![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the levels of organisation within organisms from smallest to biggest?
|
Organelles - Different parts of the cells
Cells - Smallest; functional unit, blocks, have specific functions Tissue - Similar cells working in the same way (Photosynthesis occurs in the palisade tissue) Organ - Groups of tissues working together (Leaf makes food and allows for gas exchange) System - Organs working together (Heart and Blood Vessels are the circulatory system) Organism - Made up of many organs/systems |
|
|
Describe the structure of an animal cell and a plant cell.
|
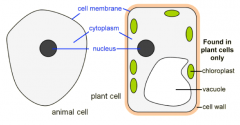
Animal cells contains a cell membrane, a cytoplasm and a nucleus. Plant cells contains all of the above as well as chloroplasts, vacuoles and cell walls.
|
|
|
What is the function of a nucleus?
|
Controls what the cell does. Contains instructions to make new cells
|
|
|
What is the function of a cytoplasm?
|
Chemical reactions go on inside the cytoplasm, which keep the cell alive.
|
|
|
What is the function of a cell membrane?
|
Thin skin around the cell. Gives cell shape and controls what goes in/out (partially permeable).
|
|
|
What is the function of a cell wall?
|
Outside the thin cell membrane. Made of tough cellulose which strengthens cell, provides support.
|
|
|
What is the function of a chloroplast?
|
Found in cells that carry out photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll to trap light energy.
|
|
|
What is the function of a vacuole?
|
Plant cell has a large permanent vacuole filled with a liquid called cell sap.
|
|
|
What is the function of cell sap?
|
Contains sucrose, water, amino acids, glucose, salts, stores materials, mechanical support for non-woody plants.
|
|
|
What are the differences between plant cells and animal cells?
|
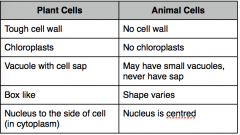
|
|
|
Define diffusion.
|
The movement of particles from a high concentration to a lower concentration until they are spread out evenly.
|
|
|
Define osmosis.
|
The passage of water molecules from a dilute solution into a more concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane (the diffusion of water).
|
|
|
Define active transport.
|
The uptake of particles by cells against a concentration gradient. Active transport needs energy
|
|
|
What is the difference between turgid and flaccid cells?
|
Turgid cells are full of water and have a firm shape while when water passes out through osmosis (when placed in a strong solution), the cell becomes flaccid and the cell membrane peels away into the cell.
|
|
|
How does the surface area:volume ratio affect the rate of movement of substances into and out of cells?
|
The higher the surface area:volume ratio, the faster the rate of diffusion. More surface area increases the rate at which substances pass through the cell.
|
|
|
How does the temperature affect the rate of movement of substances into and out of cells?
|
Tempurature increases the rate of diffusion as particles have increased kinetic energy.
|
|
|
How does the concentration gradient affect the rate of movement of substances into and out of cells?
|
The rate of the movement of substances is directly proportional to the concentration gradient. The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of movement.
|

