![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define a scalar field ϕ on ℝ^3 |
A map ϕ:ℝ^3→ℝ |
|
|
Define a vector field F on ℝ^3
|
A map F:ℝ^3→ℝ^3
|
|
|
Define when a set U⊆ℝ^n is open |
x∈U ∃ε>0 st B(x;ε)={y∈ℝ^n:|x-y|<ε}⊂U |
|
|
Give three properties of double integrals inherited from single integrals |
Linearity Order (weak inequality) Domain Splitting |
|
|
Given two coordinates u(x,y) and v(x,y) which depend on variables x and y define the Jacobian |
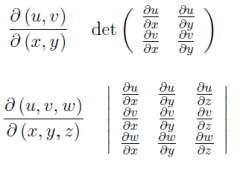
|
|
|
Let f:R→S be a bijection between two regions of ℝ^2 which is differentiable, invertible and has well defined non-zero Jacobians. Let (u,v)=f(x,y) and ψ(x,y)=ψ(u,v) Then... |
∫∫ ψ(u,v) dudv=∫∫ ψ(x,y) Ju,v dxdy ∫∫ ψ(x,y) dxdy=∫∫ ψ(u,v) Jx,y dudv |
|
|
Define the centre of mass of a body with density ρ(r) |
r'=(1/M)∫∫∫rρ(r)dV Where M is the total mass of the body |
|
|
Define a smooth parametrised surface |
r:U→ℝ^3:(u,v)↦(x(u,v),y(u,v),z(u,v)) |
|
|
Define the tangent plane to r(U) at p
|
The plane containing p which is parallel to the vectors of the u and v partial derivatives of r at p |
|
|
What is ∫∫F.dS |
∫∫F(r(u,v)).(u∧v)dudv |
|
|
What is ∫∫FdS |
∫∫F(r(u,v))|u∧v|dudv |
|
|
What is ∫∫ϕdS |
∫∫ϕ(r(u,v))(u∧v)dudv |
|
|
What is ∫∫ϕdS |
∫∫ϕ(r(u,v))|u∧v|dudv |
|
|
Define the solid angle |
Ω=∫∫(er.dS)/r^2=∫∫(r.dS)/r^3 |
|
|
Define a curve |
A piecewise smooth function γ:I→ℝ^3 |
|
|
Define simple |
1-1 with the possible exception that γ(a)=γ(b) |
|
|
Define closed |
γ(a)=γ(b) |
|
|
Define the line integral of F along C |
∫F.dr=a∫bF(γ(t)).γ'(t)dt |
|
|
Define the line integral of ϕ along C |
∫ϕds=a∫bϕ(γ(t)).|γ'(t)|dt |
|
|
Define ∫Fds Where F=(f1,f2,f3) |
(∫f1ds,∫f2ds,∫f3ds) |
|
|
Define arc length |
∫ds=a∫b|γ'(t)|dt |
|
|
How do you calculate word done by a particle moving along C? |
∫F.dr Where F is the force acting on the particle |
|
|
Prove that if F=ϕ and γ:[a,b]→S is any curve st γ(a)=p, γ(b)=p then
∫γ F(r).dr=ϕ(q)=ϕ(p) |

|
|
|
Define conservative |
A vector field F:S→ℝ^3 is conservative if ∃ϕ:S→ℝ st F=ϕ ϕ is said to be the (scalar) potential |
|
|
Define path connected |
∀p,q∈S ∃γ:[a,b]→S st γ(a)=p and γ(b)=p |
|
|
Prove that if ϕ=0 on a path-connected set S then ϕ is constant and two potentials fo F in this region differ by a constant |
For any curve with endpoints p, q we have ϕ(q)-ϕ(p)=∫γ ϕ.dr=0 As a given p is connected to any q∈S by a curve ϕ is constant over the region If F=ϕ=ψ then (ϕ-ψ)=0 so ϕ-ψ is constant |
|
|
Give two equivalent statements to F is conservative |
Given any two points p,q∈S and curve γ in S starting at p and ending at q the integral ∫γ F(r).dr is independent of the choice of curve For any simple closed curve γ ∫γ F(r).dr=0 |
|
|
Define the deleted neighbourhood |
B'δ=(x;δ)=B(x;δ)\{x} |
|
|
Define the gradient of ϕ (∇ϕ) |
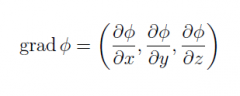
|
|
|
Define the divergence of F (∇.F) |

|
|
|
Define the curl of F (∇∧F) |
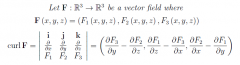
|
|
|
Define the Laplacian |
div grad=∇.∇ |
|
|
Define an orthonormal basis for ℝ^3 |
ei.ej=1 if i=j =0 if i≠j |
|
|
Prove that if e1,e2,e3 is a right-handed orthonormal basis of ℝ^3 with associate coordinates X,Y,Z defined by the identity Xe1+Ye2+Ze3=xi+yj+zk then their independent directional derivatives added equal each other |
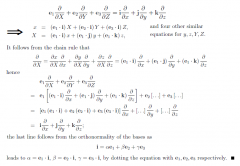
|

