![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Structure |
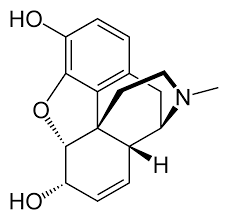
Phenanthrene 5 rings |
|
|
|
Preparations |
Liquid Oral IV Intrathecal |
|
|
|
Isomers |
Levorotatory is active isomer |
|
|
|
Pka |
7.9 - weak base 23% unionised at phys pH |
|
|
|
Lipid solubility Potency |
Poor relative potency - 1 |
|
|
|
Pharmacokinetics - Absorption |
Oral availability variable ~30% ionised in stomach - therefore absorbed later Bioavailability ~ 25% as 7% taken up by lungs |
oral/bioavailability |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics - Distribution |
PPB - 35% Vd - 3L/Kg |
PPB Vd |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics - Metabolism |
Liver, **kidney 75% ⇒ M3G inactive 10% ⇒ M6G active (same duration, 13 x potency) 5% ⇒ demethylated to normorphine |
Location Metabolites and activity |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics - Excretion |
Clearance 16ml/kg/min 90% renal 10% bile none unchanged. T𝜷1/2 = 2hrs |
Clearance rate Proportion renal/liver % unchanged. |
|
|
Pharmacodynamics - Opioid receptor effects |
- Activation of opioid receptors - GPCR - Inhibit adenylate cyclase - decreased cAMP - Increase K conductance = hyperpolarise membrane - Block presynaptic ca channels = reduce nervous transmission. |
|
|
|
Pharmacodynamics - CNS |
Analgesia - Visceral > m/skel Euphoria Miosis Decreased Cerebral BF Decreased ICP Sedation Euphoria |
|
|
|
Pharmacodynamics - CVS |
Central vagal excitation = bradycardia Mildly negatively inotropic ↓ SVR secondary to histamine release. = ↓ in C.O. and MAP |
|
|
|
Pharmacodynamics - Resp |
Due to agnoism at mu2 ↓RR and ↓MV TV can ↑ or ↓ ↓ of pontine and medullar ventilatory centres - shifts CO2 response to right, and can cause apnoea/pauses and periodic breathing Cough suppressant |
|
|
|
Pharmacodynamics - GIT |
↓ motility and gastric emptying Risk of biliary/sphincter oddi spasm |
|
|
|
Pharmacodynamics - Renal |
Reduced due to reduced CO |
|
|
|
Obstetrics |
rapid placental transfer no affect on uterine tone |
|
|
|
Side effects |
Nausea Pruritis Heaviness, warmth His release: |
|
|
|
Interactions |
Cardiac effects worsened in combo with N20 or benzos MAOI = exaggerated CNS depression |
|

