![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous reactions.
|
Heterogeneous reactions involve reactions in two different phases whilst a homogeneous reaction's reactants and products exist in a single phase.
|
|
|
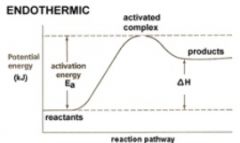
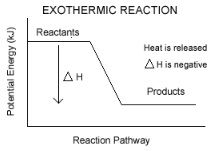
How does the energy of the activated complex compare with the energies of reactants and products?
|
The activated complex has more energy than the reactants and products.
|
|
|
What are the 5 factors that influence the rate of reaction?
|
The nature of the reactants, surface area, temperature, concentration, and the presence of a catalyst.
|
|
|
Explain the importance of the collision theory in chemical reaction.
|
Determines if and in what order a reaction will occur.
|
|
|
Explain the importance of the rate determining step in chemical reactions.
|
It's the slowest step.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Draw an energy profile with and without a catalyst.
|
Catalyzed will have a high hump, uncatalyzed will have second highest hump, and enzyme catalyst will have the lower hump.
|
|
|
Write the rate reaction and explain each variable.
|
R = k[A]^n[B]^m
R = reaction rate k = specific rate constant [A]/[B] = molar concentrations of reactants n/m = respective powers to which the concentrations are raised and represented. |
|
|
What is the reaction mechanism?
|
The step-by-step sequence of reactions by which the overall chemical change occurs.
|
|
|
What are intermediates?
|
Species that appear in some steps but not in the net equation.
|
|
|
What is the collision theory?
|
The set of assumptions regarding collisions and reactions.
|
|
|
What is activation energy?
|
The minimum energy required to transform the reactants into an activated complex.
|
|
|
What is an activated complex?
|
A transitional structure that results from an effective collision and that persists while old bonds are breaking and new bonds are forming.
|
|
|
What is a catalyst?
|
A substance that changes the rate of a chemical reactions without itself being permanently consumed.
|
|
|
What is the action of a catalyst called?
|
Catalysis.
|
|
|
What is a a homogeneous catalyst?
|
A catalyst that is in the same phase as all the reactants and products in a reaction system.
|
|
|
What is a heterogeneous catalyst?
|
A catalyst that has different phases than it's reactant's.
|
|
|
What is the order in a reactant?
|
The power to which a reactant concentration is raised.
|
|
|
What is the rate law of a reaction?
|
An equation that relates reaction rate and concentrations of reactants.
|
|
|
An order of ____ means that the rate does not depend on the concentration of the reactant, as long as some of the reactant is present.
|
zero
|

