflexion
|
flexing the ankle such that the superior surface of the foot pulls up toward the shin
|
|
|
Plantar flexion
|
extending the ankle (pointing the toes)
|
|
|
Functions of Muscular tissue:
|
Body movement
Maintenance of posture Respiration Production of body heat Communication Constriction of organs and vessels Heart beat |
|
|
Properties of Muscle:
Contractility |
Ability of a muscle to shorten with force
|
|
|
Properties of Muscle:
Excitability |
Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus
|
|
|
Properties of Muscle:
Extensibility |
Muscle can be stretched to its normal
resting length and beyond to a limited degree |
|
|
Properties of Muscle
Elasticity |
Ability of muscle to recoil to original resting length after stretched
|
|
|
Muscle Tissue
Three types of muscles: |
Skeletal
Smooth Cardiac |
|
|
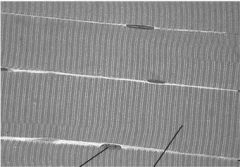
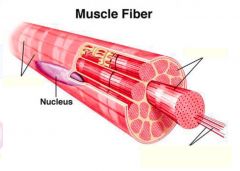
Skeletal
* Long, cylindrical and multinucleate, attached to bones * Nuclei on cell periphery * Fibers appear striated, voluntary |
|
|
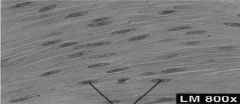
Smooth
* Spindleshaped, no striations, nucleus in cellcenter * Involuntary * Walls of hollow organs, blood vessels, eye, glands, skin |
|
|
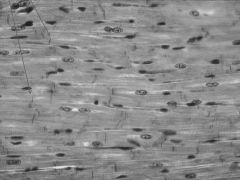
* Heart
* Yshaped, visibly striated, involuntary * Intercalated disks between cells |
|
|
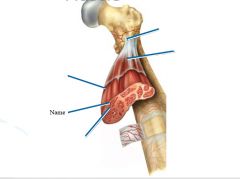
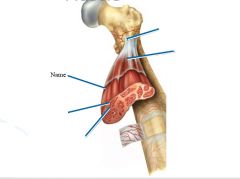
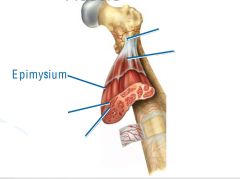
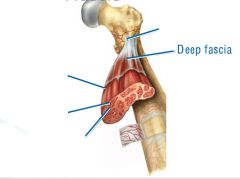
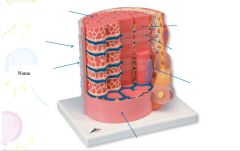
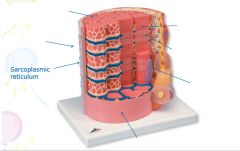
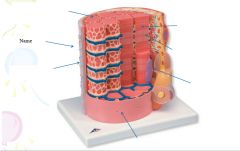
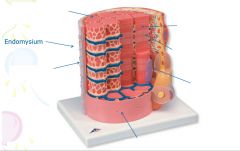
