![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Decreasing Body Weight (Non-Drug)
|
- Obese pts have increased insulin secretion causing increase Na+ reabsorption (water
follows), so blood volume increases = increased BP - Obese pts have increased SNS activity |
|
|
Restricting Sodium Intake (Non-Drug)
|
- When levels are too high it causes excess water to be reabsorbed by kidneys
- Increased blood volume = increased BP - Limiting salt intake to 5g/day decrease BP 12/6 |
|
|
Physical Exercise (Non-Drug)
|
- Regular exercise decreases BP by 10mmHg
- Decreased fluid volume |
|
|
Potassium Supplementation (Non-Drug)
|
- Increased K+ causes...
- Decreased BP - Increased sodium excretion - Decreased renin release - Pts taking ACE inhibitors should not be on a high potassium diet |
|
|
Smoking Cessation (Non-Drug)
|
- Just quit.
|
|
|
Alcohol Restriction (Non-Drug)
|
- Excessive alcohol increases BP
- Can decrease response to antihypertensive drugs |
|
|
Main Classes of Diuretics (3) and Mechanism of Action (General)
|
- Loop, Thiazide, and Potassium Sparing diuretics
- Block Na+ and Cl- ion reabsorption from the nephron - This prevents water reabsorption - Decreases blood volume = decreased BP |
|
|
Loop Diuretics
|
- Most effective diuretic
- Block Na+ and Cl- ion reabsorption in ascending Limb of Henle - Usually reserved for: - Edema, severe renal failure, and severe hypertension that didn't respond to mild drugs |
|
|
Adverse Effects of Loop Diuretics
|
- Hypokalemia (decreased K+ in blood)
- may cause cardiac dysrhythmias - Hyponatremia (decreased (Na+ in blood) - Dehydration - Hypotension |
|
|
Thiazide Diuretics
|
- Most commonly used
- Block Na+ and Cl- reabsorption in distal tubule |
|
|
Adverse Effects of Thiazide Diuretics
|
- Hypokalemia (decreased K+ in blood)
- may cause cardiac dysrhythmias - Dehydration - Hyponatremia (decreased Na+ in blood) |
|
|
Potassium Sparing Diuretics
|
- Minimal lowering of BP
- Inhibit aldosterone receptors in collecting duct - Causes increased Na+ excretion and K+ retention - Should not be used with ACE inhibitors or ARBs |
|
|
Beta Blockers (affect on cardiac beta 1 receptors)
|
- Bind of catecholamines (i.e. epinephrine) to these receptors causes increased CO
- Beta blockers block beta receptors causing decreased CO - suffix "olo" (e.g. propanolol) |
|
|
Beta Blockers (affect on juxtaglomerular cells)
|
- These cells release renin which activates RAAS
- Beta blockers block beta receptors causing decreased RAAS activity - suffix "olo" (e.g. propanolol) |
|
|
Classes of Beta Blockers
|
1st Generation Beta Blockers
- Produce non-selective blockade - Could inhibit beta 2 (in the lung) receptors 2nd Generation Beta Blockers - Produce selective blockade |
|
|
Adverse Effects of Beta Blockers
|
- Bradycardia
- Decreased CO - Heart failure (rare) - Rebound hypertension when withdrawn abruptly - Bronchospasm (Non-selective beta blockers) - Glycogenolysis inhibition (Non-selective) |
|
|
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors
(mechanisms of action) |
Decreases angiotensin II production causing:
- Vasodilation - Decrease total blood volume Inhibit bradykinin breakdown causing: - Vasodilation - suffix "pril" (e.g. captopril) |
|
|
Adverse Effects of ACE Inhibitors
|
- Hyperkalemia (increased K+ in blood)
- Persistent cough - Angioedema - Certain NSAIDs may decrease ACE Inhibitor effect |
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
(mechanism of action) |
-Blocks binding of angiotensin II to its receptor causing:
- Causes vasodilation - Increases Na+ and water secretion - suffix "sartan" (e.g. valsartan) |
|
|
Direct Renin Inhibitors (DRIs)
(mechanism of action) |
- Binds to renin inhibiting conversion of
angiotensinogen ot angiotensin I |
|
|
Adverse Effects of DRIs
|
- Hyperkalemia (increased K+ in blood)
- Diarrhea |
|
|
Calcium Channel Blockers (mechanism of action and sub classes)
|
- Blocks entry of calcium into heart and smooth muscle cells decreasing contraction
Subclasses - Dyhydropyridine calcium channel blockers - Non-dyhydropyridine calcium channel blockers |
|
|
Dyhydropyridine Calcium Channel Blockers
(mechanism of action) |
- Decrease arteriolar smooth muscle calcium influx resulting in vasodilation
- suffix "dipine" (e.g. nifedipine) |
|
|
Adverse Effects of Dyhydropyridine Calcium Channel Blockers
|
- Flushing
- Dizziness - Headache - Peripheral Edema - Reflex tachycardia - Rash |
|
|
Non-Dyhydropyridine Calcium Channel Blockers
(mechanism of action) |
- Block calcium channels in both the heart and vessels
- Decrease CO |
|
|
Adverse Effects of Non-Dyhydropyridine Calcium Channel Blockers
|
- Constipation
- Dizziness - Flushing - Headache - Edema - May compromise cardiac function |
|
|
Centrally Acting Alpha 2 Receptor Agonists
(mechanism of action) |
- Bind to and activate alpha 2 receptors in brainstem decreasing sympathetic outflow to heart and vessels
- Causes decreased CO and peripheral resistance |
|
|
Adverse Effects of Centrally Acting Alpha 2
Receptor Agonists |
- Drowsiness
- Dry mouth - Rebound hypertension if withdrawn abruptly |
|
|
Treatment Algorithm - Hypertension Only
|
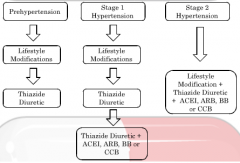
|
|
|
Treatment Algorithm - Diabetes and Renal
Disease |
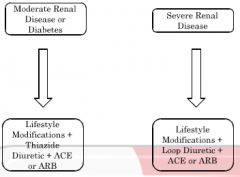
|

