![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Macromolecules |
Very large molecules that make up living things. We have lots of them. Made up of mostly Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen. Are polymers made up of monomers. |
|
|
|
Polymers and Monomers |
Polymer- A large molecule consisting of many identical or similar building blocks linked by covalent bonds. Monomers- The building blocks of a polymer. |
Train |
|
|
Metabolism |
All enzyme reactions in the body. (build & break) |
|
|
|
Anabolism |
Chemical reaction (type of metabolism) that builds larger molecules from small ones through Dehydration Synthesis (condensation). |
|
|
|
Dehydration Synthesis Reaction |
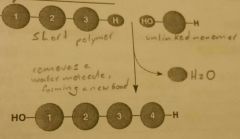
Removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. |
|
|
|
Hydrolysis |
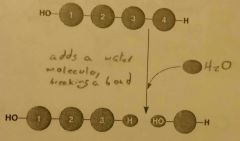
Adds a water molecule, breaking a bond. |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Type of organic molecule mostly for energy. ( CH2O )x, carbón and water. In fruits, vegetables and grains. |
|
|
|
Catabolism |
Chemical reaction (type of metabolism) that breaks down large molecules into smaller ones through Hydrolysis. (occurs during digestion) |
|
|
|
Monosaccharides |
Single sugars with 3-7 carbons. Monomer. Hexose or Pentose (sided) rings. Used as a primary energy source. 3 types, all reducing sugars. - glucose=blood sugar - fructose=fruit sugar - galactose=milk sugar |
|
|
|
Disaccharides |
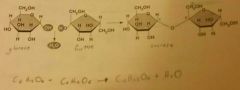
Double sugars ( C12H22O11 ) of 2 monosaccharides. Used as energy source and building blocks for larger molecules. |
|
|
|
Polysaccharides |
Complex carbohydrates made up of several 100s/1000s of monosaccharides. Two types both made of entirely glucose. |
|
|
|
Types of Disaccharides |
Maltose- glucose + glucose Lactose- glucose + galactose ( both reducing sugars) Sucrose- glucose + fructose |
|
|
|
Storage polysaccharides |
For energy storage. Made of alpha glucose. Humans can digest. |
|
|
|
Alpha glucose |
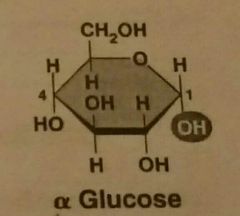
|
|
|
|
Glycogen |
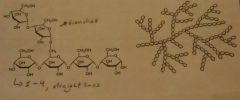
Storage polysaccharides in animals. Found in liver and muscles, easily digested. a1➡4 with a1➡6 branches |
|
|
|
Glycosidic linkages (alpha) |
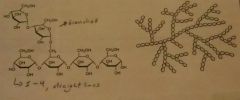
a1➡4 straight line a1➡6 branch |
|
|
|
Starch |
Storage polysaccharides in plants. Found in potatoes, legumes and grains. |
|
|
|
Types of starch |
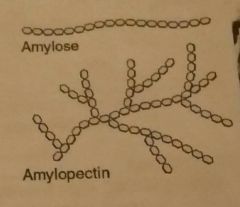
Amylose- a1➡4 slower digestion, less space/soluble/common (20-30%) Amylopectin- a1➡4 with a1➡6 branches easily digested, more space/soluble/common (70-80%) |
|
|
|
Structural Polysaccharides |
Used as structural material. Made of beta glucose. Indigestible fibre. |
|
|
|
Beta Glucose |
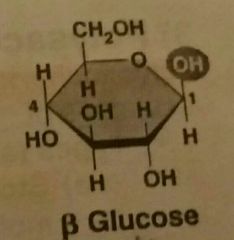
|
|
|
|
Chitin |
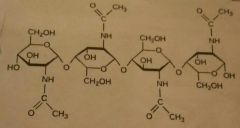
Structural polysaccharides in animals. B1➡4 often combined with calcium carbonate. Used by arthropods (insects, spiders and crustaceans) to build their exoskeleton. |