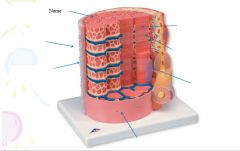
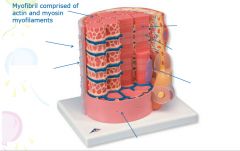
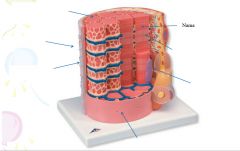
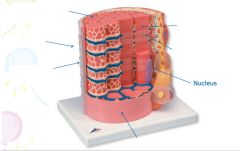
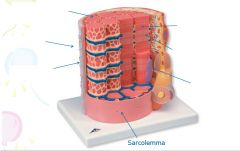
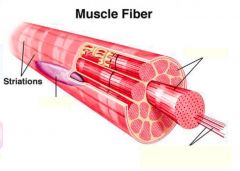
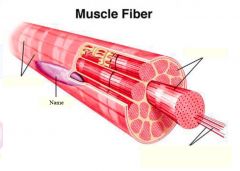
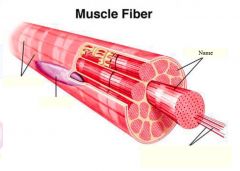
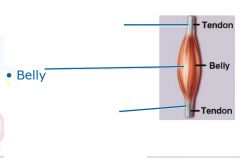
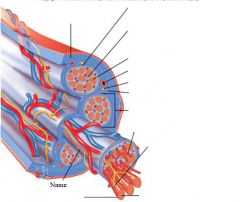
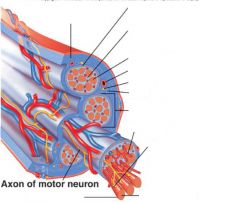
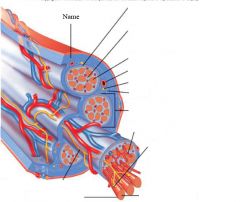
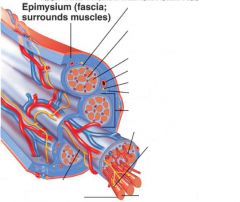
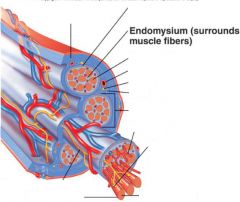
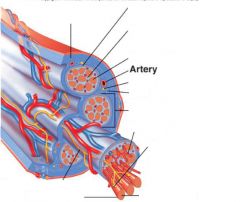
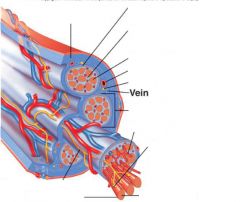
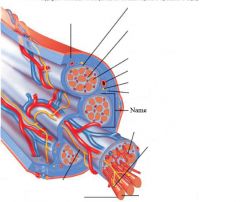
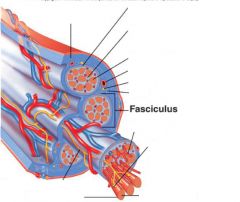
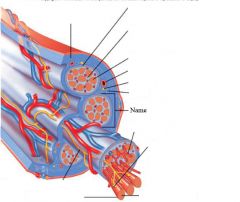
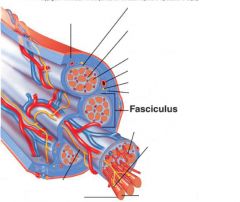
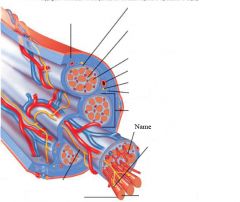
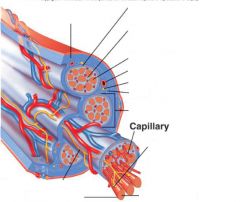
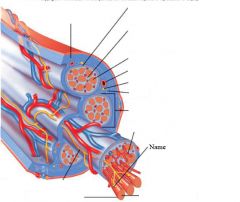
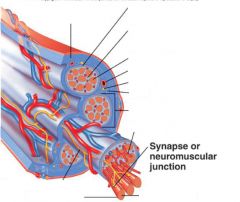
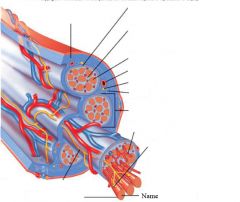
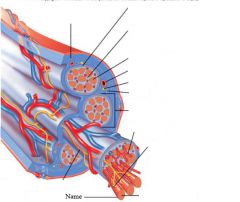
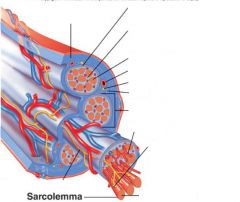
covers whole muscle belly
|
Epimysium
|
|
|
blends into connective tissue that separates
|
Epimysium
|
|
|
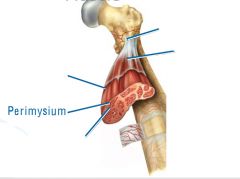
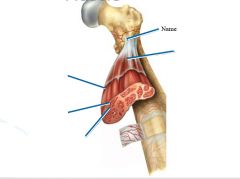
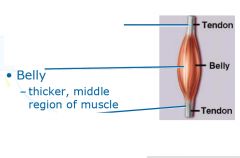
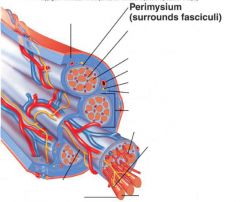
slightly thicker layer of connective tissue
|
Perimysium
|
|
|
surrounds a bundle of cells called a fascicle
|
Perimysium
|
|
|
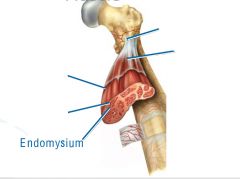
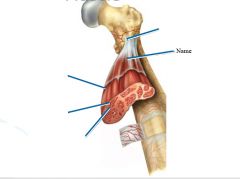
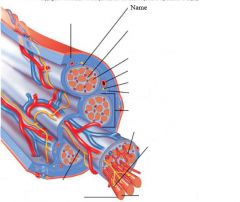
thin layer of areolar tissue surrounding each cell
|
Endomysium
|
|
|
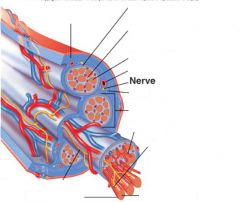
