![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is visible light?
|
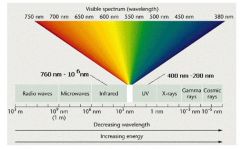
It is a form of energy. It is also a part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Page 4 & 3 |
|
|
What theory explains the behavior of light?
|
1.Corpuscular/Quantum Theory: Light composed of particles called photons that move in straight lines.
2.Electromagnetic Wave Theory: States that light travels as waves Page 3 |
|
|
How much is the speed of light?
|
In the air, it is 186,000 miles per second or 300,000 kilometers per second.
Page 3 |
|
|
What is the definition of a wavelength?
|
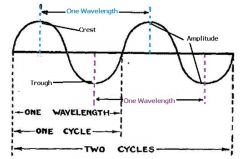
It is the distance between 2 crests, 2 troughs, or from beginning to end of a wave.
Page 3 |
|
|
What is the amplitude of a wave?
|
It is the height or depth of a wave.
Page 3 |
|
|
How much is the wavelength of visible light?
|
It extends from 380 nanometers to 760 nanometers.
Page 4 |
|
|
What is the crest of a wave?
|
It is the highest point of a wave.
Page 3 |
|
|
What is the trough of the wave?
|
The deepest point of a wave.
Page 3 |
|
|
Which wavelengths are more dangerous for humans?
|
The shorter wavelengths that are under 400 nanometers are more dangerous. They cause more radiation.
Page 4 |
|
|
What is dispersion?
|
The breaking down of white light into its component colors.
Page 7 |
|
|
What is the wavelength of the UV(Ultra Violet) radiation?
|
Wavelengths shorter than 400 nanometers which are subdivided into UVA, UVB, and UVC.
Page 4 |
|
|
What is the wavelength of infrared radiation?
|
Wavelength in 760 to 10^6 nanometers. It lies beyond visible light.(Longer)
Page 6 |
|
|
How many UV radiation's do we have and which part of the eye absorbs these radiations?
|
There are 3 kinds of radiation: UVA, UVB, and UVC.
UVA and UVB is absorbed by the cornea and crystalline lens. UVC is absorbed by the ozone layer of the atmosphere. Page 4 |
|
|
What are the complications of the UV radiation?
|
They cause welders burn, snow blindness, cataracts, retinal damage, macular degeneration, eclipse burn, pterygium, and pinguecula.
Page 4 & 5 |
|
|
How can we feel the infrared radiation?
|
It induces heat.
Page 6 |
|
|
What is heterochromic light?
|
It is light made up of more than one wavelength or color.
Page 7 |
|
|
What is monochromic light?
|
It is light made up of one wavelength or color.
Page 7 |
|
|
What are the colors of the white light?
|
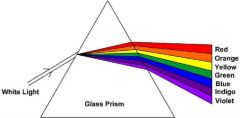
Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue (Cyan), Indigo, and Violet.
R.O.Y.G.B.I.V. Page 7 |
|
|
Which color do we see the best?
|
Green
Page 7 |
|
|
What are the main colors?
|
Green, Blue (cyan), Red
Page 7 |
|
|
How can we see the colors?
|
When the light enters the eye and where the wavelength lands around the retina.
The cone cells on the retina. Page 7 |
|
|
What is refractive index?
|
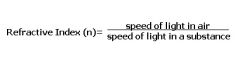
Comparison of the speed of light in the air with the speed of light in an optical substance.
|
|
|
What is light transmission?
|
It is the ratio of the light entering an optical material and the light exiting after being reflected, absorbed, and refracted.
Page 11 |
|
|
What is light absorption?
|
The amount of light that stays in an optical material.
Page 10 |
|
|
What is refraction?
|
The bending of light.
Page 9 |
|
|
Light Passing Through CR-39?
|
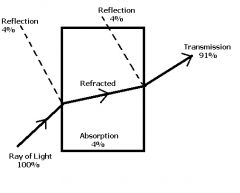
|
|
|
What is reflection? How can you increase it?
|
Reflection is when a beam of light strikes a material and part of it bounces back. It is increased with a mirror coat on the lenses.
Page 10 & 12 |
|
|
As refractive index increases,...
|
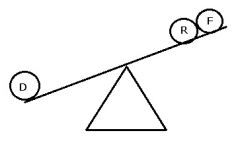
Reflection increases
Lens thickness decreases Absorption increases Transmission is decreased Lens power increases UV protection increases Refraction increases |
|
|
How can we increase the absorption?
|
By tinting or color coating the lens.
Page 12 |
|
|
How can we increase the transmission?
|
By decreasing reflection by adding anti-reflective (AR) coating.
Page 12 |
|
|
What is AR coating? How thick is it? Who do you recommend it to?
|
It is a thin layer/s applied to the surface of the lens. It should be 1/4 a wavelength thick. Recommend it to everyone, especially drivers.
