![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
186 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ACSESS |
The Association of Canadian Search, Employment and Staffing Services |
|
|
Accommodation |
Refers to a requirement that may result in the modification of work practices, job procedures, policies, hours of work and work schedules, or facilities such that the target individual is able to perform the work. |
|
|
Adverse Impact |
Occurs when the selection rate of a protected or target group is lower than that for the relative comparison group. |
|
|
Assessment Centers |
Use of multiple assessors and multiple approaches to assess managers. They are costly with mixed results due to lack of standardization. |
|
|
Attribution Bias |
An interview situation whereby an acknowledged competency in an area unrelated to the work (e.g. playing chess) results in the interviewer falsely attributing a competency (e.g. strategic planning) to the candidate. |
|
|
Attrition |
A form of "natural" turnover in that it refers to the unforced employee departures due to "natural" causes such as: retirement, death, disability or spousal transfer. |
|
|
BARS |
Behaviourally Anchored Rating Scales |
|
|
Behavioural Description Interview |
Uses questions relating to past behaviours. The underlying assumption is that the best predictor of future performance is past performance. Research has shown this type of interviewing to be more effective than others. |
|
|
Behavioural Evaluation |
Assesses whether the training resulted in a change in actual employee behaviour on the job. |
|
|
Behaviourally-anchored |
An appraisal system where the assessment is made against "behavioural" standards that have been developed by the organization. |
|
|
Biographical Information Blank (BIB) |
A pre-selection questionnaire in which applicants are asked to provide job-related information on their personal background and life experiences. |
|
|
Bona Fide Occupational Requirement |
Are a basis for discriminatory practices on the grounds that the practice or requirement was adopted in good faith and is necessary in order to have properly qualified persons in the position for which the recruitment and selection is taking place. A justifiable reason for discrimination based on business reasons of safety or effectiveness. |
|
|
Career Planning |
Is the HRP process whereby employees are encouraged to identify their career goals within the organization and a realistic development, work assignment and career progression plan is developed for each employee. |
|
|
Competencies |
They are the skills, knowledge, attitudes and motivations of employees, expressed as observable behaviours. |
|
|
Construct Validity |
The degree to which a given test successfully measures an abstract trait (e.g. personality or IQ). Example: creative arts tests, honesty tests |
|
|
Content Validity |
The degree to which the content of the test is representative of the competency that it is intended to measure. Example: typing tests, driver’s license examinations |
|
|
Contrast or Context Bias |
Can occur in an interview situation where the candidate is only assessed in relation with other candidates rather than an absolute standard of competency. |
|
|
Criterion-related Validity |
Validity of a selection process test assessed by comparing the test scores with a non-test criterion. For example, test for leadership skills will match the test scores with the traits displayed by known leaders. The extent to which a selection tool predicts, or significantly correlates with, important elements of work behaviour. A high score indicates high job performance potential; a low score is predictive of low job performance |
|
|
Differential Validity |
It is gaining more prominence due to its human rights implications. In this case, the issue is whether the test or selection method is valid for only one demographic group (e.g. white males) but not for members of one or more target groups and therefore represents a form of systemic discrimination. |
|
|
Direct Discrimination |
This discrimination may be "malicious" or "non-malicious" depending upon the intentions of those who are responsible for the discrimination. Some - such as not having male guards for female prisoners or baring vision impaired individuals from work as airline pilots or bus drivers - is permitted. |
|
|
Employee Branding |
Reflects the reputation of an organization. |
|
|
Employment Equity |
Legislation designed to eliminate historical employment discrimination against four "target groups": women, aboriginals, people with disabilities and members of visible minorities. |
|
|
False Positives |
When the selection technique identifies an applicant possess a competency when he/she does not. |
|
|
First Impression Bias |
An interviewer shortcoming whereby a characteristic of the candidate creates a favourable first impression on the interviewer who then unconsciously leads the interview in a way that supports the first impression. |
|
|
Forced Distribution |
Sometimes known as "rank and yank" appraisal systems that result in a perception of unfairness and employee dissatisfaction. |
