![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Tap root system |
Mustard |
|
|
|
Fibrous root system |
Wheat |
|
|
|
Adventitious roots |
Grass Monstera Banyan |
|
|
|
Modifications of root for storage |
Carrot and turnip - Tap root Sweet Potato - adventitious roots |
|
|
|
Pneumatophores found in |
Rhizophora |
|
|
|
Type of root in raddish |
Fusiform |
|
|
|
Type of root in carrot |
Conical |
|
|
|
Type of root in turnip |
Napiform |
|
|
|
Faciculated root in |
Asperagus and dahlia |
|
|
|
Root in sweet potato is called |
Iponia |
|
|
|
Modifications in stem to store food |
Potato Ginger Turmeric Zaminkand Colocasia |
They act as organs of perennation |
|
|
Tuber is seen in |
Potato |
|
|
|
Rhizome is seen in |
Ginger Turmeric Banana Pineapple Chrysanthemum |
|
|
|
Corm is seen in |
Zaminkand Colocasia |
|
|
|
Stem tendrils is found in |
Gourds and grapevine Gourds include:- Cucumber Pumpkin Watermelon |
|
|
|
Thorns are found in |
Citrus Bougainvillea |
|
|
|
Flattened photosynthetic stem |
Opuntia |
|
|
|
Cylindrical photosynthetic stem |
Euphorbia |
|
|
|
Runner is found in |
Runners spread to new niches and when older parts die, they germinate. Grass Strawberry |
|
|
|
Stolon is seen in |
Stolon is a slender lateral branch that arises from the base of the main axis and after growing aerially for sometime , they arch downwards to touch the ground. Mint Jasmine |
|
|
|
Offset is seen in |
Offset is a lateral branch of stem with short internodes and each node bearing a rosette of leaves and a tuft of roots. Pistia Eichhornia |
|
|
|
Rhizome as vegetative propagule |
Banana Pineapple Chrysanthemum |
Lateral branches arise from the lower and underground part of stem, grow horizontally under the soil and come out obliquely as leafy shoots |
|
|
Pinnately compound leaf |
Neem |
|
|
|
Palmately compound leaf |
Silk cotton |
|
|
|
Alternate phyllotaxy |
China rose Mustard Sun flower |
|
|
|
Opposite phyllotaxy |
Calotropis Guava |
|
|
|
Whorled phyllotaxy |
Alstonia |
|
|
|
Leaf tendrils |
Pea |
|
|
|
Spines as modification of leaf |
Cactus |
|
|
|
Leaf modification for storage |
Fleshy leaves in onion Garlic |
|
|
|
Australian acacia |
The leaves are small and short lived, petioles expand, become green and synthesize food |
|
|
|
Insectivorous plants |
Pitcher plant Venus fly trap Modified leaves |
|
|
|
Types of racemose inflorescence |
Raceme Spike Corymb Umbel Capitulum |
|
|
|
Raceme is seen in |
Mustard Radish |
|
|
|
Spike is seen in |
Grass |
|
|
|
Corymb is seen in |
Cauliflower |
|
|
|
Umbel is seen in |
Coriander |
|
|
|
Capitulum is seen in |
Ray and disc flowers of sunflower and marigold |
|
|
|
Racemose example |
Mustard Radhish Grass Cauliflower Coriander Ray and disc flowers of sunflower and Marigold |
|
|
|
Cymose example |
Grapes |
|
|
|
Perianth |
Calyx and corolla fuse together to form a single unit In lily |
|
|
|
Actinomorphic example |
Mustard Datura Chilli |
CADM |
|
|
Zygomorphic example |
Pea Gulmohar Bean Cassia |
BC GP Z |
|
|
Asymmetric example |
Canna |
|
|
|
Bract |
Reduced leaf found at the base of the pedicel |
|
|
|
Hypogynous flower |
It has superior ovary Mustard China rose Brinjal |
|
|
|
Perigynous flower |
It has half inferior ovary Plum Rose Peach |
|
|
|
Epigynous flowers |
It has inferior ovary Guava Cucumber Ray florets of sunflower |
|
|
|
Unit of calyx |
Sepals |
|
|
|
Sepals United |
Gamosepalous Brinjal Cotton Datura |
|
|
|
Sepals free |
Polysepalous Mustard Radish |
|
|
|
Petals United |
Gamopetalous |
|
|
|
Petals free |
Polypetalous |
|
|
|
Tubular Corolla is found in |
Datura Petunia |
|
|
|
Valvate Aestivation |

