![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What will happen to animal cell that is hypotonic |
It will get lysed or burst |
|
|
What happened to animal cell that is isotonic? |
It will be normal because the water is balanced |
|
|
What happened to animal cell when it is hypertonic? |
It will be shrivelled because the water go out |
|
|
What happened to plant cell that is hypotonic? |
It will be turgid because there is the cell wall keeping it from bursting |
|
|
What happened to plant cell that is isotonic? |
It will be flaccid/normal |
|
|
What happened to plant cell that is hypertonic? |
It will be plasmolysed because the water goes out of the cell and the cell membrane detaches from the cell wall |
|
|
Does passive movement need energy? How does it move through the gradient? State an example. |
Passive movement doesn't need energy. They moved down the gradient high to low. Diffusion and osmosis. |
|
|
Does active movement need energy? If yes where do they get the energy? How does it move through the gradient? State an example. |
Active movements need energy. From respiration. It moves against gradient low too high. Ion transport. |
|
|
What is the permeability of cell membrane? |
Partially permeable / semi permeable |
|
|
Meaning of fully permeable |
They let all substance go through |
|
|
Meaning of semipermeable |
They let only let certain size of substance to pass through |
|
|
Meaning of selective permeable |
They let only certain type of substance to pass through |
|
|
Is diffusion faster in high temperature or low temperature and why? |
High temperature, bcz the particle moves faster. |
|
|
Meaning of permeability |
Degree of passibilty |
|
|
Hypotonic |
Lower concentrations of solute/ high water potential. Water go IN |
|
|
Hypertonic |
Higher concentrations of solute/low water potential
Water goes out (What happen when you hyper - active you sweat when u sweat water goes out) |
|
|
Isotonic |
Balance water potential and solute |
|
|
Diffusion example |
-The spreading of perfume
-Gas exchange |
|
|
Osmosis example |
Red blood cells swelling to freshwater and plant root taking water. (Everything that have to do with water) |
|
|
Diffusion meaning |
Movement from higher concentrations to lower concentrations. Until it is even |
|
|
Osmosis meaning |
The movement of water from high water potential (low solute) to low water potential (high solute). Until it is even. |
|
|
Diffusion in Aveolus |
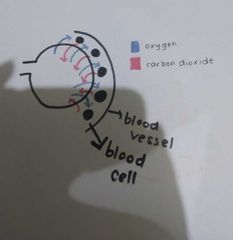
-The Alveolus which have high concentration of oxygen will give it to the blood which have low concentrations of oxygen (since it has been use)
-The blood which have high concentration of carbon dioxide will give it to the alveolus which have low concentrations of carbon dioxide |
|
|
Concentration gradient across the cell membrane |
The bigger the concentration different / gradient the faster
Because if it's a small gradient some of the particle already spread.
Kek Kalo you bikin teh kan lebih cepat diffuse di menit 1 dari pada menit 5 soalnya di menit 5 particle nya udh ada yang nge diffuse |
|
|
Thickness of membrane |
Thinner the fastest |
|
|
Surface of membrane |
Increased/bigger surface are the faster |

