![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
178 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
BODY MECHANICS?
|
-efficient, safe and coordinated use of the body to produce motion & balance
-coordinated efforts of the musculoskeletal & nervous systmes as a person Moves, Lifts, Bends, Stands, Sits, Lies down, & completes Daily Activities |
|
|
Safe client handling prevents?
|
-injuries to nurses & clients when moving and transferring
|
|
|
MOBILITY?
|
ability to move free & indepentdent in purposeful mvmt
-requires voluntary motor & complete sensory control of all body regions -refers to adapting and having self-awareness of the environment -musculoskeletal/Nervous systems are essential to mobility |
|
|
IMMOBILITY?
|
- Inability to move freely (can be temporary or permanent, partial or complete)
-increase risk of complications the greater the amt of immobility the longer the immobilization |
|
|
-Static position?
|
-ie. sitting position
|
|
|
FRICTION:
|
force that occurs in a direction to oppose movement
nurses use an ergonomic assistive device (ie. full body sling) to lift client off the surface of bed and move them up, helps to reduce friction, tearing, and shearing of skin |
|
|
What are some example of LONG bones?
|
Contribute to Height:
-femur -fibula -tibia in Legs And Length: -phalages of fingers & toes |
|
|
Examples of SHORT bones?
|
-carpel bones in the foot and toes
-permit mvmt of extremites |
|
|
Examples of FLAT bones?
|
-skull
-ribs (provide structural contour) |
|
|
Examples of IRREGULAR bones?
|
-vertebral column
-Mandible (some bones of skull) |
|
|
PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURES:
|
-fractures caused by weakened bone tissue
|
|
|
Connection b/w bones?
|
-JOINTS
|
|
|
Bones jointed by bones?
|
-SYNOSTOTIC JOINT=NO movement
ie. adult skull |
|
|
CARTILAGINOUS JOINT or Synchondrosis joint?
|
-cartilage unites bony somponents
-allows for bone growth -provides stability ie. the first sternocostal joint |
|
|
FIBROUS JOINT, or Syndesmosis joint?
|
- ligament or membrane unites 2 bony surfaces
-the fibers of ligaments are flexible and stretch permits a limited amt of mvmt ie. tibia & fibula (paired boes of the lower leg) |
|
|
Freely movable joint?
|
-SYNOVIAL JOINT, aka, true joint
ie. ball and socket (hip joint) ie. hinge joint (interphalangeal joints of fingers |
|
|
Binds joints together and connecting bones & cartilages
Elastic and aid joint flexibility and support |
LIGAMENTS
|
|
|
Connect Muscle to Bone?
|
TENDONS
ie. Achilles tendon (tendo calcaneus) |
|
|
CARTILAGE:
|
-nonvascular supporting connective tissue located chiefly in the joints & thorax, trachea, larynx, nose and ears
|
|
|
UNOSSIFIED?
|
-Not Hardened
|
|
|
CONCENTRIC TENSION?
|
-increased muscle contraction causes muscle shortening resulting in mvmt
ie when a client uses an overhead trapeze to pull up in bed |
|
|
ECCENTRIC TENSION?
|
-Helps control the speed and direction of mvmt
ie. when a client lowers back to the bed after uses an overhead trapeze to pull up eccentric and concentric muscle action is necessary for active mvmt and is referred to as dynamic or ISOTONIC CONTRACTION |
|
|
ISOMETRIC CONTRACTION?
|
-aka Static contraction
-causes an increase in muscle tension or muscle work but NO shortening or active mvmt of the muscle ie. flexing and relaxing a muscle, quadriceps |
|
|
Voluntary mvmt?
|
-combo of isotonic and isometric contractions
|
|
|
Energy expenditure?
|
-increased respiratory rate and increased work on the heart
p. 1223 |
|
|
LEVERAGE
|
-inducting or compelling force
ie.humerus, ulna and radius and the associated joint, such as elbow, act together as a LEVER |
|
|
The position of the body in relation to the surrounding space
|
POSTURE
-Muscles of lower extremities, trunk, neck and back are concerned w/ Posture |
|
|
MUSCLE TONE:
|
-Helps maintain fuctional positions such as sitting or standing w/o excess muscle fatigue and is maintained through continual use of muscles.
