![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the functions and major parts of the endocrine system?
|
regulates and controls growth, development & metabolism - pituitary, adrenals, and thyroid
|
|
|
What are the functions and major parts of the Skeletal system?
|
store, move, protect - joints and bones
|
|
|
What are the functions and major parts of the Lymphatic system?
|
Collects fluid, immune - lymph nodes, spleen
|
|
|
What are the functions and major parts of the muscular system?
|
movement, contracts - muscles
|
|
|
What are the functions and major parts of the nervous system?
|
Coordinates body's response to changes, relays, processes and analyze - brain, spinal cord
|
|
|
What are the functions and major parts of the reproductive system?
|
continue species - testis, ovary
|
|
|
What are the functions and major parts of the excretory system?
|
remove cellular waste - Kidneys
|
|
|
What are the functions and major parts of the integumentary system?
|
protect against drying, disease, sun dammage - hair, skin, and nails.
|
|
|
What are the levels of organization?
|
Cells/tissue/organs/organ systems
|
|
|
Define homeostasis and give an example.
|
Homeostasis is to maintain a constant internal environment.
Controling your body temp. by sweating, shivering and diverting blood flow |
|
|
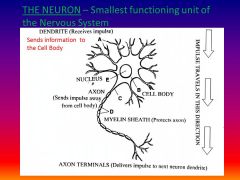
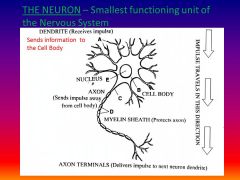
What is a neuron and give the function?
|
smallest structural & functional unit - carries impulses
|
|
|
Give the function of the lymphatic system
|
collects fluids, immune- lymph nodes, spleen
|
|
|
What are the three types of neurons and how are they classified?
|
Sensory, motor, and interneuron- classified by the direction they carry impluse
|
|
|
What is a neurotransmitter? Function?
|
Chemical that transmit nerve impluses across synapse
|
|
|
List the path of an impulse
|
Dendrite (collect infro), cell body, axon, end terminals (release neurotransmitters)
|
|
|
Give the function of the cerebrum
|
largest part, ability to think and reason, right side controls the left, left side controls right
|
|
|
Give the function of the medulla oblongata-
|
controls heartbeat, blood pressure, respiration rate
|
|
|
Give the function of the cerebellum
|
muscle coordination
|
|
|
List the sensory receptors and where they are located
|
Pain (everywhere except brain)
thermoreceptors (sense temperature) photoreceptors (for light found in ere with cones and rods), chemoreceptors (in nose and tongue, hold nose to lessen taste) mechanoreceptors (balance) |
|
|
Describe and give examples of a depressant
|
slows down reflexes, poor judgment, disrupt coordination. Alcohol
|
|
|
Describe and give an exampeles of a stimulant
|
Speeds up heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. Ex: Methamphetamines
|
|
|
How many bones does an adult have?
|
206
|
|
|
Name and describe the parts of a bone
|
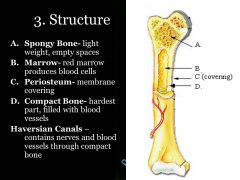
Haversian canals (contains nerves and blood vessels), periosteum (membrane that surrounds bones), compact (hard part) spongy (has holes at the ends of bone) marrow (makes blood cells)
|
|
|
Define ossification. In whom does it occur?
|
Cartilage turns to bone. Occurs in embryos, newborns, and teenagers
|
|
|
How much muscle is in the body?
|
more than 40%
|
|
|
What is a ligament?
|
Attaches bone to bone
|
|
|
What is a tendon
|
Attaches muscle to bone
|
|
|
Name the joints and give example
|
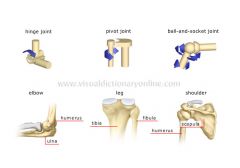
Ball and Socket (shoulder and hip), Hinge (knee, elbow), immovable (skull), partially moveable (ribs)
|
|
|
How does a muscle contract?
|
sliding filament theory, actin and myosin slides
|
|
|
Name three types of muscle and give their location
|
Skeletal (attached to skeleton), Smooth (organs), Cardiac (heart)
|
|
|
How does a joint bend?
|
Antagonistic, muscle contracts
|
|
|
Name the layers of the skin
|
Epidermis and dermis
|
|
|
Name the parts of the integumentary system
|
Skin, hair, and nails
|
|
|
What protein is found in the integumentary system?
|
Keratin
|
|
|
Symphatic system VS parasymphathetic system
|
Symphatic system - "stress" heart rate and blood pressure increases.
