![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the characteristics of a monopolistic competition model? (6)
|
- free entry/exit
- large number of buyers/sellers with little market power each - firms produce differenciated goods - there is perfect knowledge in the market - firms maximise profits in the short run - each firm has a downwards sloping demand curve because products are not homogenous so as price increases demand falls |
|
|
Examples of firms in monopolistic competiton?
|
H&M, Zara, florist, hairdressers, restaurants
|
|
|
Short run equilibirum position for a monopolistically competitive firm?
|
firms can make a supernormal profit in the short run.
due to lack of barriers to entry, the supernormal profits attract new firms into the industry. so, as supply increases and market price falls, supernormal profits are competed away in the long run this is because each firm's share of demand falls and the demand curve shifts to the left |
|
|
what determines how much supernormal profit is earned in the short run by mono comp?
|
their ability to differenciate products by using brand names and advertising
|
|
|
why are firms still allocatively inefficient in the short run?
|
because p>mc
|
|
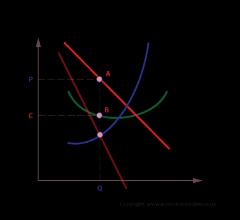
|
short run equilibrium position in monopolistic competition
|
|
|
in the long run, where is the demand curve for mono comp?
|
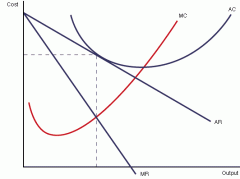
at a tangent to average cost
|
|
|
why are monopolisticaly competitive firms productively inefficient in the long run?
|
because firms dont produce at the lowest part of the AC curve which makes the firm productively inefficient as the firm has extra capacity (not producing along the PPC)
|
|
|
In the long run, which two rules for monopolistic competition hold?
|
AC=AR - because freedom of entry/exit ensures that firms cant make supernormal profits in the long run
MC=MR - because all firms are profit maximisers |
|
|
Explain the MC=MR long run rule for monopolistic comp?
|
because all firms are profit maximisers
|
|
|
Explain the AC=AR long run rule for monopolistic comp?
|
freedom of entry/exit ensures that all firms cannot earn supernormal profits
|
|
|
why is non price competition key in this market structure?
|
as all firms produce differenciated products
|
|
|
define price competition and all the types (5)
|
the use of difference price strategies including:
- going rate - loss leader - penetration - promotional -psychological |
|
|
Explain going rate pricing as a method of price competition?
|
price based on the average charged by all firms in the industry
|
|
|
Explain loss leader pricing as a method of price competition?
|
setting a price below cost price to entice consumers. these consumers then may also buy related and more expensive products by the same firm
|
|
|
Explain penetration pricing as a method of price competition?
|
used by new entrants to set a low introductory price when entering the market to establish market share
|
|
|
Explain promotional pricing as a method of price competition?
|
charging a low price to attract consumers to raise brand awareness and customer loyalty
|
|
|
Explain psychological pricing as a method of price competition?
|
£9.99 can seem a lot cheaper than £10
|
|
|
What are the methods of non-price competition?(6)
|
- ADVERTISING
- BRANDING, used to gain customer loyalty - PACKAGING, distinguish products from one another and creates a selling point - PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT, special features, limited edition - QUALITY OF SERVICE - QUALITY OF AFTER SALES SERVICE, warranty, technical support, delivery service |
|
|
Monopolistically competitive firms are neither EFFICIENTLY or ALLOCATIVELY productive in the SHORT OR LONG runs
|
OK
|
|
|
Why do inefficiencies occur in this market?
|
due to the large amount of choice that consumers have
|
|
|
why are these firms allocatively inefficient?
|
these firms are price makers and have a small share of market power (much smaller than monopoly) so P>MC
price exceeds marginal cost = allocatively inefficient |
|
|
why are these firms not productively efficient?
|
they do not produce on the lowest part of their average total cost curve as there are limited opportunities to exploit economies of scale
|
|
|
perfect comp and monopolistic comp both have small producers
|
SIMILARITY
|
|
|
monopolistic comp can product differenciate but monopolists cannot do this because they are the only supplier
|
DIFFERENCE
|
|
|
choice is greater for consumers in monopolistic comp than in perfect comp (as firms only supply homogenous products in perfect comp)
|
DIFFERENCE
|
|
|
monopolistic comp can enjoy economies of scale although this is limited by the size of the firm and the differenciated products they supply
|
POSITIVE
|
|
|
firms in perfect comp are productively and allocatively efficient in the long run but those in monopolistic comp are not
|
DIFFERENCE
|
|
|
monopolist comp and monopoly are inefficient market structures
|
SIMILARITY
|
|
|
monopolistic comp firms have much less power than monopolies
|
DIFFERENCE
|
|
|
While competition is beneficial, natural monopolies avoid/eliminate wasteful competiton
|
good
|
|
|
both perfect comp and mono comp have barriers to entry/exit
|
SIMILARITY
|
|
|
monopolists can earn abnormal profits in the long run due to the nature of barriers to entry
|
TRUE
|