*ADLs help maintain muscle tone |
|
|
When is muscle tone decrease?
|
-client is immobile or on prolonged bed rest
|
|
|
NEUROTRANSMITTERS?
|
chemicals (acetylcholine, dopamine, norephinephrine), transfer electric impulses from the nerve across the neuromuscluar juction to the muscle
Disorder= Parkinsonism |
|
|
Freely movable joint?
|
-SYNOVIAL JOINT, aka, true joint
ie. ball and socket (hip joint) ie. hinge joint (interphalangeal joints of fingers |
|
|
Binds joints together and connecting bones & cartilages
Elastic and aid joint flexibility and support |
LIGAMENTS
|
|
|
Connect Muscle to Bone?
|
TENDONS
ie. Achilles tendon (tendo calcaneus) |
|
|
CARTILAGE:
|
-nonvascular supporting connective tissue located chiefly in the joints & thorax, trachea, larynx, nose and ears
|
|
|
UNOSSIFIED?
|
-Not Hardened
|
|
|
Damage to the CNS results in?
|
-impaired body alignment, balance and mobility
ie. head injury, ischemia from a stroke or brain attack (CVA) |
|
|
Damage to the Cerebellum causes problems w/?
|
-balance
|
|
|
MUSCLE ATROPHY:
|
-loss of muscle tone and joint stiffness
|
|
|
TORTICOLLIS
|
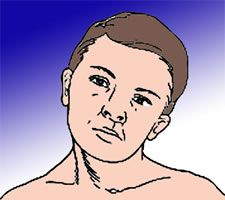
Inclining of head to affected side, SCM muscle is contracted
-Cause is congenital or acquired -TX: surgery, heat, support, gentle ROM |
|
|
KYPHOSIS
|
increased convexity in curvature of thoracic spine
-humpback |
|
|
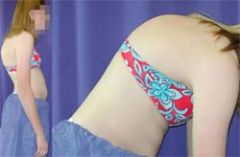
SCOLIOSIS
|

Lateral "S" or "C" shape spinal column w/ vertebral rotation, unequal heights of hip ans shoulders
|
|
|
KNOCK-KNEE (GENU VALGUM)
|
-legs curved inward so that knees come together as person walks
Causes: congential, Rickets Tx: knee braces, surgery |
|
|
BOWLEGS (GENU VARUM)
|
-One or both legs bent outward at knee, normal until 2 to 3 years of age
Cause: congenital, Rickets Tx: slowing rate of curving if not corrected by growth RIckets: increase vit D, Ca and phosphorus intake |
|
|
CLUBFOOT
|
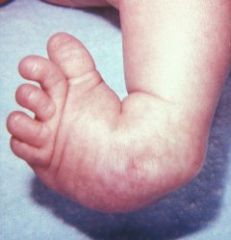
95% medical deviation and plantar flexion of foot (equinovarus)
5%: Lateral deviation and Dorsi-flexion (calcaneovalgus) Cause: congential Tx: casts, splint (denis browne splint), surgery |
|
|
The principles of body mechanics are based on?
|
-alignment
-balance -gravity -friction |
|
|
Movement is Dependent on an intact?
|
-skeletal system
-skeletal muscles -nervous system |
|
|
Assessment of the client focuses on ?
|
-mobility
-ROM -Gait -exercise status -activity tolerance -body alignment (standing, sitting, and lying) |
|
|
Nursing Interventions are designed to :
|
-maintain mobility
-prevent of minimize the complications of immobility |
|
|
Factors affecting Mobility include:
|
-alteration in muscles
-injury to the musculoskeletal system -abnormal posture -impaired CNS -clients's health status and age |
|
|
Reason for Immobility:
|
-physical inactivity (BR or BRP), Doctors order
-Physical restriction of mvmt (cast) in traction -Sensory Deprivation (isolation room) |
|
|
BED REST:
|
restricts client to the bed for therapeutic reasons
duration depends on the illness or injury and the client's prior state of health |
|
|
NANDA defines: IMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY as:
|
-a limitation in independent, purposeful physical mvmt of the body or 1 or more extremities
|
|
|
"Hazards of Imobility"
|
-cluster of symptoms
-effects of muscular deconditioning associated w/ the lack of physical activity -Systemic effects or Metabolic changes (wound healing) |
|
|
What % of muscle strength is losed in a person of average wt/ht and w/o chronic illness on Bed Rest?
|
3%/ day
|
|
|
DISUSE ATROPHY?