|
|
GATB |
General Aptitude Test Battery, a widely used multidimensional cognitive ability or aptitude test. |
|
|
Graphic Rating Scales |
Rating scales that are either numerical (such as 1 to 5 with one being a low or poor rating and 5 being high or excellent) or descriptive (such as poor, fair, good, excellent; or unsatisfactory satisfactory, more than satisfactory; or does not meet expectations, meets expectations and exceeds expectations) |
|
|
Halo Bias |
An assessment shortcoming whereby a candidate's strength in one area leads the interviewer to rate the candidate as having strength in all areas. |
|
|
Headcount Analysis |
The process of analyzing employee numbers; can include data collection and analysis on a wide variety of areas, such as: demographics, skill levels, turnover, training activities, movement, etc. |
|
|
Inter-rater Reliability |
Measures consistency between two raters. |
|
|
Internal Consistency |
On a test, where there are a number of questions designed to measure one competency or vocational interest, the results for each of the questions should be similar. |
|
|
Job Sharing |
Where employees, with the agreement of management, voluntarily agree to share the work involved in a job and receive pay and benefits in proportion to their share of the work. |
|
|
Markov Analysis |
A form of headcount analysis that estimates the internal supply of possible candidates based upon tracking the internal movement of employees and developing a transitional probability matrix. |
|
|
Meiorin Ruling |
Established an important precedent concerning duty to accommodate. It is a Supreme Court decision involving a female Attack Forest Fire Fighter. |
|
|
Multi-Source Feedback (360) |
Where individuals who interact with the employee provide feedback based on their perspective. Typically this type of feedback includes: self, manager, subordinates, peers and if possible customers. Peer review, team review and 360 feedback are all variations. |
|
|
Negligent Hiring |
Refers to the liability of organizations when they hire an applicant who goes on to commit a criminal act as an employee. The company can be held liable if it is shown that it was negligent in its review of the employee's application or in not undertaking a criminal records check where necessary. |
|
|
NOC |
National Occupational Classification: A Human Resources Development Canada (HRDC) created inventory of over 500 occupational unit groups and 30,000 job titles.
|
|
|
Notice |
The amount of time between the time employees are informed of their termination and the actual date of termination. There is statutory requirement under labour standards legislation in Canada, although due to common law court decisions most companies provide an amount (or severance in lieu) greater than what is called for in the statutes. |
|
|
Outplacement/Downsizing/Rightsizing |
Is the process of reducing employee headcount through non-voluntary termination of employment. Generally, it is accompanied by the payment of severance pay and the provision of relocation counselling. |
|
|
Personality Assessments |
Assessment device for predicting job performance consists of: conscientiousness, emotional stability, openness to new experiences, agreeableness, and extroversion. There are sometimes called the "big five". (OCEAN) openness to new experiences, conscientiousness, extroversion, agreeableness, neuroticism |
|
|
Predictive Validity |
Predictive validity is the extent to which performance on a test is related to later performance that the test was designed to predict. |
|
|
Reliability |
A measure of whether a selection tool is dependable or consistent from one time to another if used with the same group of individuals. The degree to which interviews, tests, and other selection procedures yield comparable data over time and alternative measures. |
|
|
Replacement Charts |
A succession planning/HR planning tool that identifies positions in the organization the same as an organizational chart, but in terms of the potential candidates for succession to those positions. |
|
|
RJP |
Realistic job preview - An information sharing technique whereby applicants are given an honest, unvarnished and factual description of the job "warts and all" by an existing job incumbent or employee who is very familiar with the work, and are then asked whether they wish to continue with their application. Positive benefits of RJP
|
|
|
Severance Pay |
The amount of salary or pay continuance a company provides to terminated employees in lieu of notice. It is usually determined by the employee's length of services with the organization, age and position. |
|
|
Situational Response Interview |
Uses questions related to hypothetical job situations and asks candidates how they would respond. |
|
|
SMART |
An acronym for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant and Time-based. |
|
|
Socialization |
An ongoing process and an important activity for successfully reinforcing the values, attitudes and standards expected by the organization. Orientation is one component of this process. |
