![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The bond market and money market are linked through wealth. According to John Maynard Keynes's liquidity preference framework, wealth is divided between two assets:
|
wealth is divided between two assets: interest-bearing bonds and non-interest-bearing money.
|
|
|
Total wealth equals the quantity of bonds plus the quantity of money in the economy:
|
Wealth = Quantity of Bonds + Quantity of Money
|
|
|
In equilibrium, the quantity of bonds supplied equals the quantity demanded. Likewise, the quantity of money supplied equals the quantity demanded in money market equilibrium. Therefore:
|
W = B^s + M^s = B^d + M^d
Rewriting this expression yields: B^s - B^d = M^d - M^s |
|
|
For the following question, consider how a change in the composition of wealth affects the bond and money markets. Suppose that people decide to hold more of their wealth as money.
Using the following diagram, illustrate how this change in preferences affects the money market. Drag the appropriate curve(s) to show what happens to the equilibrium interest rate. |
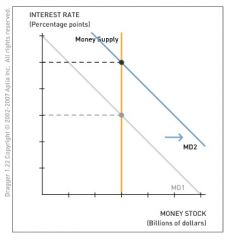
People willingly hold more money (relative to bonds), causing an increase in money demand, which increases the equilibrium interest rate.
|
|
|
For the following question, consider how a change in the composition of wealth affects the bond and money markets. Suppose that people decide to hold more of their wealth as money.
Using the following diagram, illustrate how this change in preferences affects the bond market. Drag the appropriate curve(s) to show what happens to the equilibrium bond price. |
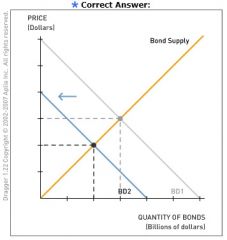
People willingly hold more money (relative to bonds), causing an increase in money demand. This means people must hold less of their wealth as bonds. This causes a decrease in bond demand, a decrease in the equilibrium bond price and an increase in the equilibrium interest rate.
|
|
|
When people shift their wealth from money into bonds, this causes an increase in the equilibrium interest rate.
True or False |
False-
If people shift wealth into bonds from money, money demand falls and the interest rate falls. In terms of the bond market, the increased bond demand causes an increase in the equilibrium bond price and a decrease in the interest rate. |
|
|
The following question considers how changes in the interest rate affect the bond and money markets.
Why is the money demand curve downward sloping in a market in which the interest rate is rising? |
As the interest rate rises, the opportunity cost of holding wealth as money rises.
When the interest rate rises, people forgo more interest when they choose to hold money instead of bonds. People shift their wealth from money into bonds. The result increases the quantity of bonds demanded and decreases the quantity of money demanded. The purchasing power of money falls when the price level rises. |
|
|
The following question considers how changes in the interest rate affect the bond and money markets.
Using the diagram, illustrate how an increase in the bond price affects the quantity of money demanded or the money demand curve. Assume the bond yield is the same as the interest rate in the money market. |
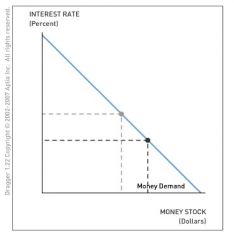
The increase in the equilibrium bond price implies a decrease in the interest rate. Recall that the bond price and interest rate (yield) are negatively related. The increase in the bond price, and the corresponding decrease in interest rate or yield, causes people to shift their wealth from bonds to money, thereby increasing the quantity of money demanded.
|
|
|
The following question uses the money market to analyze how changes in money demand or money supply or both affect the equilibrium interest rate. Drag the appropriate curve(s) to show how the following situation affects the money market.
The central bank increases the money supply. Assume no change in income, the price level, or the expected inflation rate. |
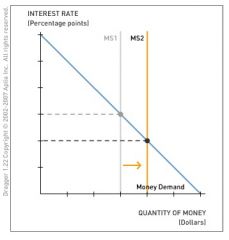
When the central bank increases the money supply, the money supply shifts right and the equilibrium interest rate decreases. Because income, the price level, and the expected inflation rate do not change, no other shifts in the money demand and supply curves occur.
|
|
|
The following question uses the money market to analyze how changes in money demand or money supply or both affect the equilibrium interest rate. Drag the appropriate curve(s) to show how the following situation affects the money market.
The expected inflation rate increases. |
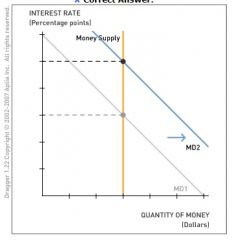
When the expected inflation rate increases, people buy more before prices rise in the future. To spend more, people hold more money, causing an increase in money demand and the interest rate. Because income and the price level do not change, no other shifts in the money demand and supply curves occur.
|
|
|
An economic research paper demonstrates that when the money supply rises, the interest rate falls immediately, but then rises over longer periods.
The research paper cited above implies the following? |
The liquidity effect dominates in the short term, while the income, the price level, and the expected inflation rate effects dominate over the long term.
The liquidity effect refers to the decrease in the interest rate caused by an increase in the money supply. An increase in money supply also causes an increase in income, the price level, and the expected inflation rate. These three effects put upward pressure on interest rates. |
|
|
An economic research paper demonstrates that when the money supply rises, the interest rate falls immediately, but then rises over longer periods.
Another research paper verifies these results, but shows how the liquidity effect has diminished over time. Which of the following could explain this? |
People adjust their inflation rate expectations sooner.
If people adjust their inflation rate expectations sooner, the expected inflation rate effect may appear in the short term. As people revise their inflation rate expectations, changes in money demand offset changes in money supply, so the liquidity effect weakens. |
|
|
An economic research paper demonstrates that when the money supply rises, the interest rate falls immediately, but then rises over longer periods.
Using the money market diagram below, illustrate a situation in which an increase in the money supply leads to an immediate change in inflation rate expectations. Drag the appropriate curve or curves to show the change in policy and inflation rate expectations. |
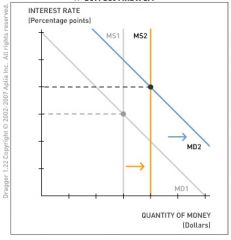
The increase in the money supply causes a rightward shift in the money supply curve. Inflation rate expectations increase because of the increase in the money supply growth rate. The money demand shifts rightward as people hold more money. If the expected inflation rate effect dominates the liquidity effect, the interest rate increases.
|