|
-describes the tendency of cells and tissue to reduce in size and function in response to prolonged inactivity resulting from bed rest, trauma, casting or local nerve damage
|
|
|
Objectives of BED REST:
|
-reducing physical activity and the O2 needs of the body
-reducing pain, including postoperative pain or after acute injury to the lower back -allowing ill or debilitated clients to rest -allowing exhausted clients the opportunity for uninterrupted rest |
|
|
The severity of the impairment depends on:
|
-clients overall health, degree, and length of immobility and Age
(Systemic Effect p 1225) |
|
|
The Endocrine System maintains and regulates vital functions such as:
|
-response to stress and injury
-growth & development -reproduction -maintenance of the internal environment -energy production, utilization, and storage |
|
|
Immobility disrupts normal Metabolic functioning by:
(Metabolic Changes) |
-decreasing BMR (thyroid hormone increases BMR)
-altering the metabolism of carbs, fats, and protein: causing fluid, electrolyte and Ca imbalances -Causes GI disturbances(decreased appetite & slowing peristalsis) *BMR may increase as a result of a Fever or wound healing |
|
|
NEGATIVE NITROGEN BALANCE:
|
A condition in which nitrogen output exceeds nitrogen intake, resulting in the body’s need to draw on its own stores of protein for energy; may be caused by dietary imbalances, illness, infection, anxiety, or stress, Immobiltiy
|
|
|
NEGATIVE NITROGEN BALANCE:
|
-decreased appetite
-calories and proteins deficient -protein is constantly being broken down and excreted at a greater rate than taken in -protein that is breaking down is also breaing down you MUSCLE MASS -organs loss muscle mass -can happen to a healthy person placed on Bed Rest |
|
|
ChangeS in the Metabolic (endocrine system) caused by immobility includes:
|
-negative nitrogen balance
-loss of wt -alteration of Ca, Fluid & electrolytes -RESORPTION of CALCIUM from bones -decreased urinary elimination of Ca resulting in HYPERCALCEMIA |
|
|
When do Pathological Fractures occur?
|
-if calcium reabsorption continues as athe client remains on bed rest or continues to be immobile
|
|
|
Neuromuscular Effects of HYPERcalcemia include:
|
-lethargy
-depressed reflexes (+1) -constipation -mental confusion -coma -Slow heart rate |
|
|
GI functioning effects of Immobility:
|
-decreased motility of intestines
-decreased absorption of H2O in the colon and dehydration may occur -Constipation may lead to Impaction -Fecal impaction can cause bowel obstruction (partial or complete) -could cause fluid or electrolyte imbalances |
|
|
Foods high in Fiber:
|
-apple w/ peeling
-whole grain bread -orka -prunes broc -green leafy vegetables -letuce -grapes -grapefruit -bananas -oranges |
|
|
Pseudodiarrhea?
|
-results from a fecal impaction (accumulation of hardened feces)
-liquid stool passing around the area of impaction |
|
|
The lack of pressure on the bones (non wt bearing) triggers:
|
-Ca loss from the Bones
Weight bearing keeps us from releasing Ca from our bones to the blood stream If Ca level is too high, can give Mg |
|
|
When does Bone Demineralization occur?
|
2 to 3 days after onset of Immobility
|
|
|
Bone effects of Immobility may lead to?
|
*May lead to pathological Fracture (bone breaks for no reason) and/or Osteoporosis
|
|
|
Changes in Metabolic system as a result of Immobility?
|
-glucose intolerance due to decrease activity of pancreas
-insulin resistance may Increase -fluid and Electrolye imbalances may include Na, K and water (may increase or decrease |
|
|
ASSESSMENT of the METABOLIC SYSTEM:
|
-Anthropometric Measurements (measures you skin folds), dietician will measure
-Muscle Atrophy (decrease in muscle mass) -I & O (fluid balance) -Dehydration (check mucous membrane in mouth) Skin (dry), urine (dark) -Labs (look at albumin levels) -edema -skin turgor -wound healing -dietary intake *If a child crys and doesn't produce tears, it's a sign of Dehyration* |
|
|
ATROPHY=
|
-Disuse
|
|
|
Nursing INTERVENTIONS for Metabolic system
|
-provide high-calorie and high -protein diet w/ additional Vit B and C
-high caloric intake provides sufficient fuel to meet metabolic needs and to replace subcutaneous tissue -Increase fluids (If bowel is functioning, can use a NG if there's not a breakage in the cervical area of neck) Pro Mod- protein supplement (powder form) |
|
|
ATELECTASIS
|
collapse of alveoli
-bronchioles become blocked by secretions and the distal Alveoli (air sac) collapse causing Hypoventilation -keep pt breathing good to prevent alveoli from collapsing |
|
|
HYPOSTATIC PNEUMONIA
|
-Inflammation of the lung from stasis or pulling of secretions)
|
|
|
BRONCHOPNEUMONIA:
|
-mucus accumulates in the air passages creating an excellent medium to grow bacteria
|
|
|
Cough and Deep breath technique?
