![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Recombinant DNA |
A DNA molecule composed of DNA sequences derived from multiple sources |
|
|
DNA cloning: - A variety of techniques, referred to as __(a)__ technology, are used in DNA cloning - Allows preparation of large numbers of __(b)__ DNA molecules, often __(c)__ |
a. Recombinant DNA technology b. Identical c. Genes |
|
|
a. What is a nuclease? b. What is the difference between endonuclease and exonuclease? c. What is a restriction endonuclease? d. How long are restriction sites? |
a. An enzyme that cleaves/hydrolyzes the ester bond in a phosphodiester bond i.e. cuts up polynucleotide sequences b. Endonucleases cleave phosphodiester bonds within a polynucleotide chain, exonucleases cleave phosphodiester bonds at the ends of a polynucleotide chain c. A bacterial enzyme which cleaves a polynucleotide chain at restriction sites d. 4-8 bp |
|
|
How do bacteria protect their genome from their own restriction endonucleases/enzymes? |
- Via modification enzymes (made of DNA methyltransferase) - Modification enzymes have same recognition sites as their corresponding restriction endonucleases - Methylated recognition sequence cannot be cleaves by restriction endonucleases - Therefore genome is protected from cleavage |
|
|
- Cloning a fragment of DNA requires a specifically engineered vector - A cloning vector is DNA (usually a __(a)__), that can be used to __(b)__ an incorporated DNA sequence in a host cell - Vectors contain selectable markers + replication origins to allow __(c)__ and __(d)__ of the vector in the host - They also contain __(e)__ (aka __(f)__), these are synthetically generated sequences of DNA containing a series of tandem __(g)__ used in cloning vectors for creating __(h)__ molecules |
a. Plasmid b. Propagate c. Identification d. Maintenance e. Multiple Cloning Sites (MCS's) f. Polylinkers g. Restriction endonuclease sites h. Recombinant |
|
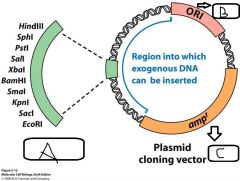
|
a. Polylinker b. Origin of replication c. Selectable marker |
|
|
Inserting DNA fragments into vectors: - Restriction Endonucleases cleave DNA into defined fragments - DNA fragments with sticky/blunt ends can be inserted into DNA with the aid of __(a)__ - (a) __(b)__ joins the ends of restriction fragment + vector DNA that have __(c)__ (i.e. restricted with the same __(d)__) |
a. DNA ligase b. Covalently c. Complimentary ends d. Endonuclease |
|
|
Bacterial transformation + selection: - In the lab, transformation occurs by mixing host bacteria with recombinant plasmids - In the presence of __(a)__ and the application of a method called __(b)__ which occurs at __(c)__ - Bacteria take up the R.plasmid and acquire __(d)__ from the __(e)__ in the __(f)__ - This allows for selection of bacteria that contain the R.plasmid on an agar plate containing the relevant __(g)__ |
a. CaCl2 b. Heat Shock c. 42 degrees celcius d. Antibiotic Resistance e. Selective marker f. Plasmid g. Antibiotic |
|
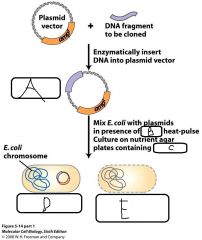
|
a. Recombinant Plasmid b. CaCl2 c. Ampicillin d. Recombinant bacteria live e. Bacteria which don't take up R.plasmid die |
|
|
Amplification + Plasmid Purification: - COLONIES are picked from the agar plate and grow in __(a)__ containing __(b)__ to produce millions of __(c)__ bacteria - Plasmid DNA can then be isolated from the bacteria - Using methods such as the __(d)__ based Spin -Column |
a. Liquid Broth b. Antibiotic c. Transformed d. Alkaline-lysis |
|
|
Screening for false positives: - False positives created because some plasmids __(a)__ without an inserted cloned DNA fragment - __(b)__ allows the identification of bacteria that contain the vector WITH an insert (i.e. __(c)__ clone) - The insertion of a DNA fragment __(d)__ the lacZ gene, meaning bacteria grown in the presence of X-gal are __(e)__ instead of __(f)__ - __(g)__ colonies are selected and used to prepare more plasmid DNA or further analysis |
a. Recircularise b. Blue/white selection c. Positive d. Interrupts e. White f. Blue g. White |
|
|
- Cloning vectors may be __(a)__, __(b)__, __(c)__, __(d)__ or __(e)__ - __(f)__ can be propagated in multiple types of host cell - Expression vectors contain __(g)__ that allow transcription of any cloned |
a. Bacterial Plasmids b. Phages c. Cosmids d. BAC's e. YAC's (Yeast Artificial Chromosomes) f. Shuttle vectors g. Promotors |
|
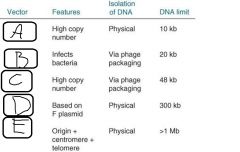
|
a. Plasmid b. Phage c. Cosmid d. BAC e. YAC (Yeast Artificial Chromosome) |
|
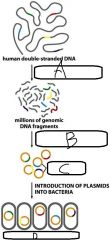
|
a. Cleavage of DNA via Restriction Endonucleases b. Insertion of DNA into plasmid vectors c. Recombinant DNA plasmids d. Human genomic DNA library |
|
|
Screening of DNA libraries: - Screening is required to identify _____ |
Clones of interest |
|
|
- A DNA library is __(a)__ - The set of clones collectively represents __(b)__ - This is useful for representing the __(c)__ of simple organisms - More useful to construct __(d)__ libraries for higher eukaryotes |
a. A collection of DNA molecules each CLONED into a VECTOR b. All the DNA sequences in a genome c. Genomic content d. cDNA libraries |
|
|
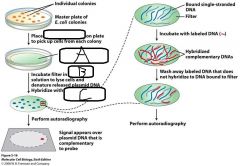
Screening DNA libraries: - Most genomic or cDNA libraries contain 100,000s of individual clones - Screening is required to identify __(a)__ - __(b)__ of a labelled oligonucleotide probe to complementary sequences can identify specific __(c)__ - Hybridization is the ability of __(d)__ - A Probe is __(e)__ |
a. Clones of interest b. Hybridization c. Nucleic acid sequences d. Complementary, single stranded DNA/RNAs to base pair specifically with each other e. RADIOACTIVE nucleic acid (DNA/RNA), used to IDENTIFY a complementary fragment |
|
|
a. Nitrocellulose filter b. Alkaline c. Labelled PROBE |

