![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Common Features: Is the weakness proximal or distal? |
Proximal > distal |
|
|
What kind of drug can cause a muscular myopathy? |
Statins |
|
|
What is a very high serum CK indicative of? |
A rapidly progressive myopathy |
|
|
What is a high serum CK indicative of? |
A progressive myopathy |
|
|
What is a normal serum CK indicative of? |
Either a chronic myopathy or a normal patient |
|
|
What is a decreased amplitude/frequency on EMG indicative of? |
A muscular myopathy because the muscle fibers are unable to produce an AP |
|
|
What is the Gold standard for dx of a muscular myopathy? |
Muscle biopsy |
|
|
What is an ischemic exercise test useful for? |
If a metabolic myopathy is suspected |
|
|
What is a genetic test useful for? |
If an inherited myopathy is suspected |
|
|
Duchenne's: Inheritance pattern |
X-linked |
|
|
Duchenne's: Gene affected |
Deletion in the dystrophin gene that results in a loss of the reading frame |
|
|
Duchenne's: Onset |
Early childhoof |
|
|
Duchenne's: What happens to the calves? |
Calf hypertrophy Replacement of the muscle with adipose tissue |
|
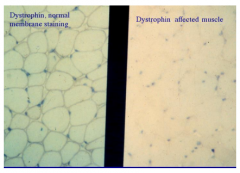
In what disease would you see this type of staining pattern? |
Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy |
|
|
Duchenne's: Prognosis if not treated |
Wheelchair bound by 13 Ventilator by 18-20 |
|
|
Duchenne's: Treatment |
Prednisone |
|
|
Duchenne's: Most common COD |
Cardiomyopathy |
|
|
Becker's: Mutation |
Dystrophin, as in Duchenne's |
|
|
Becker's: Why is it milder compared to Duchenne's? |
Although the mutation is larger in Becker's, the reading frame is unchanged |
|
|
Becker's: Onset |
Late and slowly progressive |
|
|
Becker's: Why is it usually detected? |
Cardiomyopathy |
|
|
Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy: What is it? |
An inherited sarcolemmopathy A group of diseases Catch-all dx because we do not know much about it |
|
|
Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy: What proteins are mutated? |
Membrane proteins other than dystrophin Sarcoglycan, dysferlin, emerin, caveolin |
|
|
Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy: Weakness pattern? What is the exception? |
Proximal symmetric weakness Exception: Miyoshi myopathy - distal weakness |
|
|
Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy: Emery-Dreifus MD? |
MD + severe contractures |
|
|
Facioscapulohumeral musuclar dystrophy: Inheritance pattern |
AD |
|
|
Facioscapulohumeral musuclar dystrophy: Mutation |
Deletion in chromosome 4 |
|
|
Facioscapulohumeral musuclar dystrophy: What bones are affected? |
Facial bones Scapula Humerus |
|
|
Facioscapulohumeral musuclar dystrophy: Rapidly or slowly progressive? |
Slowly progressive |
|
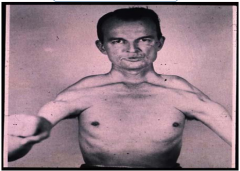
What condition is this? |
Facioscapulohumeral musuclar dystrophy |
|
|
Facioscapulohumeral musuclar dystrophy: When does it present? |
2nd decade of life |
|
|
Facioscapulohumeral musuclar dystrophy: Most common symptom |
Shoulder weakness |
|
|
Facioscapulohumeral musuclar dystrophy: Popeye's arm |
Loss of muscle mass in biceps and triceps and the forearm remains |
|
|
Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy: Inheritance pattern |
AD |
|
|
Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy: Mutation (both types) |
Triple repeat Type I - Triple CTG on chromosome 19 Type II - Triple CCTG on chromosome 3 |
|
|
Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy: Difference between Type I and Type II |
Type I worsens from generation to generation Type II has no child form |
|
|
Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy: Weakness pattern |
Distal weakness Hands and legs before face and neck |
|
|
Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy: When does mental retardation become a symptom? |
When childhood onset |
|

Dx? |
Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy |
|
|
Cholesterol Lower Agents Myopathy: Cause |
Statins Risk increase with 2 statins, statin + antilipemic, statin + some Abx |
|
|
Cholesterol Lower Agents Myopathy: 2 types |
1. Subacute to chronic - mild proximal weakness, reversible 2. Acute/subacute - high serum CK, acute renal failure, myalgia, muscle tenderness, muscle weakness, myoglobinuria |
|
|
Dermatomyotitis Myopathy: Inflammation pattern? What cell type is predominant? |
Perimysial inflammation B cell predominant |
|
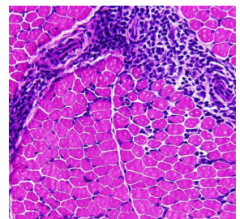
Dx? |
Dermatomyotitis Myopathy |
|
|
Dermatomyotitis Myopathy: Weakness pattern? |
Bilateral, proximal muscle weakness |
|
|
Heliotrope rash |
Rash on the eyelid |
|
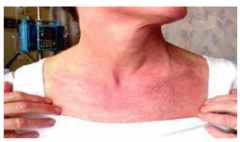
What kind of rash is this? |
V-shawl rash |
|
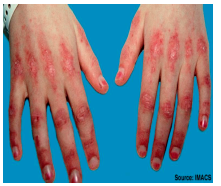
What kind of rash is this? |
Grotton's papules |
|
|
Dermatomyotitis Myopathy: What other condition is it associated with? |
Malignancy |
|
|
Dermatomyotitis Myopathy: What happens to the CK? |
Elevated CK |
|
|
Polymyositis Myopathy: Inflammation pattern? What cells are involved? |
Endomysial inflammation CD8 T-cell predominant |
|
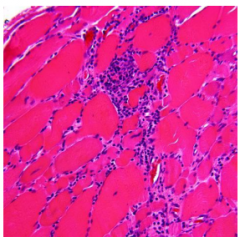
Dx? |
Polymyositis Myopathy |
|
|
Polymyositis Myopathy: Symptoms |
Proximal weakness Weakness of neck flexion No skin rash |
|
|
Inclusion Body Myositis: Pathology |
Polymyositis features + inclusion bodies |
|
|
Inclusion Body Myositis: Weakness pattern |
Distal (quadriceps, long finger and wrist flexors) Slowly progressive Asymmetric weakness |
|
|
Inclusion Body Myositis: Tx? |
There is no tx |
|
|
Exercise intolerant diseases? |
Phosphorylase (glycogen) Phosphofructokinase (glycogen) CPT (lipid) |
|
|
Static myopathy |
Exercise tolerant Progressive weakness |
|
|
Dynamic myopathy |
Exercise intolerant |