allows room for capillaries and nerve fibers
|
Endomysium
|
|
|
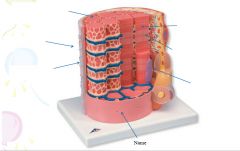
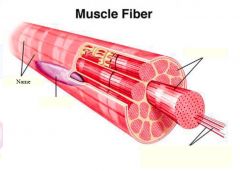
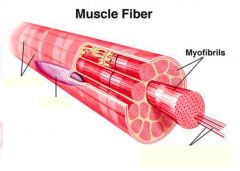
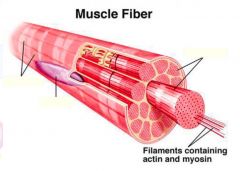
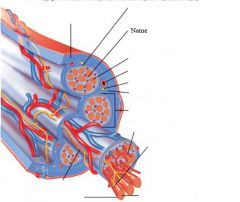
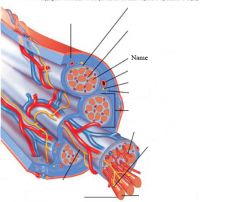
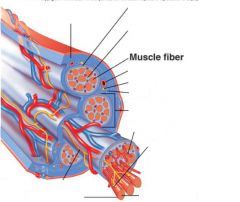
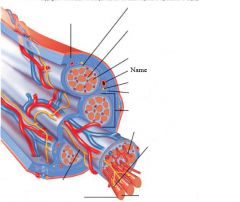
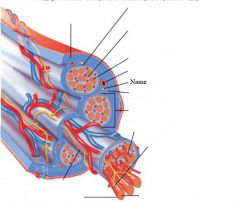
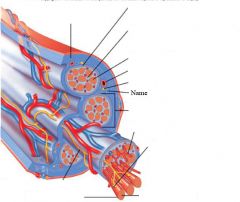
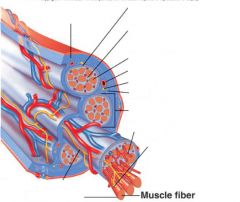
Muscle fibers=
|
individual muscle cells
|
|
|
Fascicle=
|
a group of several muscle fibers
joined by connective tissue called endomysium |
|
|
Perimysium=
|
connective tissue surrounding each fascicle
|
|
|
Muscle=
|
a group of fasicles surrounded by
a tough layer of connective tissue called epimysium |
|
|
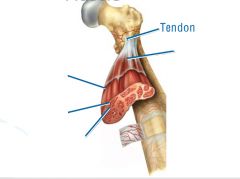
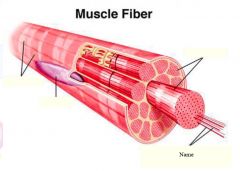
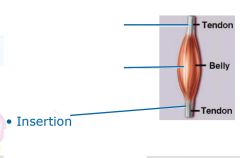
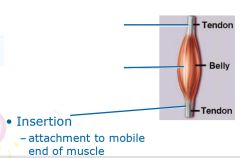
Tendon=
|
extension of epimysium from the muscle as a ropelike cord to the bone
|
|
|
Agonist
|
Prime Mover
|
|
|
Synergist
|
Muscles often contract at the same time as the agonist
|
|
|
Antagonist
|
Muscles that oppose the the action of the agonist
|
|
|
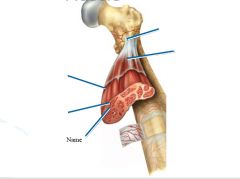
Fixator
|
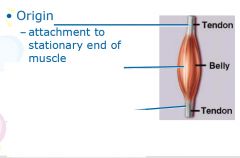
Prevent movement of the bone attached to the origin end of the muscle.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
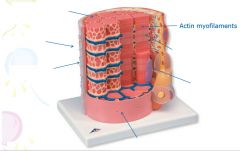
|
|
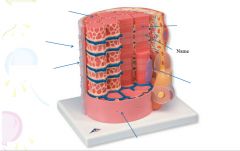
|
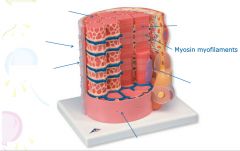
|
|
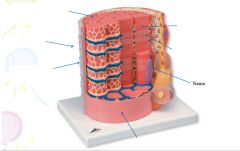
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

