![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the commonality in acne, rosacea, hirsuitism and alopecia?
|
they all occur around the pylosebaceous unit
|
|
|
Where do sebaceous glands empty their contents?
|
into the hair follicle
|
|
|
At puberty, what changes happen at the pilosebaceous unit?
|
-hyperkeratinization blocks pores
-sebaceous gland hyperplasia and hypersecretion --> as a result, P. acnes grows --> leads to inflammation |
|
|
What are the 4 stages in the pathogenesis of acne
|
early comedome
later comedome inflammatory papule/pustule nodule/cyst |
|
|
What is the difference between open and closed comedome? What is the same?
|
whitehead - closed -> hair follicle is completely closed
blackhead - open -> keratin is stuck they are both non-inflammatory |
|
|
What are the treatments for mild acne?
|
-topical retinoids
-benzoyl -topical abx (clindamycin, erythomycin) -keratolytics (salicylic acid) |
|
|
What are the treatments for moderate acne?
|
topical retinoids
birth control pills oral abx (tetracycline, erythromycin) ** tetracycline does bad things to the teeth of children under 12 and fetusses ** |
|
|
What are the treatments for severe acne?
|
systemic retinoid (acutane)
|
|
|
How does OCP work in women for acne?
|
OCP reduces your circulating testosterone
|
|
|
If you have strictly comedomal acne (no inflammation), then what would you use?
|
-topical retinoid
|
|
|
If you have inflammatory acne, what would you use?
|
-topical retinoid + systemic abx
|
|
|
What is rosacea?
|
-a lot of redness
-tendency to flush easily -acne-like component -starts in the 20s and 30s -an inflammatory process around the hair follicles |
|
|
What are the clinical features of rosacea?
|
-erythema, flushing
-inflammatory papules -telangiectasiae -rhinophyma -nose, cheeks, glabella, chin, eyes, cornea |
|
|
Someone has a red face with teleangectasias and no comedomes. What is it?
|
rosacea
|
|
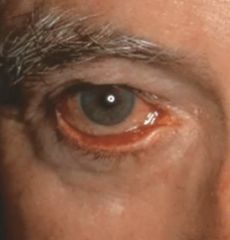
What does this guy have?
|
ocular rosacea
|
|
|
How do you manage roasacea?
|
-avoid triggers (EtOH, heat, cold, wind, spices)
-topical metronidazole -systemic tetracyclines -laser surg, rhinophyma |
|
|
What treatment do you avoid in rosacea?
|
TOPICAL CORTICOSTEROIDS
|
|
|
What is the definition of hirsutism?
|
excess terminal hair growth in women where it is normally found on men
-it is specifically in androgen sepcific areas |
|
|
What is the pathophys of hirsutism?
|
-androgen precursor in the ovary (androstendedione)
-available (free) testosterone converted to dihyrdrotestosterone (DHT) -binds to androgen receptors in androgen dependent areas |
|
|
What is the key ingredient in hirsutism, androgenetic alopecia and acne in women?
|
binding of DHT to the androgen receptors!
|
|
|
Where can the abnormalities be in hirsutism?
|
-ovary: too much androgen precursor
-adrenals: too much DHEA -skin: too sensitive to availability of testosterone |
|
|
What feedback mechanisms serve to reduce free testosterone?
|
-estrogen (ovaries)
-cortisol (adrenals) |
|
|
What happens when DHT binds to a receptor on a hair follicle?
|
convert vellus hairs into coarse, dark terminal hairs
|
|
|
Someone has hirsutism, but normal androgen levels. Why?
|
-increased sensitivity of the hair follicles to androgen
|
|
|
What is worrying in hirsutism history?
|
-rapid onset
-rapid progression -menstrual irregularity -infertility -severity -other virilization signs (muscularity, deep voice) -central obesity -acanthosis nigricans |
|
|
When would you test for elevated androgen levels in women with hirsutism?
|
moderate or severe hirsutism
OR any degree of hirsutism if it is -sudden onset -rapid progression OR associated with ANY of: -menstrual irregularity -infertility -central obesity -acanthosis nigricans -clitoromegaly |
|
|
What is the investigation for hirsutism?
|
-total and bioavailable testosterone
-DHEAS, LH, FSH -chol/TG/glucose -pregnancy test if amennorheic |
|
|
What is the most common symptom associated with hirsutism
|
-polycystic ovarian syndrome
|
|
|
What drugs are associated with hirsutism?
|
-anabolic steroids
-valproic acid -androgenic progestins |
|
|
What is the treatment for hirsutism?
|
-removal
-oral contraceptives with an antiandrogen -eflornithine cream -dc drugs |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis for androgenic alopecia?
|
-not an inherent problem in production of androgens
-increased sensitivity to DHT |
|
|
What is the pattern of alopecia in women?
|
-preservation of hairline
-diffuse thinning -frontal scalp and crown |
|
|
If a woman presents with a history "I'm losing tons of hair everytime I shower"
|
-it is NOT androgenic alopecia
|
|
|
What is the treatment of androgenic alopecia?
|
men: topical minoxidi, oral finasteride, hair transplantation
women: topical minoxidil, OCP, spironolactone (androgen receptor antagonist), hair transplant |