|
|
Succession Planning |
Is the HRP process whereby key positions in the organization are identified along with potential candidates from within the organization who can succeed to these positions. |
|
|
Supplemental Unemployment Benefits (SUB) |
These are the benefits an employee would receive in addition to what they are eligible through government EI programs. They usually represent the difference between what an employee receives from EI and their normal salary. |
|
|
Survivor Syndrome |
The psycho-sociological phenomenon that occurs with employees who are retained by the organization when there has been a termination or a number of terminations within their employee group. It is characterized by feelings of guilt, betrayal, detachment, alienation, anxiety and stress. |
|
|
Systematic Change |
A long term alternative of an organization. |
|
|
Systemic Discrimination |
Occurs when an organization adopts a policy, in good faith, that indirectly leads to discriminatory practices. This form of discrimination is much harder to detect because it is "built into" a company's recruitment and selection practices. The exclusion of members of certain groups through the application of employment policies or practices based on criteria that are not job-related |
|
|
Target Group/Designated Groups |
Generally associated with Federal Employment Equity requirements, the four groups targeted for reducing inequities are: women, aboriginals, persons with disabilities and visible minorities. |
|
|
Trait-characteristic Based |
An appraisal system based on assessing items such as: determination, initiative, loyalty, etc. that is highly subjective and very difficult or impossible to measure in an objective manner. |
|
|
Turnover |
An important concept in the HRP process; the rate at which employees leave the organization relative to the number of employees who stay with the organization. Within this definition, there are two kinds: good and bad. |
|
|
Undue hardship |
When determining whether the duty to accommodate, the following are considered: costs, administrative and supervisory burden, economic benefits that they employer recovers, disruption or legal liability to other employees or to the trade union, health and safety. |
|
|
Correlation Coefficient |
Expressed as either a positive or negative number, where a minus 1.00 means there is a perfect, negative correlation in the relationship between the test and what is it trying to predict and a plus 1.00 means there is a perfect, positive correlation. A number ranging from 0.00, denoting a complete absence of relationship, to 1.00 and to -1.00, indicating a perfect positive and perfect negative relationship, respectively |
|
|
Weighted Assessments/Weighted Application Blanks (WABS) |
Assigns values to different elements of the application form that are most strongly required to perform the job successfully. |
|
|
Wallace v. UGG |
Canada's Supreme Court recognized that dismissals which occur in bad faith or where the employer bullies the employee through the dismissal, will call for unique damages, which practitioners and judges have taken to calling Wallace damages. |
|
|
Human Capital |
The knowledge, skills and capabilities of employees that add economic value to an organization |
|
|
The most pressing competitive issues facing firms |
|
|
|
Disadvantages in Employment |
|
|
|
Benefits of employment equity |
|
|
|
Canadian Human Rights Act Enforcement |
|
|
|
Pay Equity (in CHRA) |
Equal pay for work of equal value |
|
|
Employment Equity - who must implement? |
Employers and Crown corporations that have 100 employees or more and that are regulated under the Canada Labour Code must implement employment equity and report on their results. |
|
|
Employment Equity Act Employer Duties |
|
|
|
Employment Equity Act |
|
|
|
Implementation of Employment Equity within Organizations |
|
|
|
Senior management commitment - employment equity |
|
|
|
Data Collection - Employment Equity |
Stock data
Flow data
|
|
|
Self Identification Form should contain: |
|
|
|
Workforce Utilization Analysis |
|
|
|
Special Measures |
Special measures are initiatives designed to accelerate the entry, development and promotion of members of designated groups |
|
|
Principles of Duty to Accommodation |
|
|
|
Establishment of a workplan (Employment Equity) |
|
|
|
Employer's Duty to Prevent Harassment |
|
|
|
Sexual Harassment |
Unwelcome advances, requests for sexual favors, and other verbal or physical conduct of a sexual nature in the working environment |
|
|
Sexual Harassment Behaviours |
|
|
|
Diversity Management |
The optimization of an organizations multicultural workforce in order to reach business objectives
|
|
|
Culture Organization-wide Image |
|
|
|
Concern for Equality |
|
|
|
Opportunity Career Development |
|
|
|
Hiring Practices |
|
|
|
Leadership Management Practices |
|
|
|
Why Diversity? |
|
|
|
Job |
A group of related activities and duties |
|
|
Position |
The different duties and responsibilities performed by only one employee |
