![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Rotation |
Movement around its longitudinal axis |
|
|
Flexion |
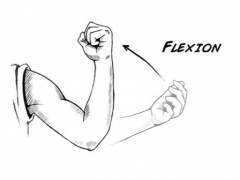
Decrease in angle |
|
|
Extension |
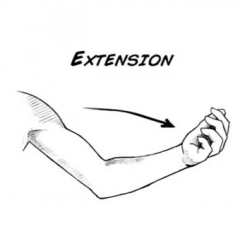
Increase in angle |
|
|
Hyperextension |
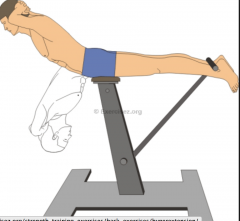
Extension beyond normal limits. |
|
|
Lateral flexion |
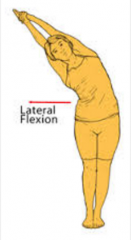
Movement of trunk away from midline |
|
|
Abduction |
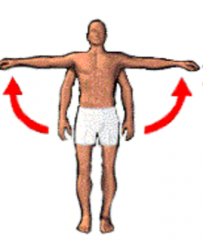
Movement away from midline |
|
|
Adduction |
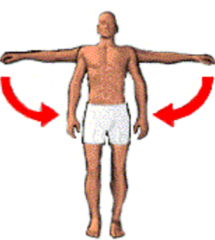
Movement towards midline. |
|
|
Circumduction |
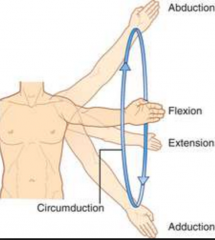
Circular Flexion, abduction, extension and Hyperextension in succession |
|
|
Elevation |
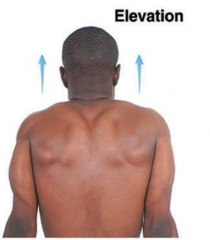
Upward movement |
|
|
Depression |
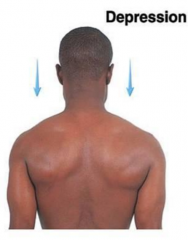
Downward movement |
|
|
Protraction |
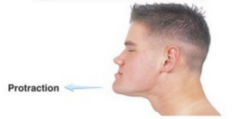
Movement forward in transverse plane |
|
|
Retraction |
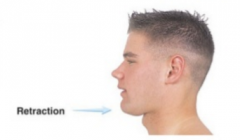
Movement back in transverse plane |
|
|
Inversion |
Sole turn in |
|
|
Eversion |
Sole turns out |
|
|
Dorsiflexion |
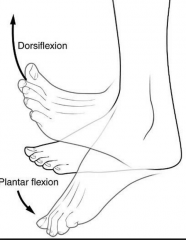
Bending foot up |
|
|
Plantar flexion |
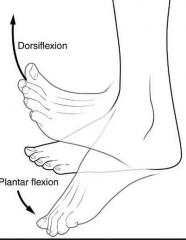
Bend foot down |
|
|
Supination |
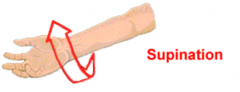
Movement of forearm to turn palm up |
|
|
Pronation |
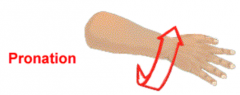
Movement of forearm to turn Palm towards the back |
|
|
Opposition |
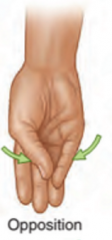
Movement of thumb across Palm to touch fingertips |
|
|
What are the two differenttypes of molecular transport in the human body? Direction and energy used? |
Active (Energy needed) Passive (Down concentrationgradient & no energy used) |
|
|
Name three types of PASSIVETRANSPORT. |
Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis |
|
|
Name three types of ACTIVETRANSPORT? |
Sodium Potassium Pump Endocytosis Exocytosis |
|
|
Diffusion: Substance size,most efficient when…, occurs in … |
Small substances high to lowconcentration Larger gradients and warmertemperatures Gases, liquids, ion solutions |
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion:Substance size, how, regulation, e.g.? |
Large substances high to low Protein carrier forms proteinchannel and deposits substance on other side Specific one substance only Substances too large todiffuse e.g. Glucose, Amino Acids |
|
|
Osmosis: What? Why? |
Water down concentrationgradient. Usually when molecules (notwater) cant be moved via diffusion. Isotonic, hypertonichypotonic |
|
|
Sodium Potassium Pump: What?How? E.g. |
Substances to area of low tohigh ATP used to activate proteincarrier molecules. Sodium, Potassium, Calcium,Hydrogen |
|
|
Endocytosis: Types? Whathappens? |
Phagocytosis and pinocytosis. Particles engulfed byinvagination of membrane forming a vacuole.Lysosomes adhere to vacuoleand release enzymes to digest contents. |
|
|
Exocytosis: What? Whathappens. E.g. |
Removal of waste. Reverse of endocytosis. Secretory granules formed byGolgi, residue of phagocytosis. |
|
|
How many joints are there in the body? |
187 |
|
|
Three types of joint? |
Fibrous (Sutures) Cartilaginous Synovial |
|
|
What is a fibrous joint? Example Also known as... |
Fixed bones held together by connective tissue. Skull bones only. Sutures |
|
|
What is a cartilaginous joint? Example |
Immovable and slightly movable joint connected by cartilage (no cavity) e.g. pad of fibrocartilage in intervertebral disk |
|
|
What is a synovial joint? |
Freely moveable joint. |
|
|
6 types of synovial joint and examples. |
1. Ball and socket (hip and shoulder) 2. Hinge (knee and elbow) 3. Pivot (neck axis up and down) 4. Planar - intercarpal 5. Ellipsoid - wrist 6. Saddle -thumb |
|
|
Movement associated with a hinge joint? (2) e.g. |
Flexion and extension Elbow |
|
|
Movements associated with a pivot joint? e.g. |
Pronation Supination e.g. turning wrist inside and out via radius |
|
|
What makes up a joint from outside in? |
- Articular (joint) capsule - Synovial membrane (flush with articular cartilage) -Synovial cavity plus synovial fluid. |

