![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Assumptions for a pure monopoly
|
- Only one firm in the industry
- The product is unique - Barriers to entry: Legal barriers (patent) Sunk costs (large fixed costs) Capital costs (brand name) Scale economies Strategic barriers (limit pricing) - Monopoly short run profit maximiser |
|
|
|
Disadvantages of a monoply
|
- Allocative inefficiency leading to deadweight loss. Abnormal profits are made at the expense of economic efficiency. Monopolist restrict output to charge a higher price, loss of consumer surplus.
- Productive inefficiency - X inefficient |
|
|
|
Advantages of a monopoly
|
- Economies of scale leading to lower prices
- Abnormal profits used for research and development making them dynamically efficient - Restricting output may improve resource allocation |
|
|
|
Monopolies and international competitiveness
|
British economy needs multinational companies operating on a large scale to compete effectively in global markets.
|
|
|
|
Natural monopoly argument
|
A natural monopoly occurs when there are large economies of scale; the minimum efficient scale is higher than the total demand of an industry.
There is only room for one supplier to fully exploit the economies of scale. There are high fixed costs for new firms to enter. If the government control natural monopoly losses are made |
|
|
|
Natural monopoly argument
|
A natural monopoly occurs when there are large economies of scale; the minimum efficient scale is higher than the total demand of an industry.
There is only room for one supplier to fully exploit the economies of scale. There are high fixed costs for new firms to enter. If the government control natural monopoly losses are made |
|
|
|
Contestability
|
The threat of competition in a contestable market will make monopolies keep prices down and costs under control.
|
|
|
|
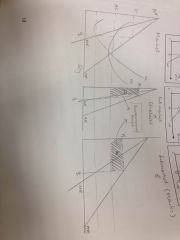
Price discriminatiob
|
Price discrimination is when different prices are set for the same good or service depending on the different price elasticities.
The output will be the same as under perfect competition so there is no deadweight loss, but the monopolist will appropriate all of the consumer surplus. |
|

