![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Positon |
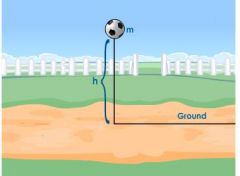
the location relative to a reference point; a vector quantity because it does have a direction
|
|
|
Vector |
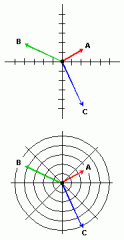
how fast something is moving and in what direction it is moving |
|
|
Acceleration |
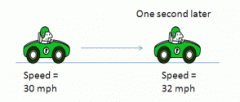
the rate of change of velocity |
|
|
Net Force |
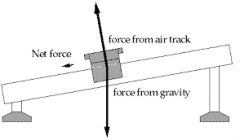
the sum of all the forcesacting on an object |
|
|
Newton's First Law |
also known as the law of inertia, states that an object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by unbalanced force |
|
|
Reference Point |
a basis or standard for evaluation, assessment, or comparison; a criterion. |
|
|
Motion |
a continuous change in the position of an object |
|
|
Centripetal acceleration |
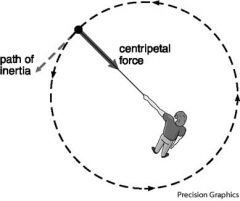
The tangential speed is constant, but the direction of the tangential velocity vector changes as the object rotates |
|
|
Inertia |

a tendency to do nothing or to remain unchanged |
|
|
Newton’s Second Law |
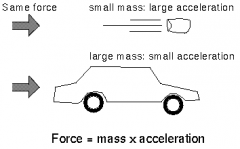
The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object |
|
|
Speed |

way of measuring how quickly something is moving or being done, or something moving fast |
|
|
Velocity |
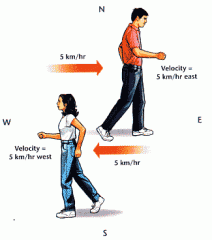
physical vector quantity, measured in metres per second |
|
|
Force |
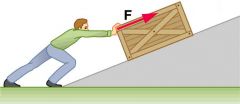
strength or energy as an attribute of physical action or movement |
|
|
Newton |
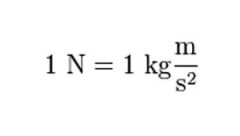
equal to the force needed to accelerate a mass of one kilogram one meter per second per second, used to measure force |
|
|
Newtons third law |
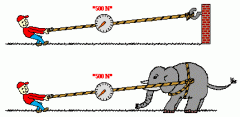
in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects; size of the forces on the first object equals the size of the force on the second object |

