![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the word morphology used by dermatologists to describe? |
Form and structure of skin lesions |
|
|
What are the key elements in establishing the diagnosis? |
Morphologic characteristics of skin lesions |
|
|
What are the two steps in establishing the morphology of any given skin condition? |
1. Careful visual and tactile inspection 2. Application of correct descriptors |
|
|
What six identifiers should you include in a "visual" inspection? |
1. Palpability (indicated by shadow) 2. Color 3. Shape 5. Size 6. Location |
|
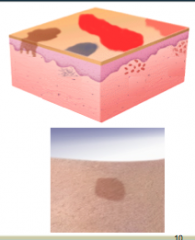
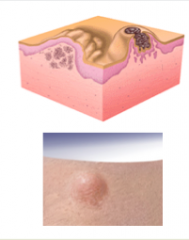
Describe the MACULE. |
Macule = FLAT (cannot feel it) |
|
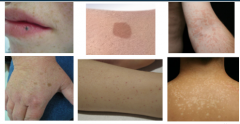
What is shown here? |
Macules |
|
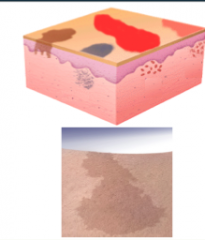
Describe PATCHES. What are they larger than? |
Patches = flat and larger than 1 cm LARGER than macules |
|
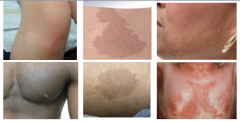
What is shown here? |
PATCHES |
|
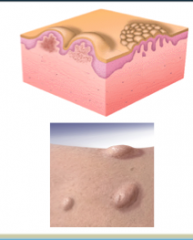
Describe papules. Causes of papules? |
RAISED lesions LESS than 1 cm Proliferation of cells in epidermis or superficial dermis |
|
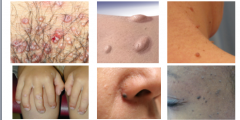
What is in the image here? |
PAPULES |
|
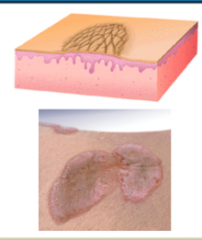
Describe PLAQUES What causes them? |
RAISED, greater than 1 cm
Cause = proliferation of cells in epidermis or superficial dermis |
|
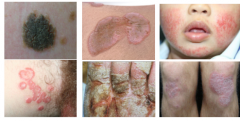
What is shown here? |
Plaques |
|
Describe nodules ("small knots"). What are they caused by? |
Cause = proliferation of cells into MID-DEEP dermis |
|
What is shown? |
Nodules |
|
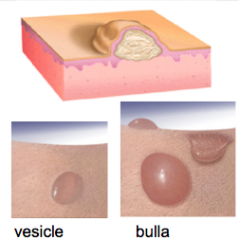
Describe VESICLES ("little bladder"). What is a large blister called? |
Vesicle = fluid-filled papule (small blisters) Bulla ("bubble") = large (> 1cm) blister |
|
What is shown here? |
Vesicles |
|
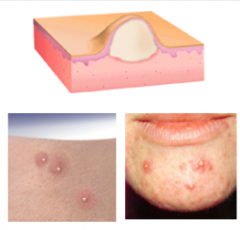
Describe PUSTULE Contents? Two other similar lesions. |
Pustule = contains pus = leukocytes and thin fluid called "liquor puris."
Furuncle and abscess |
|
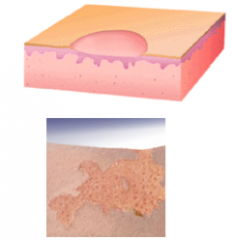
What are erosions? When do they occur? What happens to them? |
Erosion = loss of part or all of the epidermis
Occur after vesicle forms and the top peels off
Weep and become crusted |
|
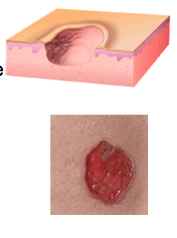
Ulcers are complete loss of the ____________ in addition to part of the ___________. Do they heal with scarring? What lesion doesn't? |
Epidermis, dermis Yes = ulcers heal with scarring Erosions = do not heal with scarring |
|
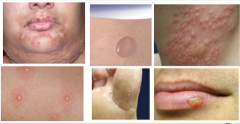
Describe the lesion and identify it. Elevated, flat, or depressed? Size, shape, color, border, configuration, distribution |
Small, flat lesion = MACULE
Size = 3 - 10 mm Shape = round to oval Color = pink to tan Border = sharp, irregular borders Configuration = septate, in no particular pattern Distribution = Upper chest, back, and flexures of arms |
|
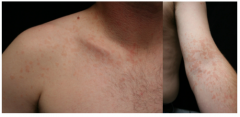
What was the test performed to make the diagnosis? Diagnosis? Primary lesion? |
Potassium hydroxide exam Tinea versicolor (primary lesion = macule) |
|

|
B = feel flat D = be any shape |
|
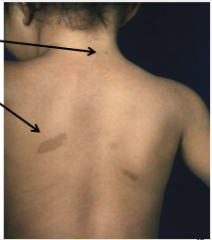
Identify the two lesions. |
Top = macule (<1cm) Bottom = patch (>1cm) |
|
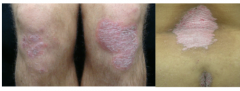
How would you describe these skin findings? Raise, flat, or depressed? Size, shape, color, borders, texture, configuration, distribution |
Large, plateau-like, raised lesions = plaques
Size = 3 to 10 cm Shape = round to geographic (map-like) Color = pink Sharp borders = sharply circumscribed Texture = scaly Configuration = symmetrical Distribution = extensor surfaces (knees, elbows), back, gluteal cleft |
|
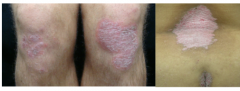
Diagnosis? Primary lesion in this case? |
Psoriasis Plaque |
|
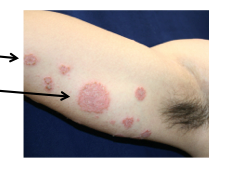
Identify the two different lesions. |
Left = papule Right = plaque |
|
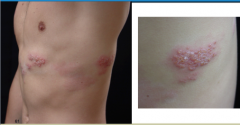
How would you describe these skin findings? Raised, flat, or depressed? Do they have fluid in them? Size, shape, color, texture, configuration, distribution. |
Raised, contain fluid, small = vesicles
Size = 2-5 mm Shape = round to oval Color = clear, with a background erythematous patch Texture = fluid-filled Configuration = grouped vesicles Distribution = Unilateral dermatomal distribution on the left chest
|
|
|
Define distribution. Define configuration. |
Distribution = location(s) on the body Configuration = how the lesions are arranged or relate to each other |
|
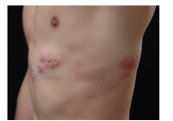
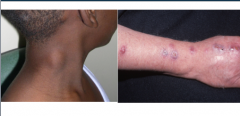
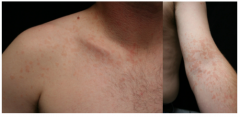
What is the term for lesions that are grouped but also follow a linear pattern around the trunk? |
Segmental or "dermatomal" distribution |
|
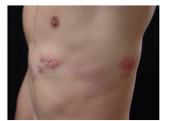
What is the diagnosis? What is the primary lesion? |
Shingles Primary lesion = vesicle |
|
Complete the table. |
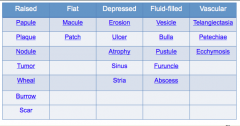
|
|

|

|

