![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the forecast period for the moving average? |
It is simply two periods (i.e. weeks) ahead of the exponential moving average |
|
|
What is the forecast period for the exponential moving average?
|
It is simply the one period (i.e. weeks) ahead of the exponential moving average
|
|
|
How to you calculate the accuracy of moving average using the mean square. |
Mean Square (moving average) Sum Difference^2 ________ Number of points compared Difference = Actual – Forecast |
|
|
How to you compare the accuracy of moving average vs exponential moving average using the mean square?
|
The lower the MSE, the closer is the forecast to the observed data
|
|
|
If there is a trend what method should you use? |
Holts method takes into consideration the trend
|
|
|
If there is a trend and seasons what method should you use? |
Holt Winters Method |
|
|
Write a report on your findings and on the assumptions you have made.Discuss the relevance ofmethods used and recommend possible improvements.
|
|
|
|
Describe the three major categories of forecasting techniques. Give at least two relevant examples for each ofthe categories.
|
Three categories of major forecasting techniques are:
|
|
|
How do you calculate a 3 point moving average? |
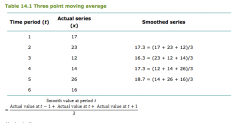
|
|
|
How to do you calculate an exponential moving average? |
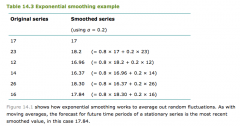
|
|
|
How do you calculate Holtz Method? |
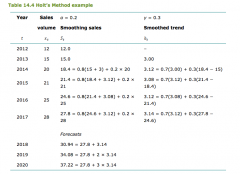
|
|
|
Write a report on your findings. Indicate any other information you would consider relevant. Detail your recommendations for further research and analysis?
|
|
|
|
How do you set out the calculations for Holtz method? |
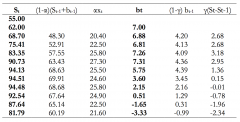
|
|
|
How do set out the calculation to forecast for Holtz method? |
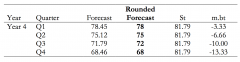
|
|
|
Holtz Method
Write a short report describing any assumptions you have made andcommenting on the reliability of the forecasts? Discuss the relevance of any alternative models that could have been used. |
|