|
-take 2 deep breaths
-on 3rd deep breath hold and cough into arm |
|
|
SOB uses ______ muscles?
|
-Accessory
(observe neck mvmt and lift shirt and LOOK) |
|
|
Mucus in the bronchi increase when the client is in what postions?
|
-supine
-lateral -prone |
|
|
Mucus is an excellent place for ______ to grow
|
-bacteria
|
|
|
Changes take place in the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM, due to Immobility?
|
-DECREASED RESPIRATORY mvmt resulting in decrease oxygenation and Carbon Dioxide exchange
-STASIS of SECRETIONS and decreased and weakened respiratory muscles resulting in Atelectasis and Hypostatic pneumonia -decreased cough response |
|
|
Assessment for RESPIRATORY SYSTEM:
|
Assess Every 2 Hours:
-observe the chest wall mvmt for symmetry (up & down) -auscultate lung sounds -count Respirations -observe for productive cough, (note color, amt, consistency of secretions) -any SOB (want client to turn, cough and deep breath every 2 hours) |
|
|
Assessment findings that indicate pneumonia include:
|
-productive cough w/ greenish-yellowish sputum
-fever -pain on breathing -crackles =heard during inspiration, crackling, bubbly sounds "popping" -wheezes=musical sounds -dyspnea |
|
|
Nursing Interventions for RESPIRATORY SYSTEM:
|
Resipiratory intervention will aid alveolar expansion & prevent atelectasis
- Reposition every 2 hours -TCDB q 1-2 hours while awake -yawn q hr while awake or use incentive spirometer -take 3 deep breaths and cough with the third exhalation (tech. produces a forceful, productive cough w/o excessive fatigue) -remove abd binders q 2 hours & ensure placement -Auscultate lungs for effectiveness of chest physiotherapy or respiratory therapy -consume a min of 2,000 mL/day (unless contraindicated) = helps keep mucociliary clearance normal, secrections will be easily removed w/ coughing & appear thin, watery and clear *w/o adwquate hydration, secrections become thick, tenacious & difficult to remove *fluids also help w/ bowel/urine elimination and aids in circulation &skin integrity -CPT chest physiotherapy -Judicious use of Narcotics |
|
|
CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY:
|
-Percussion and positioning
-method for preventing pneumonia and keeping the airway clear -helps drain secretions from specfic segments of the bronchi and lungs into the trachea, (client will breath better) -often provide by Respiratory therapist |
|
|
Respiratory Intervention for an unconscious client w/ artificial airways?
|
-can't always effectively cough on their own
*Nurse expand the chest and lungs using an Ambu-bag and clear secretions by suctioning the airway when needed |
|
|
CARDIOVASCULAR changes due to Immobility?
|
-ORTHOSTATIC HYPOTENSION
-decrease fluid volume in circulatory system -stasis of bld in the legs -decreased autonomic response occurs -DECREASED CARDIC OUTPUT, leading to poor cardiac effectiveness, which results in increased workload on the heart, decline in B/P -Increased oxygenation requirement -INCREASED RISK OF THROMBUS development |
|
|
ORTHOSTATIC HYPOTENSION:
|
-increase in heart rate of more than 15%
- a drop of 15mm/Hg or > Systolic B/P or -a drop of 10mm/Hg or > in Diastolic B/P when the client changes from the supin to standing position ie. lying: 170/94 sitting:160/88 standing: 120/72 |
|
|
ORTHOSTATIC HYPOTENSION is due to:
|
1. decrease in circulating fluid volume (client may have lost some blood)
2. pooling of blood in lower extremites 3. decrease in autonomic response |
|
|
S/S of Orthostatic Hypotension
|
-lightheadness
vertigo weakness fatigue lack of energy head or neck discomfort syncope or near syncope (LOC) |
|
|
Syncope:
|
A brief loss of consciousness caused by a sudden fall of blood pressure or failure of the cardiac systole, resulting in cerebral anemia.