|
|
|
Cellulose |
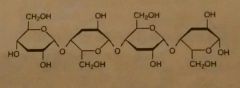
Structural polysaccharides in plants. B1➡4, straight parallel chains held together by H-bond. Found in fruits, vegetables and grains. Makes cell wall. |
Termites |
|
|
Glycosidic Linkages (beta) |
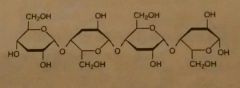
B1➡4 each upside down. H-bond. Straight parallel chains. |
|
|
|
Lipids |
Organic molecules with an oily, greasy or waxy consistency that are insoluble in water. Found in meats, dairy, nuts and plant oil. It's monomers are glycerol and fatty acid chains. |
|
|
|
Triglycerides |

Type of lipid with 3 fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule. Long term energy storage and physical and thermal insulation. 2.5 times more energy than carbs, but hard to transport in body. |
|
|
|
Fats |
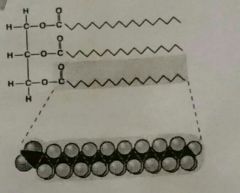
Triglyceride of animal origin. Solid at room temperature. Saturated fatty acids, no double bonds. |
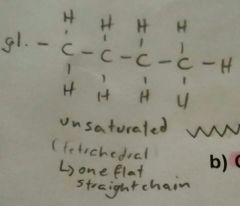
|
|
|
Oils |
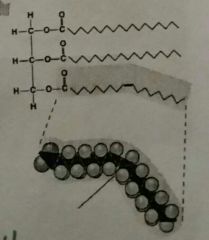
Triglyceride of plant origin. Liquid at room temperature. Unsaturated fatty acids, aka double bonds. |
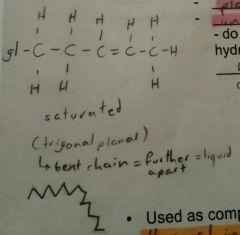
|
|
|
Double Bonds in Oil |
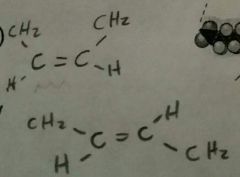
Cis- same side (healthier) Trans- opposite side |
|
|
|
Hydrogenated |
Synthetically converted to saturated fats by adding Hydrogen. ( to be kept solid) |
Margarine |
|
|
Phospholipids |
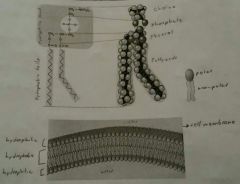
Type of lipid made up of a glycerol, 2 fatty acids and a phosphate. Main component of cell membrane. Hydrophilic head and Hydrophobic tails. |
|
|
|
Sterols (Steroids) |
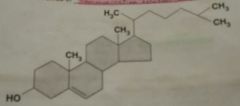
Type of lipid with complex ring structure. In hormones, for communication between cells. Sex- testosterone, estrogen, progesterol Stress- cortisol Kidneys/blood pressure regulation- aldosterone cholesterol |
|
|
|
Proteins |
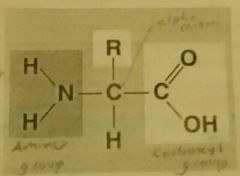
Type of macromolecule with one or more polypeptides folded up or coiled together in a 3d shape (conformation). Found in animal products and byproducts, nuts and legumes. It's monomer are amino acids. (20 different amino acids) Structure: carbon with an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen and a variable R (functional) group. |
|
|
|
Polypeptides |
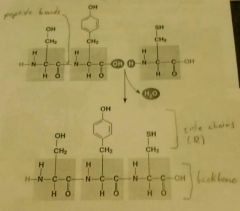
Polymers of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds (covalent). Each has an unique sequence of amino acids. Sequence determines 3d shape, 3d shape determines function. |
|
|
|
Polarity of Amino Acids |
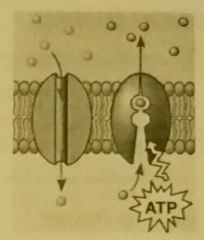
Determined by R groups, can be important to protein function. Hydrophilic channels through membranes: polar amino acids allow polar substances through. (non-polar embedded within the membrane, polar region portrudes) Specifity of active sites: (&complementary shape) attract or repel substrate from active cite. |