Page 13 & 14 |
|
|
Write the refractive index of the following materials:
CR-39 Crown Glass Flint Polycarbonate Standard High Index Plastic High Index Glass |
CR-39: 1.498
Crown Glass:1.523 Flint:1.60 Polycarbonate:1.586 Standard:1.530 High Index Plastic:Up to 1.70 High Index Glass: Up to 1.90 Page 8 & 9 |
|
|
How much is total transmission of light in a CR-39 lens?
|
91% is transmitted.
Page 11 |
|
|
What wavelengths are usually transmitted through a clear CR-39 lens?
|
Allows above 350 nm.
Blocks below 350 nm. Page 11 |
|
|
What is the best tint for indoors?
|
Pink or rose tint.
Page 12 |
|
|
What is the best tint for shooting?
|
Yellow tint.
Page 12 |
|
|
What do you recommend for an aphakic patient?
|
CR-39 lenses, photochromic, CRT lenses. Anything that offers UV protection.
Page 11 & 16 |
|
|
What is the best lens for a computer programmer?
|
Cathode Ray Tube Lenses (CRT). These lenses have a UV blocker, AR coating, and a tint.
Page 19 |
|
|
What are photochromic and transition lenses?
|
Lenses that change their shade when they are exposed to UV radiation. They become darker.
Page 16 |
|
|
What is ptosis and what is the device used to correct it?
|
Ptosis is the drooping of the upper or lower eyelid. A ptosis crutch is used to correct the drooping.
Page 67 & 68 |
|
|
What does a blu-blocker lens do?
|
It cuts off the blue and shorter wavelengths. They are reddish-orange in color.
Page 18 |
|
|
What is photophobia and what would you recommend?
|
It is light sensitivity. Recommendation would be tinted lenses or polarized lenses.
|
|
|
What would you recommend to a driver?
|
Glare control lenses.(Polarized)
Page 17 |
|
|
What would you recommend for fishing?
|
Glare control lenses.(Polarized)
Page 17 |
|
|
What would you recommend to a skier?
|
No anti-glare lenses due to the inability to see ice on slopes. Suggestion would be anti-fog lenses.
Page 15 & 17 |
|
|
When the light source is more than 20 feet away, it will be a ........ light.
|
When the light source is more than 20 feet away, it will be a light.
Page 23 |
|
|
When the light source is less than 20 feet away, it will be a ........ light.
|
When the light source is less than 20 feet away, it will be a light.
Page 23 |
|
|
The best lens to reduce glare is a ........ lens.
|
The best lens to reduce glare is a lens.
Page 17 |
|
|
The physiological blind spot is when the image is formed at the .......... .
|
The physiological blind spot is when the image is formed at the .
Page 62 |
|
|
The best lens for a cataract patient is a .......... lens.
|
The best lens for a cataract patient is a lens.
Page 18 |
|
|
The ........ is located in the middle of the iris.
|
The is located in the middle of the iris.
Page 61 |
|
|
What are the cones? Where are they located? What are the functions?
|
It is a cell of the retina responsible for color perception. They are for central vision and visual acuity. They cannot function at night. They are located on the macula. There are 6,000,000 in the eye.
Page 62 |
|
|
What are the rods? Where are they located? What are the functions?
|
A cell of the retina located at the periphery of the retina. They can function at night. They are peripheral vision. There are 120,000,000 in the eye.
Page 62 |
|
|
Where is the macula and what is its function?
|
It is on the visual axis. It is for central vision and visual acuity color.
Page 62 |
|
|
Where does vision happen?
|
(Fusion) It happens in the brain.
|
|
|
A black surface .......... and a white surface ........... all the colors of the white light.
|
A black surface and a white surface all the colors of the white light.
|
|
|
The (blind or ametrope) is a patient with refractive deficiencies who can be helped with ordinary prescriptive glasses.
|
The is a patient with refractive deficiencies who can be helped with ordinary prescriptive glasses.
|
|
|
The patient with severe visual impairment becomes (presbyopic or low vision) and cannot be helped with ordinary prescriptive glasses.
|
The patient with severe visual impairment becomes and cannot be helped with ordinary prescriptive glasses.
|
|
|
The main causes of low vision are:
|
Macular degeneration, cataract, glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy.
Page 176 - 178 |
|
|
The technique for making objects appear larger is known as:
|
Magnification.
Page 179 |
|
|
Three ways of creating magnification are:
|
Relative distance magnification, linear magnification, and angular magnification.
Page 179 - 180 |
|
|
When you move closer to a distant object, it appears: (Same/Smaller/Larger)
|
When you move closer to a distant object, it appears: .
|
|
|
Hand magnifier 2x has the dioptic power of (-2.00/+4.00/+8.00).
|
Hand magnifier 2x has the dioptic power of <+8.00>.
Page 180 |
|
|
The Snellen Chart is used to check: (central visual acuity/periphery vision).
|
The Snellen Chart is used to check: .
Page 72 |
|
|
The visual acuity of (20/20 or 20/200) is most likely that of a legally blind patient.
|
The visual acuity of <20/200> is most likely that of a legally blind patient.
Page 173 |
|
|
The low vision patient is likely to use their auditory senses: (more/less).
|
The low vision patient is likely to use their auditory senses: .
Page 173 |

