![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
115 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anaerobic - ATP-PC system |
High intensity short duration Phosphocrestine releases energy to construct ATP 15 seconds |
|
|
Anaerobic glycolysis |
Stored glycogen split into glucose and through glycolysis, split into pyruvic acid Energy released forms ATP Forms lactic acid 30-40 seconds |
|
|
Aerobic metabolism |
Used during low intensity long duration exercise Oxygen system yields most ATP but requires more work Oxidation of food |
|
|
Class 1 lever |
|
|
|
Class 2 lever |
Back (Definitio |
|
|
Class 3 lever |
Back (Definitio |
|
|
Fibrous joints (synarthroses) |
Suture- union of two bones Syndesmosis- bone connected to bone by fibrous membrane Gomphosis- connect through hole like tooth |
|
|
Cartilaginous joints (amphiaryhrosis) |
Synchondrosis- hyaline cartilage adjoins two ossifying centers of bone Symphysis- two bones covered with hyaline |
|
|
Synovial joints (diarthrosis) |
Hinge Pivot Condyloid- MCP joint Saddle- CMC Plane Ball and socket |
|
|
Free nerve endings |
Mechanical stress and noxious mechanical or bio mechanical stimuli |
|
|
Golgi tendon organs |
Tension or stretch on tissue |
|
|
Pacinian corpuscles |
Vibration, movement, joint position |
|
|
Ruffini endings |
Stretching of joint capsule, amplitude and velocity of joint position |
|
|
Golgi-mazzoni corpuscles |
Compression of joint capsule |
|
|
Type 1 vs 2 muscle fibers |
1: aerobic, red, tonic, slow, oxidative 2: anaerobic, white, physic, fast twitch, glycolytic |
|
|
Muscle spindle vs golgi tendon organs |
MS: through muscle belly, sense muscle length and rate of change of length, stretch GTO: in tendons, tension |
|
|
TMJ muscle actions |
Depress: Lat pterygoid, suprahyoid, infrahyoid Elevate: temporalis, massager, med pterygoid Protrusion: masseter, both pterygoids Retrusion: temporalis, masseter, digastric Lateral: both pterygoids, masseter, temporalis |
|
|
Scapula movement |
Back (Definition |
|
|
GH joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
SC joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
AC joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
Radiohumeral joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
Ulnohumeral joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
Proximal radioulnar joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
Radiocarpal joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
Iliofemoral joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
Tibiofemoral joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
Pes anserine |
Gracilis, semitendinosus, sartorius Medial and distal of tibial tuberosity |
|
|
Talocrural joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
Subtalar joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
Midtarsal joint |
Back (Definition |
|
|
A-O joint |
Condylar synovial joint Flexion and extension |
|
|
AA joint |
Plane synovial joint Mostly rotation |
|
|
Zygaphoseal joint |
Formed by right and left superior and inferior articular facets |
|
|
Cervical flexion |
SCM Longus colli Scalenes |
|
|
Cervical extension |
Splenius cervicis Semispinalis cervicis Iliocostalis cervicis Longissimus cervicis Multifidus Trapezius |
|
|
Cervical rotation and lateral bend |
SCM Scalenes Splenius cervicis Longissimus cervicis Iliocostalis cervicis Levator scapulae Multifidus |
|
|
Alar ligament |
Attaches to dens of axis to occipital condyles Resists flexion, contralateral side bend, contralateral rotation Limits Saginaw plane translation between atlas and occiput |
|
|
Cruciform ligament |
Vertical and horizontal portions Vertical connects dens to foramen magnum Horizontal connects dens with atlas |
|
|
Ligamentum flavum |
Connects laminate of each vertebrae Limits flexion and rotation |
|
|
Ligamentum nuchae |
Cervical spine, limits flexion |
|
|
Uncovertebral joints |
Formed between lateral projections on inferior surface of vertebral body to superior surface of vertebra below Between C3-T1 Guide motion in Sagittal plane and limit motion in others |
|
|
Iliolumbar ligament |
Connects posterior ilium to transverse process of L5 Limits motion between L5 and S1 |
|
|
Sacrospinous ligament |
Connects ischial spine to lateral sacrum and coccyx Limits anterior rotation of sacrum on pelvis |
|
|
Normal end feel |
Back (Definition |
|
|
Abnormal end feel |
Back (Definition |
|
|
Sacrotuberous ligament |
Attaches on PSIS, lateral sacrum, coccyx, and ischial tuberosity Resists sacral anterior rotation Prevents superior translation of sacrum |
|
|