Straw |
|
|
Primary Structure of proteins |
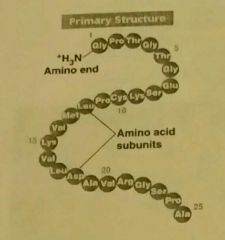
The unique sequence of amino acids. Determined by the DNA sequence. A polypeptide. |
|
|
|
Secondary Structure of proteins. |
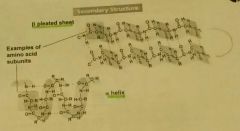
The coiling (alpha helix) and folding (beta pleated sheet) of sections of the amino acid. Caused by Hydrogen Bonds. |
|
|
|
Tertiary Structure of proteins. |
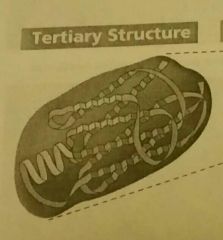
The specific shape of the 3d folding of the entire polypeptide. Interactions between the variable R groups. A functional protein. |
|
|
|
Quartenary Structure of proteins. |
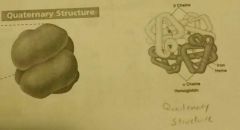
Two or more polypeptides grouped together into a functional protein. Only for some. Ex. hemoglobin |
|
|
|
Fibrous Proteins |
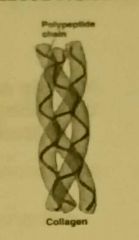
Long and narrow, with little or no tertiary structure. Insoluble in water, have structural roles. -collagen: strength in skin, tendons, cartilage and bone -keratin: strength in hair and nails -elastin: elasticity of arteries, lungs, skin and bladder -myosin: contraction of muscle fibres |
|
|
|
Globular proteins |
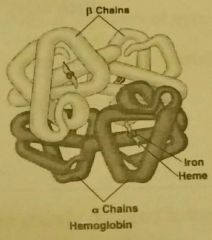
Rounded shape with complex tertiary or quartenary structure. Soluble in water with roles in metabolic reactions. -enzymes -immunoglobulins/antibiotics -transport proteins -hemoglobin: transport oxygen in red blood cells |
|
|
|
Functions of Proteins |
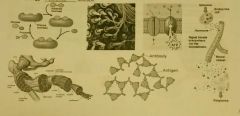
Chemical Reactions: enzymes Structural Support: muscles, tendons, bones and ligaments Movement: in muscles, actin and myosin Defense: immune system Transport: membrane transport Cellular Communication: cell receptors and hormones, insulin |
|
|
|
Nucleic Acids (polynucleotides) |
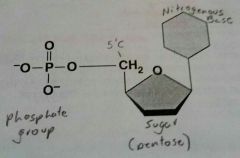
Store and transmit hereditary information that controls cellular activity. Monomer= Nucleotide containing a phosphate group, a sugar and a nitrogenous base. |
|
|
|
Nucleotide Sugars |
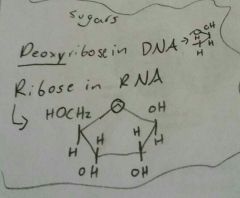
|
|
|
|
Nucleotide Nitrogenous Bases |
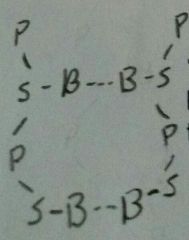
Adenine Thymine Guanine Cytytosine And Uracil in RNA only |
|
|
|
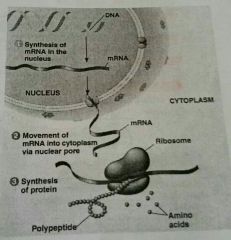
DNA and RNA |
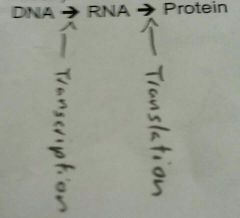
Deoxyribonucleic Acid: Stores genetic information in the nucleus. Double strand of polynucleotides in a double helix. Sequence of nitrous bases in a section codes for sequence of amino acids in protein.
Ribonucleic Acid: "reading" the DNA code, protein synthesis. Makes a copy of the code, takes it to cytoplasm, makes a protein. Single strand of polynucleotides. |
|
|
|
Micronutrients |
Required in very small amounts. Vitamins: Organic molecules -B & C water soluble. Minerals: Inorganic molecules |
V: scurvy M: dancing frog legs, toothpaste |
|
|
Cohesión and Adhesion |
Cohesion: water's attraction to itself Adhesion: water's attraction to other molecules |
Plants |