parasymphathetic system - "Peace" heart rate and blood pressure low or normal |
|
|
Desrcibe the somatic system
|
Voluntary, have control over
|
|
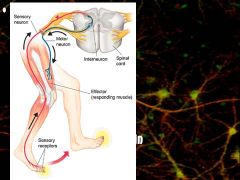
Describe the reflex arc (response)
|
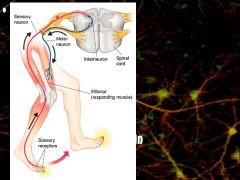
Receptor-sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, muslce (Brain NOT involved)
|
|
|
Describe antagonistic muscles and give an example
|
Work against each other (Ex: Biceps/triceps)
|
|
|
What is partial contraction and which muscles participate?
|
Muscle tone, skeletal
|
|
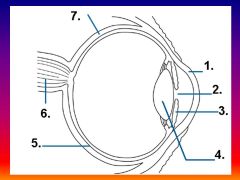
Please identify structure number 1
|
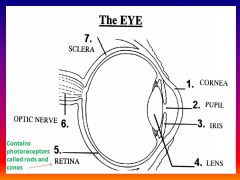
Cornea
|
|
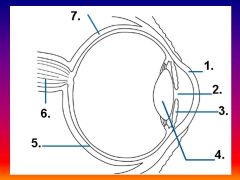
please identify structure labeled 2
|
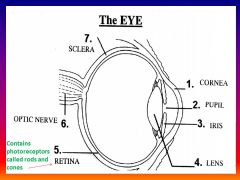
Pupil
|
|
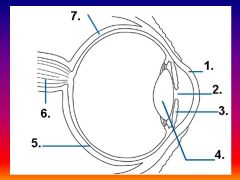
please identify structure labeled 3
|
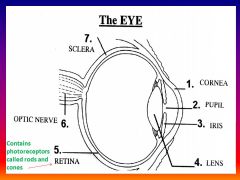
Iris
|
|
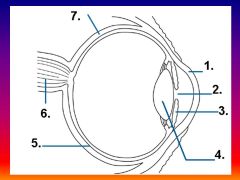
please identify structure labeled 4
|
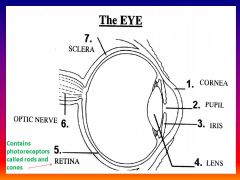
Lens
|
|
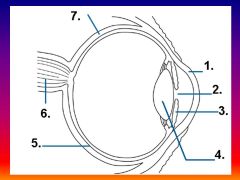
please identify structure labeled 5
|
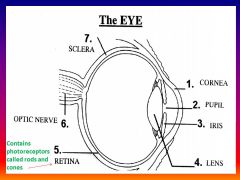
Retina
|
|
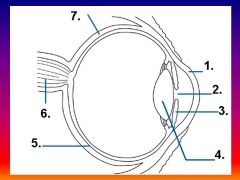
please identify structure labeled 7
|
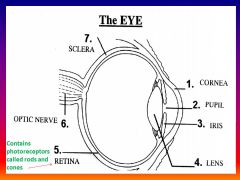
Sclera
|
|
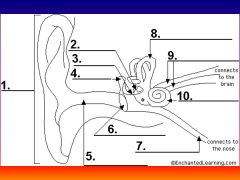
please identify structure labeled 1
|
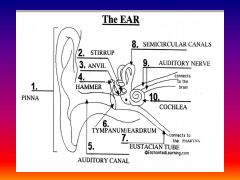
Pinna
|
|
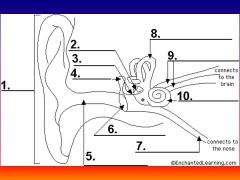
please identify structure labeled 2
|
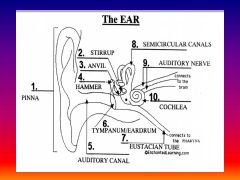
Stirrup
|
|
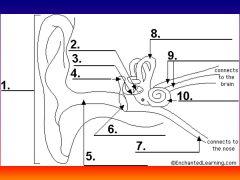
please identify structure labeled 3
|
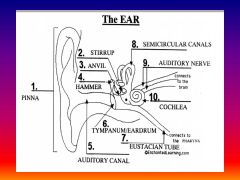
anvil
|
|
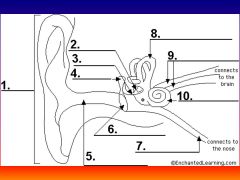
please identify structure labeled 4
|
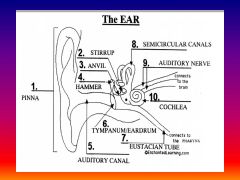
