![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
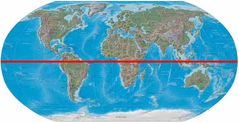
the invisible line that runs around the center of the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, divides the planet into a Northern Hemisphere and a Southern Hemisphere. |
Equator |
|
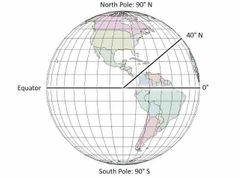
an angle which ranges from 0 degree at the equator to 90 degree at the poles (also known as parallels) |
Latitude |
|
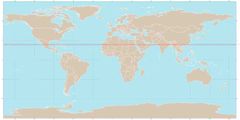
also referred to as the Northern Tropic, is the most northerly circle of latitude on Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. (23.5 degree N) |
Tropic of cancer |
|
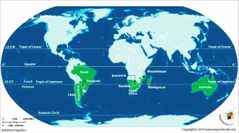
The southern most latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. Its northern equivalent is the Tropic of cancer |
Tropic of Capricorn |
|
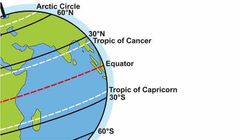
One of the two polar circles and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth. It marks the northernmost point. |
Arctic Circle |
|
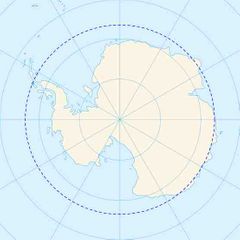
The most southerly of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of Earth. The region south of this circle is known as the |
Antarctic Circle |
|
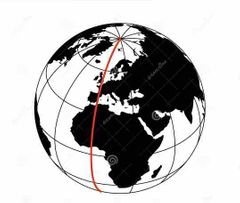
the meridian in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0 degree |
Prime Meridian |
|
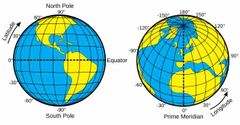
Using ___ and ___ you can describe at the location of a certain area |
Latitude and Longitude |
|

Resources that exist without any actions of human kind |
Natural resources |
|

Natural resources that are potentially useful as a source of water supply |
Water resources |
|

Are a form of environmental asset providing a range of ecosystem services. A key feature of this resource is their delivery of supporting services including the formation of and function of the soil, nutrient cycling, water cycling, structural support of vegetation and soil biodiversity |
Soil resources |
|

Is a significant factor not only in soil formation but also in sustaining diversity of plants and animals |
Climate |
|

Something that can produce heat, power life, move objects, or produce electricity. |
Energy Resources |
|

is a renewable energy source because heat is continuously produced inside the earth |
Geothermal Energy |
|
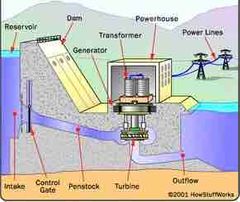
Use of water to generate energy or electricity |
Hydrothermal or hydroelectric powerplants |
|

a fossil energy source that formed deep beneath the earth’s surface |
Natural gas |
|

made from decomposing plants and animals. Found in the Earth’s crust and contain carbon and hydrogen, which can be burned for energy |
Fossil fuel |
|

It is the layer of air that extends to about 50 km form Earth’s surface. Many jet aircraft fly because it is very stable |
Stratosphere |
|

It is the layer of the Atmosphere that closest to Earth’s surface |
Troposphere |
|

It is the envelope of air that surrounds the Earth where all weather events happen |
Atmosphere |
|

It is the layer between 50 km and 80 km about the Earth’s surface, the air in this layer is very thin and cold |
Mesosphere |
|

It is between 80 km and 110 km above the Earth. Space shuttles fly in this area and it is also where the auroras found |
Thermosphere |
|
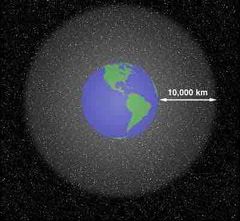
It is the upper limit of atmosphere. This layer of the atmosphere merges into space, Satellites are stationed in this area 500 km to 1000 km from Earth |
Exosphere |
|
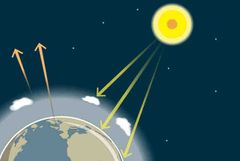
It is the process by which the Earth’s atmosphere warms up |
Greenhouse effect |
|
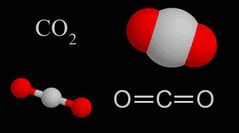
It is naturally produced when people and animals breathe |
Carbon dioxide |
|
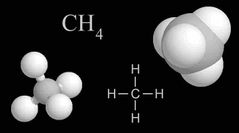
Comes from grazing animals as they digest their food and from decaying matter in wet rice fields |
Methane |
|

Are wind systems, usually bring abundant rainfall, also called amihan or habagat |
Monsoons |
|
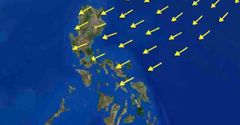
The wind blows from the high-pressure area in the Asian continent toward the low-pressure area south of the Philippines |
Amihan |
|

The wind will move from the high-pressure to the low-pressure area in the Asian continent. This monsoon wind is locally called |
Habagat |
|
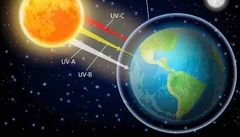
Is also naturally present in the stratosphere |
Ozone |
|

Occurs in the troposphere because this layer contains most of the water vapor |
Weather |
|

Warm air rises, and air moves toward the place where warm air is rising |
Intertropical Convergence Zone |
|
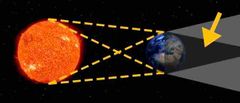
It is the darker inner region of Moon’s shadow |
Umbra |
|

Shadows are formed on astronomical objects, a darkening effect is observed |
Eclipse |
|

It is the gray outer region of the Moon’s shadow |
Penumbra |
|
In which month is the North Pole tilted away from the Sun |
June |
|
It is the half of the Earth that is north of the equator |
Northern hemisphere |
|
It is the half of Earth that is south of the equator |
Southern hemisphere |
|

Occurs when the Moon is directly on the opposite side of the Earth as the Sun |
Lunar eclipse |
|

It occurs after autumn and before spring in each year |
Winter |
|

It is occur after spring and before autumn |
Summer |
|

Has moved along its orbit, taking the Moon along |
Earth |
|

Is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region |
Season |
|
In December, which hemisphere receives direct rays from the sun |
Southern hemisphere |
|
In June, which hemisphere receives direct rays from the sun |
Northern hemisphere |
|

Defined to be celestial body that makes an orbit around a planet |
Moon |