UE reflex testing |
Biceps - C5 Brachioradialis - C6 Triceps - C7 |
|
|
Functional testing LE |
Heel walking - L4/L5 Toe walking - S1 SLR - L4-S1 |
|
|
LE reflex testing |
Patella - L4 Hamstring - L5 Achilles - S1 |
|
|
UE dermatome |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
LE dermatome testing |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Pain transmission |
A delta and C fibers A delta transmits from peripheral cutaneous structures, sharp and localized C fibers transmit from deeper tissues and slower than A delta, dull, aching, diffuse Transmit to dorsal horn, then via spinothalamic tract to thalamus, then sensory cortex |
|
|
Gate control theory |
A delta and C fibers synapse with secondary neuron, sends pain signal to brain, also synapse with inhibitory interneuron A alpha and beta neurons provide input to interneurons Stimulate a alpha and beta to inhibit or close the gate to pain |
|
|
Endogenous opiods |
Pain regulation from endorphins bind to opioid receptors throughout nervous system Controls amount of calcium and potassium moving in and out of cell during depolarization Indirectly effects release of GABA which inhibits activity of structures to help control pain |
|
|
Sacrospinous ligament |
Connects ischial spine to lateral sacrum and coccyx Limits anterior rotation of sacrum on pelvis |
|
|
Normal end feel |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Abnormal end feel |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Sacrotuberous ligament |
Attaches on PSIS, lateral sacrum, coccyx, and ischial tuberosity Resists sacral anterior rotation Prevents superior translation of sacrum |
|
|
UE reflex testing |
Biceps - C5 Brachioradialis - C6 Triceps - C7 |
|
|
Functional testing LE |
Heel walking - L4/L5 Toe walking - S1 SLR - L4-S1 |
|
|
LE reflex testing |
Patella - L4 Hamstring - L5 Achilles - S1 |
|
|
UE dermatome |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
LE dermatome testing |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Pain transmission |
A delta and C fibers A delta transmits from peripheral cutaneous structures, sharp and localized C fibers transmit from deeper tissues and slower than A delta, dull, aching, diffuse Transmit to dorsal horn, then via spinothalamic tract to thalamus, then sensory cortex |
|
|
Gate control theory |
A delta and C fibers synapse with secondary neuron, sends pain signal to brain, also synapse with inhibitory interneuron A alpha and beta neurons provide input to interneurons Stimulate a alpha and beta to inhibit or close the gate to pain |
|
|
Endogenous opiods |
Pain regulation from endorphins bind to opioid receptors throughout nervous system Controls amount of calcium and potassium moving in and out of cell during depolarization Indirectly effects release of GABA which inhibits activity of structures to help control pain |
|
|
Allen test |
Arm 90 90 and ER, head rotate away, check radial pulse Thoracic outlet syndrome |
|
|
Costoclavicular syndrome test |
Scapula retracted, chest forward, monitor radial pulse |
|
|
Adsons test |
Arm abducted 15 degrees, hold breathe, extend head and rotate towards, extend and laterally rotate, check radial pulse |
|
|
Roos test |
90 90 and ER, slowly open and close hands |
|
|
Wright (hyperabduction) test |
Therapist moves arm into full shoulder abduction and tests radial pulse |
|
|
O brien test |
Superior labral tear Arm flexed 90, horizontal add, IR, downward force and pain, ER and decreased pain |
|
|
Jerk test |
Posterior labral lesion 90 abd, 90 elbow flex, axial force and horizontal add by therapist Clunky and sublux |
|
|
ULT median and AIN |
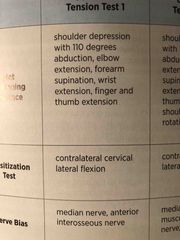
Back (Definition) |
|
|
ULT median, Musculoskeletal nerve, axillary nerve |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
ULT radial nerve |
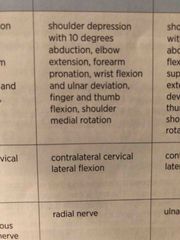
Back (Definition) |
|
|
ULT ulnar nerve |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Varus stress test |
20-30 deg flexion and varus stress Possible LCL injury |
|
|
Valgus stress test |
20-30 deg flexion and valgus stress Possible MCL injury |
|
|
Cozens and mills and lateral epicondylitis test |
Cozens - extensors wad, resisted wrist extension Mills - extensor wad, passive, elbow ext, forearm pronation, flex wrist Lat ep - resisted middle finger extension |
|
|
Cozens and mills and lateral epicondylitis test |
Cozens - extensors wad, resisted wrist extension Mills - extensor wad, passive, elbow ext, forearm pronation, flex wrist Lat ep - resisted middle finger extension |
|
|
Elbow flexion test |