Hammer
|
|
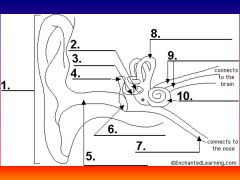
please identify structure labeled 5
|
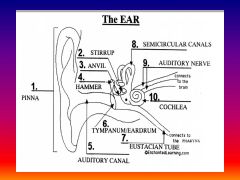
Auditory Canal
|
|
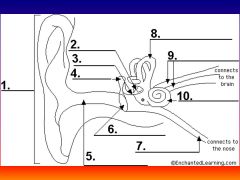
please identify structure labeled 6
|
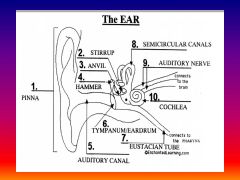
Tympanum / Ear Drum - First structure to receive sound wave
|
|
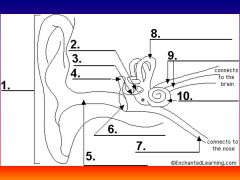
please identify structure labeled 7
|
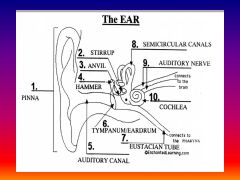
Eustacian tube
|
|
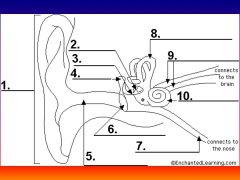
please identify structure labeled 8
|
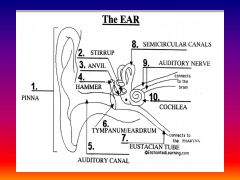
Semicircular canals - responsible for balance and body position
|
|
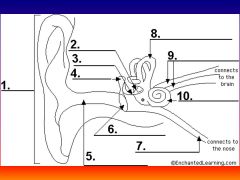
please identify structure labeled 9
|
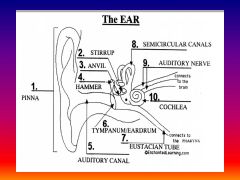
Auditory Nerve
|
|
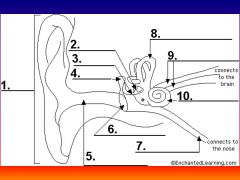
Please identify structure labeled 10
|
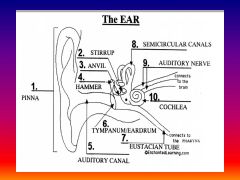
Cochlea
|
|
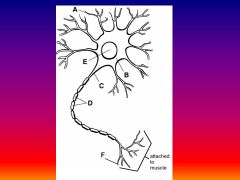
Please identify structure labeled A
|
Dendrite
|
|
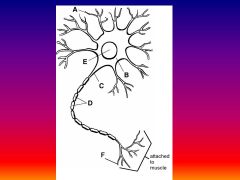
please identify structure labeled B
|
Cell Body
|
|
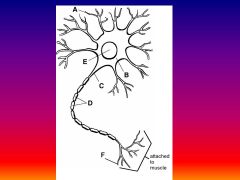
Please identify structure labeled C
|
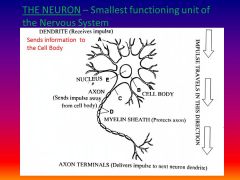
Axon
|
|
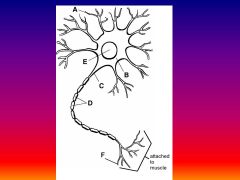
Please identify structure labeled D
|
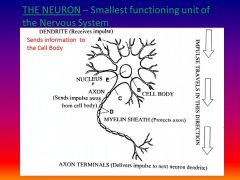
Myelin Sheath
|
|
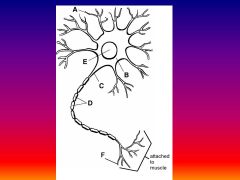
Please identify structure labeled E
|
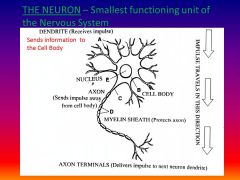
Nucleus
|
|
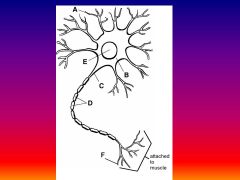
Please identify structure labeled F
|
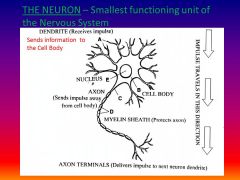
Axon Terminal
|
|
|
What is the function of the crebrum?
|
Controls voluntary activities of the body, thinking, etc.
|
|
|
What is the function of the cerebellum?
|
Controls muscle coordination
and balance |

