![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the perineum? |
The perineum is the diamond-shaped superficial area of the body located between the thighs. |
|
|
Name the 2 triangles of the perineum. |
1. Urogenital triangle 2. Anal triangle |
|
|
What does the urogenital triangle consist of? |
- External genitalia - Superficial muscles - Glands over which the external genitalia sit - Urethral openings - Vaginal openings |
|
|
What does the anal triangle consist of? |
- Anus (anal canal and external anal sphincter) |
|
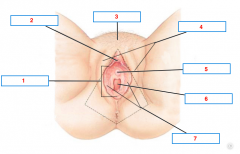
Name the structures. |
1. Vestibule 2. Clitoris 3. Mons pubis 4. Labia majora 5. Urethra 6. Vaginal opening 7. Labia minora |
|
|
Name the 3 organs/glands of the female reproductive system. |
1. Gonads 2. Reproductive tract 3. Mammary glands |
|
|
Where are the gonads and the reproductive tract found? |
In the pelvic cavity. |
|
|
What surrounds the pelvic cavity? |
Pelvic girdle. |
|
|
What is the pelvic girdle? |
The hip bones including the ilium, pubis and ischium, and part of the spinal column including the sacrum and the coccyx. |
|
|
What supports the pelvic cavity? |
The pelvic floor. |
|
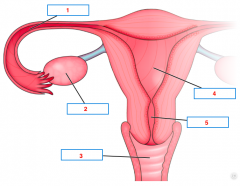
Name the structures. |
1. Fallopian tube 2. Ovary 3. Vagina 4. Uterus 5. Cervix |
|
|
What are the 2 main functions of the ovaries? |
1. Production of the female gametes - oocytes 2. Production of female sex (steroid) hormones - oestrogen's and progesterone. |
|
|
What are the 2 main functions of the fallopian tubes? |
1. Transportation of an ovulated oocyte towards the uterus 2. Site of fertilization |
|
|
What are the 2 main functions of the uterus including the cervix? |
1. Receives, retains and nourishes a zygote (fertilized oocyte). 2. Expels fetus from woman's body during labour. |
|
|
What are the 2 main functions of the vagina? |
1. Copulatory organ for sex 2. Forms the birth canal |
|
|
What is the main function of the mammary glands? |
Production of colostrum and breastmilk which nourish the baby after birth. |
|
|
What is oogenesis? |
Development of the female gamete - the oocyte (egg). |
|
|
When does oogenesis begin and end? |
In females, oogenesis begins in utero and continues until menopause. The process stops and starts along the way (during the female life cycle) and only completes if an ovulated oocyte is fertilized by a sperm. |
|
|
When are the primary oocytes produced? |
From around 6 weeks gestation until 7 months gestation. |
|
|
When do the primary oocytes undergo meiosis I? |
From 4 months gestation till they halt at 7 months gestation. |
|
|
When does meiosis I restart? |
An individual oocyte is produced each month during the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle. |
|
|
What does meiosis I result in? |
A secondary oocyte and 1st polar body. |
|
|
When does the secondary oocyte begin and halt meiosis II? |
Just prior to ovulation. |
|
|
When does the final step of oogenesis occur? |
When the oocyte is fertilised by a sperm. |
|
|
What does fertilisation produce? |
An ovum and 2nd polar body. |
|
|
What surrounds the primary oocytes? |
A single layer of granulosa (or follicular) cells. |
|
|
What does a primary oocytes and its layer of granulosa create? |
Primordial follicles. |
|
|
Name the 2 female reproductive cycles. |
1. Ovarian cycle 2. Uterine (menstrual) cycle. |
|
|
What coordinates the 2 reproductive cycles? |
Hormones of the HPO axis which align with certain phases of oogenesis. |
|
|
What is the HPO axis? |
Cascade of hormones released from the hypothalamus (H), anterior pituitary gland (P) and ovaries (O) that coordinate the events of the female reproductive cycles and oogenesis. |
|
|
What does the primordial follicle undergo during the ovarian cycle? |
Proliferation. |
|
|
Name the 3 phases of the ovarian cycle. |
1. Follicular phase 2. Ovulation 3. Luteal phase |
|
|
When does the follicular phase occur? |
Day 1 - 13 |
|
|
What 4 events happen in the follicular phase? |
1. Follicular proliferation 2. Completion of meiosis I 3. Oestrogen production 4. Start of meiosis II |
|
|
When does ovulation occur? |
Day 14 |
|
|
What event happens during ovulation? |
Release of a secondary oocyte. |
|
|
When does the luteal phase occur? |
Day 15 - 28 |
|
|
What 4 events occur during the luteal phase? |
1. Corpus luteum develops 2. Oestrogen production 3. Progesterone production 4. Corpus albicans develops |
|
|
How does the follicle progress during the ovarian cycle? |
Primordial follicle -> Primary follicle --> Secondary follicle --> Graafian follicle --> Corpus luteum --> Corpus albicans |
|
|
Describe the primary follicle. |
Develops from the primordial follicle and consists of a few layers of follicular cells surrounding the oocyte. |
|
|
Describe the secondary follicle. |
Consists of numerous layers of follicular cells surrounding the oocyte. These follicular cells will begin producing estrogens. |
|
|
Describe the graafian follicle. |
A mature follicle consisting of follicular cells surrounding the oocyte (corona radiata) and a fluid filled space (antrum) surrounded by multiple layers of follicular cells producing estrogens. |
|
|
Describe the corpus luteum. |
The collection of follicular cells that remains in the ovary after ovulation of the secondary oocyte. Will produce estrogens and progesterone. |
|
|
Describe the corpus albicans. |
The degenerated corpus luteum. The corpus albicans develops if fertilization does NOT occur. If fertilization does happen, the corpus luteum remains and does not develop into the corpus albicans. |
|
|
The uterine (menstrual) cycles encompasses the changes that occur to what part of the uterus? |
Endometrium |
|
|
What is the endometrium? |
Innermost layer of the uterine wall consisting of a base layer and a functional layer composed of epithelial tissue, glands and a rich blood supply. |
|
|
What do the events of the ovarian cycle aim to achieve? |
Prepare the uterus each month to receive, retain and nourish a zygote. |
|
|
Name the 3 phases of the ovarian cycle. |
1. Menstrual phase 2. Proliferative phase 3. Secretory phase |
|
|
When does the menstrual phase occur? |
Day 1- 5 |
|
|
What occurs during the menstrual phase? |
Shedding (loss) of the functional layer of the endometrium. |
|
|
When does the proliferative phase occur? |
Day 5 - 14 |
|
|
What occurs during the proliferative phase? |
Proliferation (growth of cells via mitosis) of the functional layer of the endometrium. |
|
|
When does the secretory phase occur? |
Day 14 - 28 |
|
|
What happens during the secretory phase? |
- Growth, lengthening and coiling of the endometrial blood vessels (which increases blood supply). - Growth and lengthening of the endometrial glands (which will secrete glycogen during the latter half of the uterine cycle) |

