![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Who is Gregor Mendel? |
An Austrian monk who discovered the modern science of genetics with his pea plants |
Pea plants |
|
|
DNA nitrogen bases? |
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine. |
A-T, G-C |
|
|
Parts of DNA? |
Phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, base |
3 things |
|
|
RNA nitrogen bases? |
Adenine, uracil, cytosine, Guanine. |
A-U, G-C |
|
|
3 types and functions of RNA |
Messenger RNA- carries copies of instructions Ribosomal RNA- builds ribosomes Transfer RNA- transfers amino acids. |
M, r, t |
|
|
Central Dogma of biology? |
Replication, transcription, translation. |
3 steps |
|
|
Transcription? |
Process of making RNA from DNA. In nucleus. RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the strands. |
|
|
|
Translation? |
Using mRNA to build protein molecules. This is done in the cytoplasm |
|
|
|
Karyotype? |
Shows all 23 homologous chromosomes |
|
|
|
Pedigree? |
A chart showing the presence or absence of a trait according to the relationship between parents, siblings, and offspring |
Family tree |
|
|
What are genetic disorders and what causes them? |
A change in DNA sequence affecting a phenotype. Caused by base changes. |
|
|
|
What are chromosomal disorders and what causes them? |
One chromosome gets changed due to error on meiosis. |
|
|
|
GMO'S- what are they? Good points? Bad points? |
Genetically modified organisms, they can change to gain a desirable trait, but they may harm your body |
|
|
|
DNA Fingerprinting? |
Analyzes sections of DNA that may have little or no function, but that vary widely from one individual to another. It can tell what disorders, if any, you have. |
|
|
|
Who is Charles Darwin? |
Developed scientific theory of biological evolution that explains how modern organisms evolved over long periods of time through decent from common ancestors. |
|
|
|
Who is Hutton? |
Presented hypothesis about how geological processes have shaped earth. |
|
|
|
Who is Lyell? |
Argued laws of nature are constant over time. Called uniformitarianism. |
|
|
|
What did Hutton and Lyell conclude? |
That earth is extremely old and that processes that have changed Earth in the past are the same processes that operate in the present. |
|
|
|
Who is Lamarck? |
Suggested that organisms could change during their lifetimes by selectively using or not using varies parts of their bodies. They can pass these aquire traits on to their offspring enabling species to change overtime |
|
|
|
Who is Malthus? |
Reasoned that if the human population grew unchecked, there wouldn't be enough living space and food for everyone. |
|
|
|
What is natural selection? |
Process by which organisms with variations most suited to their local environment survive and leave more offspring. |
Survival of the fittest. |
|
|
Conditions for natural selection? |
More individuals are born then can survive; Natural heritable variation; Variable fitness among individuals; All characteristics must be heritable. |
|
|
|
What are homologous structures? |
Shared by related species that have been inherited from a common ancestor. Ex: front limbs for reptiles and birds |
|
|
|
Analogous structures? |
Body parts that share common function, but not structure. Ex:bird wing v.s. bee wing |
|
|
|
Vestigial structures? |
Inherited from ancestors that have lost most or all of their original functions. Ex: hip bone of bottlenose dolphin. |
|
|
|
Evolution in terms of genetics? |
Evolution, in genetics, involves a change in frequency of alleles in a population over time. |
|
|
|
3 types of natural selection? |
Directional, stabilizing, and disruptive. |
|
|
|
Directional selection? |

Individuals at one end of the curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve. Average size will increase. |
|
|
|
Stabilizing selection? |

When individuals near the middle of the curve have higher fitness than individuals at either end. Fitness of smaller or larger is less than that of average size. |
|
|
|
Disruptive selection? |

Individuals at both ends of the curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle. Small and large have higher fitness than average. |
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
What are isolating mechanisms? |
Characteristics of species that reduce or prevent repeoduction. Leads to new species. |
|
|

|

Must foil |
|
|
|
DNA replication? |
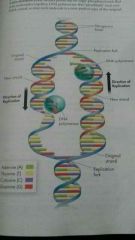
Takes place in nucleus. Strands of DNA separate. DNA polymerase attaches new strands |
|
|
|
3 types of isolation? |
Behavioral - different mating rituals Geographic Geographic barriers separate two populations Temporal - some reproduce during the day, some at night. |
|
|
|
What is a dichotomous key? |
A chart used to identify organisms based on phenotypes. |
|
|
|
Linnaean classification? |
Classification system that organizes species into taxa |
|
|
|
Levels of taxa? |
Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species. |
|
|
|
What is a cladogram? |
Diagram of depicting patterns of shared characteristics among species. Shows evolution and common ancestors. |
|
|
|
3 domains with their matching kingdoms? |
Bacteria-Eubacteria Archae- Archaebacteria Eukarya- protista, fungi, plantae, animalia |
|
|
|
Characteristics of a virus? |
Small with a capsid. All have genes. Made of protein, nucleic acid, and lipids. Nonliving |
|
|
|
Two types of viral infections? Describe? |

Lytic- virus enters, makes copies of itself, and causes cells to burst. Lysogenic- viral nucleic acid is inserted into host cells DNA, where it is copied and multiplies. |
|
|
|
Bacteriophage? |

|
|
|
|
What type of cell does each domain include? |
Bacteria- prokaryotic Archae- prokaryotic Eukarya- eukaryotic |
|
|
|
Treatments for bacterial infection? |
Physical removal, disinfectants, food storage, boiling food, sterilization by heat, antibiotics. |
|
|
|
Treatments for viral infection? |
Vaccines, antiviral drugs, personal hygiene. |
|
|
|
What is a protist? |
Eukaryotes that aren't members of fungi, plantae, or animalia kingdoms. Mostly unicellular. Extremely diverse. |
|
|
|
What is a fungi? |
Heterotrophic eukaryotes with cell walls containing chitin. |
|
|
|
Characteristics, domain, and kingdom of mammals? |
Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia. Mammals have mammary glands, are endothermic, hair, and three bones in their ears for balance. |
|