|
|
Job Family |
A group of individual jobs with similar characteristics. |
|
|
Job Specification |
Statement of the needed knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) of the person who is to perform the job |
|
|
Job Description |
Statement of the tasks, duties, and responsibilities (TDRs) of a job to be performed |
|
|
Job Requirements & Recruitment |
Determines recruitment qualifications |
|
|
Job Requirements & Selection |
Provide job duties & specifications for selection process |
|
|
Job Requirements & Performance |
Provide performance criteria for evaluating employees |
|
|
Job Requirements & Training |
Determine training needs & develop instructional programs |
|
|
Job Requirements & Compensation Management |
Provide basis for determining employee's rate of pay. |
|
|
Job Analysis |
|
|
|
Process of Job Analysis |
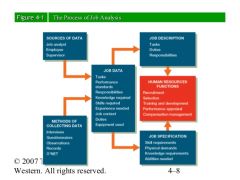
|
|
|
Performing Job Analysis |
|
|
|
Gathering Job Information |
|
|
|
Factors influencing the accuracy of job information |
|
|
|
Approaches to Job Analysis |
|
|
|
Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ) |
A questionnaire covering 194 different tasks that, by means of a five-point scale, seeks to determine the degree to which different tasks are involved in performing a particular job |
|
|
Critical Incident Method |
|
|
|
Task Inventory Analysis |
An organization-specific analysis developed by identifying—with the help of employees and managers—a list of tasks and their descriptions that are components of different jobs. |
|
|
Competency-Based Analysis |
Job analysis method which relies on building job profiles that look at the job responsibilities and the worker competencies necessary to accomplish them |
|
|
HRIS & Job Analysis |
Human resource information systems (HRIS) and specialized software help automate job analysis |
|
|
Key Elements of a Job Description |
Job Title Indicates job duties and organizational level. Job Identification Distinguishes job from all other jobs. Essential Functions (Job Duties) Indicate responsibilities entailed and results to be accomplished Job Specifications Skills required to perform the job and physical demands of the job. |
|
|
Job Title |
|
|
|
Job Identification Section |
|
|
|
Job Duties or Essential Functions, |
Statements in the job description of job duties and responsibilities that are critical for success on the job. A job function is essential if:
Statements of job duties that:
|
|
|
Job Specifications Section |
Personal qualifications an individual must possess in order to perform the duties and responsibilities. The skills required to perform the job:
The physical demands of the job:
|
|
|
Problems with Job Descriptions |
|
|
|
Writing Clear and Specific Job Descriptions |
Create statements that:
|
|
|
Determining Job Requirements |
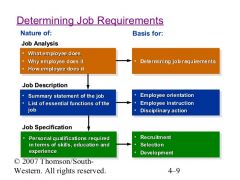
|
|
|
Job Design |
An outgrowth of job analysis that improves jobs through technological and human considerations in order to enhance organization efficiency and employee job satisfaction |
|
|
Job Enrichment (Herzberg) |
|
|
|
Job Enrichment Factors |
|
|
|
Job Characteristics Model (Hackman and Oldham) |
Job design theory that purports that three psychological states (experiencing meaningfulness of the work performed, responsibility for work outcomes, and knowledge of the results of the work performed) of a jobholder result in improved work performance, internal motivation, and lower absenteeism and turnover. |
|
|
Skill Variety (Job Characteristics) |
The degree to which a job entails a variety of different activities, which demand the use of a number of different skills and talents by the jobholder |
|
|
Task Identity (Job Characteristics) |
The degree to which the job requires completion of a whole and identifiable piece of work, that is, doing a job from beginning to end with a visible outcome |
|
|
Task significance (Job Characteristics) |
The degree to which the job has a substantial impact on the lives or work of other people, whether in the immediate organization or in the external environment |
|
|
Autonomy (Job Characteristics) |
The degree to which the job provides substantial freedom, independence, and discretion to the individual in scheduling the work and in determining the procedures to be used in carrying it out. |
|
|
Feedback (Job Characteristics) |
The degree to which carrying out the work activities required by the job results in the individual being given direct and clear information about the effectiveness of his or her performance |
|
|
Strategic Aspects of Recruiting |
|
|
|
Advantages of a promotion-from-within policy: |
|
|
|
Limitations of a promotion-from-within policy |
|
|
|
Recruitment Channels |
|
|
|
Labour Market |
|
|
|
Factors determining the relevant labour market |
|
|
|
Advantages of External Recruitment |
|
|
|
External Recruitment Channels |
|
|
|
Improving the Effectiveness of External Recruitment |
RJP's (see above) Recruiting metrics
|
|
|
Yield Ratio |
Percentage of applicants from a recruitment source that make it to the next stage of the selection process.