Flexes elbows and extends wrist Hold position 3-5 mins Positive for cubital tunnel syndrome if ulnar symptoms |
|
|
Cozens and mills and lateral epicondylitis test |
Cozens - extensors wad, resisted wrist extension Mills - extensor wad, passive, elbow ext, forearm pronation, flex wrist Lat ep - resisted middle finger extension |
|
|
Elbow flexion test |
Flexes elbows and extends wrist Hold position 3-5 mins Positive for cubital tunnel syndrome if ulnar symptoms |
|
|
Pinch grip test |
Pinch tips of index and thumb If can only press pads together, positive for anterior interosseous nerve |
|
|
Tinels sign |
Tapping cubital tunnel for ulnar nerve compression |
|
|
Allen’s test |
Open and close hand then keep hand closed, compress radial and ulnar arteries |
|
|
Bunnel littler test |
Flex proximal interphalangeal joint If can’t = tight intrinsic muscle WITH capsular tightness If can = without capsular tightness |
|
|
Tight retinacular ligament test |
Flex distal interphalangeal joint If can’t = retinacular lig. And capsule tight If can = retinacular tight |
|
|
Froments sign |
Hold piece of paper with index and thumb in pincher grasp Pull paper away Positive if flexing distal Phalanx of thumb due to adductor pollicis paralysis Ulnar nerve compromise |
|
|
Phalens test and reverse phalens |
Flex wrist and hold for 60 seconds Reverse is reverse |
|
|
Finklesteins |
Testing abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis |
|
|
Murphy’s sign |
Make fist, positive if third metacarpal is level with 2nd and 4th Dislocated lunate |
|
|
Barlow vs ortolani |
Barlow: supine, hips flexed to 90 and knees flexed, move one leg into adduction with posterior pressure looking for clunk, possible hip dislocation Ortolani: same setup as Barlow but move hips into abduction and feel resistance or clunk at 30 degrees |
|
|
Hip anterior labral tear test |
Hip in full flexion, ER, and abduction to start, moves hip into ext, IR, and add. Pain or click is positive for anterior-superior impingement or psoas tendinitis |
|
|
Craig’s test |
Normal anteversion 8-15 degrees |
|
|
FABER |
Hip test for psoas, SI, or hip joint abnormalities |
|
|
Scour test |
Positive for arthritis, avascular necrosis, or osteochondral defect |
|
|
Lateral pivot shift test |
Hip flexed and abd to 30 degrees Move knee into IR with valgus force while slowly flexing knee Positive test is shift or click between 20-40 degrees Indicative of anterolateral rotatory instability |
|
|
Slocum test |
Supine, knee flexed to 90 and hip flexed to 45, IR foot and does anterior drawer |
|
|
Mcmurrays test |
Supine, grab distal leg and palpate knee joint Knee fully flexed, IR/ER tibia and extend knee Possible posterior meniscal lesion |
|
|
Brush and tap test |
Positive for joint effusion of the knee |
|
|
Hughston plica test |
Flex knee and IR tibia while other hand moves patella medially Popping sound over medial plica |
|
|
Noble compression test |
Supine, hip slightly flexed and knee in 90 flexion Thumb on lateral epicondyle of femur and extend leg Positive if pain around 30 deg flexion ITB friction syndrome |
|
|
Anterior drawer test ankle |
Supine and stabilize distal fibula and 20 deg PF position Excessive anterior translation = ATFL ligament sprain Add inversion for calcaneofibular |
|
|
Kleiger test - ER stress test |
Seated 90 90 Rotate externally Pain is positive for syndesmotic injury IR pain and talus shift away from medial malleolus equals deltoid ligament tear |
|
|
Talar tilt test |
ABD and ADD talus Excessive adduction = CFL ligament |
|
|
Vertebral artery teat |
Supine, head into extension lateral flexion and rotation ipsilaterally |
|
|
Grades of mobilization |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Principles of stretching |
Elasticity: ability of soft tissue to return to previous length Viscoelasticity:time-dependent property of soft tissue resulting in resistance to stretch when initially applied but elongation when held longer Plasticity: allow for tissue elongation after stretch is no longer applied |
|
|
Stress strain curve |
Toe region: slack Elastic region: deformation of tissue but tissue returns to resting length Plastic region: more stress results in permanent deformation |
|
|
Stretching - creep |
Soft tissue stretched for sustained duration will elongate and not return to original length |
|
|
Stretching - stress relaxation |
Longer a stretching force is maintained, the more the tension within the tissue decreases, equaling less force to maintain stretch |
|
|
Congenital torticollis |
SCM contracture Lateral cervical flexion to same side and rotation away |

