![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many RNA pol's do prokaryotes have? |
1 |
|
|
How may RNA pol's do eukaryotes have? |
3 |
|
|
What genes do each of the eukaryotic RNA polymerise? |
1) RNA pol 1: Ribosomal RNA genes (rRNA).
2) pol 2: Protein coding genes (mRNA), small nuclear RNA genes (snRNA).
3)pol 3: Transfer RNA (tRNA), rRNA + snRNA. |
|
|
Both, eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA pols are holoenzymes, what does this mean? |
Holoenzymes are composed of several polypeptide subunits. |
|
|
What are the subunits that make up the Prokaryote RNA pol? |
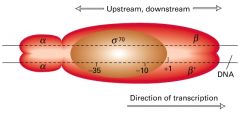
Sigma (o)- Promoter recognition
2 Alpha (a) - Assembly of the rna, activation
2 Beta (B)- catalysis ( synthesising the rna product) + termination
Omega (w)*- Assembly of the rna, folding, required for some genes
*omega subunit recent find, function still rather unkown. |
|
|
Which of the subunits, in the prokaryotic RNA pol is responsible for 'promoter recognition,'? |
Sigma subunit |
|
|
What is the name of the complex formed when RNA polymerase binds to template (antisense) dna strand? |
Closed complex |
|
|
Once, prokaryotic RNA pol has bound to the dna strand, what occurs?
What does this change the holoenzyme to? |
The sigma subunit usually dissociates before transcription begins.
Converts the holoenzyme to core enzyme |
|
|
What portion of the promoter does sigma subunit recognise? |
-35 box |
|
|
How does the closed promoter complex become an open one in prokaryotes? |
Beta subunits (sigma also has small role) break open base bairs in the -10 box (pribnow) of the promoter.
This model is supported that A-T links are two hydrogen bonds, rather than the three C-G ones, and are therefore easier to break.
once holoenzyme becomes the core enzyme, transcription starts even before it has started moving. |
|
|
For eukaryotic rna pol 2 to be recruited to the dna, what must first be formed. |
RNA Pol 2 initiation complex |
|
|
What is the first part of forming the pol 2 initiation complex?
What is the shorthand name for the complex formed |
1) transcription factor iiD TFIID binds to the dna first. This is the only transcription factor that has specific DNA-protein interaction.
2)TF2A helps TFIID bind to DNA
3) TFIIB forms the structure that RNA pol will recognise and sets the distance from TATA sequence and transcription start site.
Known as the DAB complex
|
|
|
TFIID is a multisubunit complex, what are its components? |
1) TATA binding protein (TBP) binds to TATA site on promoter, similar function to sigma subunit in prokaryotes.
2) At least 12 TBP-associated factors, these are thought to help TBP to attatch to TATA region. |
|
|
After the first part of the RNA pol 2 initiation complex has been formed (DAB), other transcription factors attach and so to does RNA pol 2.
What are some of these steps? |
TFIIF binds to polymerase, and prevents it attaching at wrong place.
TFIIF and TFIIH are recruited and complete the initiation complex.
RNA pol II has also been recruited by now
|
|
|
Why is the function of TFIIH important? |
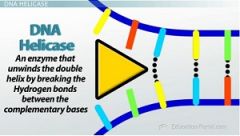
TFIIH is a helicase- breaks apart base pairs |
|
|
What must happen to the initiation complex before transcription can begin?
How does this occur? |
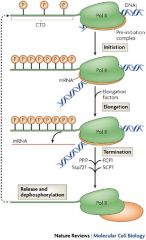
The initiation complex must be activated!
Activation occur by adding phosphate groups to largest subunit of RNA pol 2.- specifically to a region called the c-terminal domain (CTD). |
|
|
why is re-initiation a faster process then primary initiation?
What does this allow? |
TFIIH and TFIID remain as a complex with the polymerase after detaching from promoter- allowing re-initiation to occur without the need to recruit all transcription factors again.
this means that once a gene is switched on, transcription can occur from core promoter easily, until it is switched off. |