|
|
|
Cost of Recruitment (per employee hired) |
SC /H= AC + AF + RB + NC/H SC= source cost AC= advertising costs, total monthly expenditure (example: $32,000) AF= agency fees, total for the month (example: $21,000) RB= referral bonuses, total paid (example: $2,600) NC= no-cost hires, walk-ins, nonprofit agencies, etc. (example: $0) H= total hires (example: 119) Cost to hire one employee = $467 |
|
|
Job seekers |
|
|
|
The Employee’s Role in Career Planning |
|
|
|
The Organization’s Role: Establishing a Favourable Career Development Climate |
Management Participation
Setting Goals
Announcing the Program
|
|
|
Competency Analysis |
Measures three basic competencies for each job: know-how, problem solving, and accountability |
|
|
Job Progressions |
The hierarchy of jobs a new employee might experience, ranging from a starting job to jobs that require more knowledge and/or skill |
|
|
Career Paths |
Lines of advancement in an occupational field within an organization |
|
|
Promotion |
|
|
|
Transfer |
The placement of an individual in another job for which the duties, responsibilities, status, and remuneration are approximately equal to those of the previous job |
|
|
Relocation services |
Services provided to an employee who is transferred to a new location: Help in moving, in selling a home, in orienting to a new culture, and/or in learning a new language |
|
|
Outplacement services |
Services provided by organizations to help terminated employees find a new job |
|
|
Alternate Career Moves |
Promotion Demotion Exit Transfer |
|
|
Stages of Career Development |
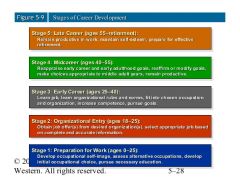
|
|
|
Career Plateau |
Situation in which for either organizational or personal reasons the probability of moving up the career ladder is low. |
|
|
Types of Plateaus |
|
|
|
Career Development Initiatives |
Career Planning Workbooks
Career Planning Workshops
Career Counseling
|
|
|
Mentors |
Executives who coach, advise, and encourage individuals of lesser rank. Mentoring functions
E-mentoring
together with individuals needing counseling |
|
|
Career Self-Management Training |
|
|
|
Selection |
The process of choosing individuals who have relevant qualifications to fill existing or projected job openings |
|
|
Job Analysis - Selection considerations |
Person-job fit:
Person-organization fit:
|
|
|
Goal of Selection: Maximize HITS |
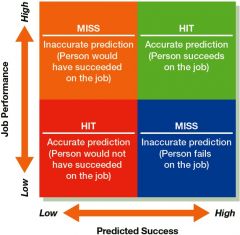
|
|
|
Steps in the Selection Process |
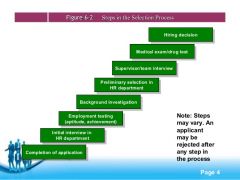
|
|
|
Validity |
The degree to which a test or selection procedure measures a person’s attributes |
|
|
Initial Screening |
|
|
|
Application Forms & Resumes |
|
|
|
Online Applications |
An Internet-based automated posting, application, and tracking process helps firms to more quickly fill positions by:
|
|
|
Employment Interviews |
Why the interview is so popular:
|
|
|
Non-directive Interview |
The applicant determines the course of the discussion, while the interviewer refrains from influencing the applicant’s remarks |
|
|
Structured Interview |
An interview in which a set of standardized questions having an established set of answers is used |
|
|
Panel Interview |
An interview in which a board of interviewers questions and observes a single candidate |
|
|
Computer and Virtual Interview |
|
|
|
Video and Digitally Recorded Interviews |
Using video conference technologies to evaluate job candidates’ technical abilities, energy level, appearance, and the like before incurring the costs of a face-to-face meeting. |
|
|
Guidelines for Employment Interviews |
|
|
|
Post Interview Screening |
|
|
|
Pre-employment Test |
An objective and standardized measure of a sample of behaviour that is used to gauge a person’s knowledge, skills, abilities, and other characteristics (KSAOs) in relation to other individuals. |
|
|
Job KnowleJdge Tests |
An achievement test that measures a person’s level of understanding about a particular job. |
|
|
Work Sample Tests |
Require the applicant to perform tasks that are actually a part of the work required on the job |
|
|
Cognitive Ability Tests |
Aptitude tests
Achievement tests
|
|
|
Polygraph Tests |
Check provincial legislation before considering use of the polygraph |
|
|
Types of Tests |
Honesty and Integrity Test Physical Ability Tests |
|
|
Medical examination |
|
|
|
Drug Testing |
The following types of testing are not allowed:
|
|
|
Concurrent Validity |
|
|
|
Cross-validation |
Verifying the results obtained from a validation study by administering a test or test battery to a different sample (drawn from the same population) |
|
|
Validity generalization |
The extent to which validity coefficients can be generalized across situations |
|
|
Selection Considerations: |
|
|
|
Can-do and Will-do factors in selection |
Can-do:
Will-do:
|
|
|
Compensatory Model |
Permits a high score in one area to make up for a low score in another area. |
|
|
Multiple Cutoff Model |
Requires an applicant to achieve a minimum level of proficiency on all selection dimensions |
|
|
Multiple Hurdle Model |
Only applicants with sufficiently high scores at each selection stage go on to subsequent stages in the selection process |
|
|
Final Decision |
|