They touch each other at the margin without overlapping
Calotropis |
|
|
|
Twisted Aestivation |
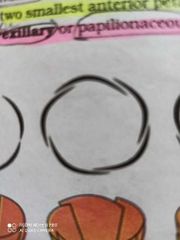
One margin overlaps the next appendage Lady's finger China rose Cotton |
|
|
|
Imbricate Aestivation |
When the margins overlap in no particular order Cassia Gulmohar |
|
|
|
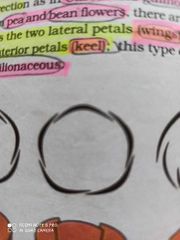
Vexillary Aestivation |

It has 5 appendages 1 large Standard 2 medium Wings 2 tiny Keel Found in pea and bean |
|
|
|
Staminode |
Sterile stamen |
|
|
|
Epipetalous condition |
When stamens are fused with petals Brinjal |
|
|
|
Epiphyllous condition |
Stamen attached to perianth Lily |
|
|
|
Polyandrous condition |
Stamens remain free |
|
|
|
Monoadelphous condition |
Stamens are grouped into one bundle China rose |
|
|
|
Diadelphous condition |
Stamens grouped into two bundles Pea |
|
|
|
Polyadelphous condition |
Stamens grouped into more than 2 bundles Citrus |
|
|
|
Variation in the length of stamens in a flower |
Salvia Mustard |
|
|
|
Carpels or pistils free |
Apocarpous Lotus Rose |
|
|
|
Carpels fused |
Syncarpous Mustard Tomato |
|
|
|
Marginal placentation |
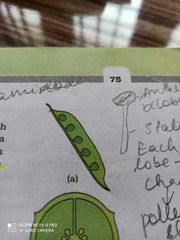
Placenta forms a ridge along the ventral suture and ovules are borne on this ridge in two rows Pea |
|
|
|
Axile Placentation |
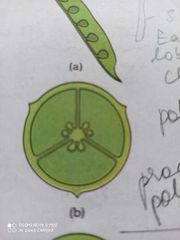
Multilocular ovary China rose Tomato Lemon |
|
|
|
Parietal placentation |
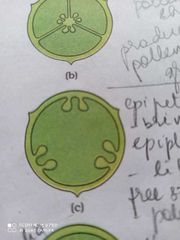
Ovules on the inner wall or peripheral part of the ovary. Mono locular It could be bilocular due to the formation of a false septum Mustard Argemone |
|
|
|
Free Central placentation |
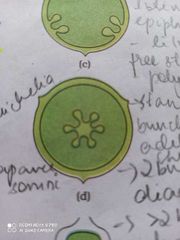
Ovules are there on central axis Septa absent Unilocular Dianthus Primrose |
|
|
|
Badal placentation |
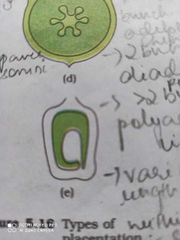
Ovule is formed at the base of the ovary Single ovule Sunflower Marigold |
|
|
|
Parts of a fruit |

|
|
|
|
Drupe |
Fruit in coconut and mango is called drupe. They develop from monocarpellary superior ovary and are single seeded |
|
|
|
Endospermic seed |
Endosperm persistent in seed Castor Most monocotyledonous seeds Maize |
|
|
|
Non endospermic seed |
Bean Gram Pea Orchids |
|
|
|
Aleurone layer |
Outer proteinaceous covering of endosperm proteinaceous covering of endosperm covering of endosperm |
|
|
|
Scutellum |
It is the cotyledon found in monocots |
|

