![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
First to say that all matter is made of atoms |
Democritus |
|
|
Substances are made of four elements: Earth, Air, Fire and Water |
Aristotle (the Greeks) |
|
|
Known as the Father of Modern Chemistry |
Antoine Lavoisier |
|
|
Stated the Law of Conservation of Mass |
Antoine Lavoisier |
|
|
Atoms combine to form compounds |
John Dalton (part 4 of his theory of the atom) |
|
|
Atoms of the same element have the same properties |
John Dalton (part 2 of his theory of the atom) |
|
|
Discovered the negatively charged particle of the atom |
JJ Thomson |
|
|
Plum Pudding Model |
JJ Thomson |
|
|
Chemical reactions involve in the rearrangement of atoms. No new atoms are created or destroyed (NOT the law of conservation of mass) |
John Dalton (part 5 of his theory of the atom) |
|
|
atoms looks like tiny, hardy, indivisible spheres |
John Dalton (part 1 of this theory of the atom) |
|
|
Named what we know as the atom, atomos (which means no cut) |
Democritus |
|
|
Discovered the positively charged center of the atom |
Ernest Rutherford |
|
|
famous for this Gold Foil Experiment |
Ernest Rutherford |
|
|
Atom is mostly empty space (first to say this) |
Ernest Rutherford |
|
|
Calculated the charge of the electron |
Robert Milikan |
|
|
His theory of the atom said that it was a positive sphere with negative particles scattered throughout |
JJ Thomson |
|
|
Discovered the neutron |
Chadwick |
|
|
His theory of the atom says that electrons move like planets around the sun |
Niels Bohr |
|
|
Planetary Model |
Niels Bohr |
|
|
Amounts of energy separate the orbit (orbitals) that electrons can be in |
Niels Bohr |
|
|
His theory of the atom uses probability to predict electron location |
E. Schrodinger |
|
|
Electron Cloud Model |
E. Schrodinger |
|
|
Atom has two parts: nucleus and electron cloud |
E. Schrodinger |
|

Whose model of the atom? |
John Dalton |
|
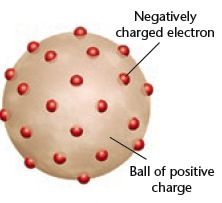
Whose model of the atom? |
JJ Thomson |
|
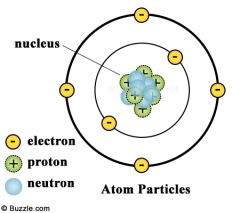
Whose model of the atom? |
Ernest Rutherford |
|
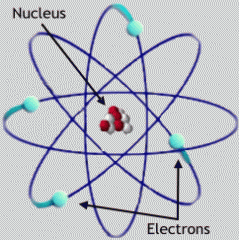
Whose model of the atom? |
Niels Bohr |
|

Whose model of the atom? |
E. Schrodinger |
|
|
negative particle found outside the nucleus |
electron (location and charge) |
|
|
positive particle found inside the nucleus |
proton (location and charge) |
|
|
neutral particle found inside the nucleus |
neutron (location and charge) |

