![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Regions of a Cell |
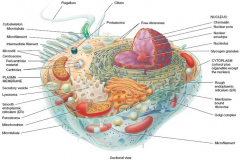
- Plasma/cell membrane - Cytoplasm - Nucleus |
|
|
Plasma Membrane (General) |
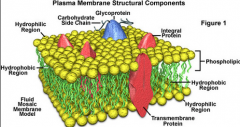
- Very thin and delicate, and very complex. - Consistency of olive oil, and the structures within it move about when necessary |
|
|
Plasma Membrane (Structures) |
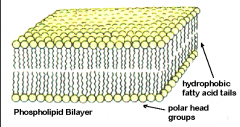
- Phospholipid bilayer - Phosphate layer is hydrophilic - Lipid tails are hydrophobic |
|
|
Glycoproteins |
- Act as identification markers to distinguish between body tissue and foreign tissue |
|
|
Ribosomes |
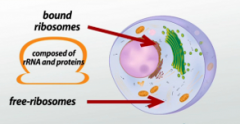
- Synthesize proteins. - Either attached to endoplasmic reticulum or are "free" in the cytoplasm |
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
- Contains the ribosomes where protein is synthesized |
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum |
- Site of steroid synthesis. No ribosomes attached |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus (complex) |
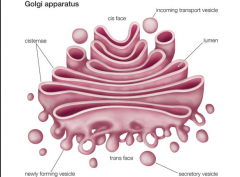
-"Traffic director" of proteins - Looks like a stack of plates - Packages proteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum for delivery inside or outside the cells - Adds other molecules in some proteins |
|
|
Lysosomes |
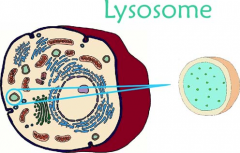
- "Housecleaners" - Sacs that bud off of the Golgi plates - Enzymes "eat" worn-out cell parts, dead cells, bacteria, etc |
|
|
Peroxiomes |
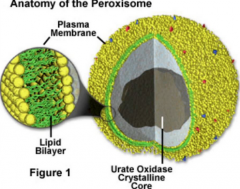
- Digest normal toxic by-products of cellular metabolism. - Numerous in liver and kidney cells |
|
|
Centrioles |
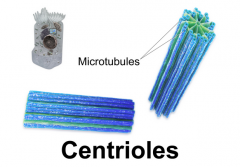
- Pair of rod-shaped structures that are perpendicular to one another - Separate chromosomes during mitosis (cell division) |
|
|
Nuclear Envelope |
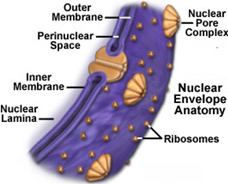
- Double-layered membrane surrounding the nucleus |
|
|
Nucleolus |
Makes ribosomes and chromatin (contains the genes) |
|
|
Chromatin |
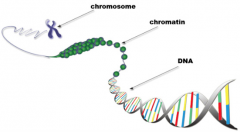
- Complex network of threads containing DNA - Forms into chromosomes when the cell is about to divide |
|
|
Osmosis |
- Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from high concentration of water to low |
|
|
Isotonic Solution |
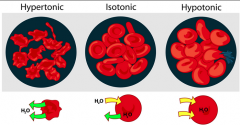
- The solute concentration in the solution is equal to the solute concentration in the RBC. The water is in equilibrium - Shape remains the same |
|
|
Hypertonic Solution |
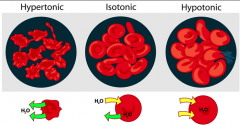
- The solute concentration of the solution contains more solutes than in the RBC. - The water will leave the cell by osmosis, and cause the cell to shrink, or crenate |
|
|
Hypotonic Solution |
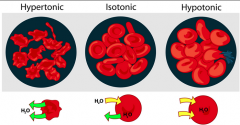
- The solute concentration of this solution contains less solutes than the RBC - Some water will enter the cell by osmosis, causing the cell to expand. It may burst or hemolyze |
|
|
Filtration |
- Movement of water and dissolved substances from an area of high pressure to low pressure |
|
|
Pinocytosis |
- "Cell drinking" |