|
|
|
Autonomic Nervous system
(Autonomic response decrease w/ orthostatic hypotension) |
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the part of the nervous system that we cannot control with our mind. The ANS regulates breathing, heart rate, digestion, immune function, sleep patterns, hormone regulation, blood pressure, blood sugar levels, tissue regeneration, and liver and kidney detoxification
|
|
|
THROMBUS FORMATION:
|
a blood clot which can occlude the lumen in a vein or artery
|
|
|
3 factors that contribute to Venous Thrombus Formation
|
1. damage to the vessel wall (ie. injury during surgical procedure)
2. alterations of blood flow (ie. slow blood flow in calf veins associated w/ bed rest) 3. alterations in blood constituents (ie. change in clotting factors or increased in plt activity) |
|
|
Cardiovascular Assessment for Immobility includes:
|
-orthostatic B/P & P /assess for vertigo
-palpate apical and peripheral pulses -auscultate the heart at apex for S3 (an early symptom of heart failure) - the older adult may not adapt well to immobility -palpate for edema in sacrum, legs and feet -palpate skin for warmth in peripheral areas to include nose, ear lobes, hands and feet -assess for DVT by observing calves for redness and palpating for warmth and tenderness -measure circumference of both calves and thighs and compare in size (calf -10cm below middle of patella) -assess Homan's sign -assess wound healing |
|
|
**How do you measure DVT and be consistent with the last nurse?**
|
**Make a Mark*
|
|
|
**Client who have orthostatic Hypotension will have?
|
-Increase pulse rate
-Decreased pulse pressure -Drop in B/P |
|
|
Isometric exercise:
|
-activities that involve muscle tension w/o muscle shortening, do not have any beneficial effect on preventing orthostatic hypotension but will improve activity tolerence
|
|
|
What are some nursing intervention for Reducing Orthostatic Hypotension?
|
-change positions gradually
-assess orthostatic BP's -get pt out of bed as soon as condition allows -have help to assist immobile pt OOB the first time, assess the situation using Safe-Client Handling Algorithm |
|
|
VALSALVA MANEUVER
|
A maneuver in which a person tries to exhale forcibly with a closed glottis (the windpipe) so that no air exits through the mouth or nose as, for example, in strenuous coughing, straining during a bowel movement, or lifting a heavy weight. The Valsalva maneuver impedes the return of venous blood to the heart.
|
|
|
Interventions to REDUCE Cardiac Workload?
|
-discourage client from using the Valsalva maneuver
-Teach client Not to hold breath when getting out of bed or moving side to side (same as doing the valsalva maneuver) |
|
|
Why do you Not want a pt to use the Valsalva maneuver?
|
-decreases venous return and cardiac output
-when the strain is released, venous return and cardiac output immediately increase & systolic B/P rise. These pressure changes produces a reflex Bradycardia and decrease B/P that can lead to sudden cardiac death in client w/ heart disease |
|
|
Step for CPR?
|
1. check for a response
2. look, listen and feel 3. start cpr, Give 2 breaths, 4 check for Pulse, if No Pulse Start Compression 30:2 ratio |
|
|
Nursing interventions to prevent DVT:
|
-OOB asap
-teach leg, foot and ankle exercise -position changes (pedal pumps-say alphabet, a-z while alternating foot w/ each letter( plantar flexion, dorsiflextion) -apply TED hose (promotes venous return) - remove & reapply at least twice a day -Admin Anticoagulant (heparin, Lovenox) -Apply SCD's (sequential compression devices) or IPC they decrease venous stasis by increasing venous return: inflat for 10-15 s and deflat for 45 to 60 sec using 40mm/Hg of pressure -Perform Homan's sign q 8 hours -ROM exercises- -Teach client to avoid crossing the legs, sitting for prolonged periods of time, wearing clothing that constricts the legs or waist, putting pillows under the knees & massaging the legs |
|
|
**Drug used in the prophylaxis of DVT?
|
LOVENOX (low molecular weight heparin, LMWH)
|
|
|
**Dosage and directions for given Lovenox?
|
*dosage: *1mg/kg
-common:30mg to 40mg subcut 2 hours before surgery and continued throughtout the postoperative period *prefilled syringes *will see bubble of air in syringe=DO NOT squeeze the bubble out (want bubble to be at the top to push in pt) -bubble/Air lock prevents bruising |
|
|
When do you contact primary care/heath care provide if assessment data indicates DVT?
|
-Immediately
|
|
|
Delegation Considerations for TED hose?
|
-apply Ted hose can be delegated
-nurse is responsible for assessing circulation to the lower extremities *Instruct NA to notify nurse if client develops leg pain or discoloration |
|
|
Delegation considerations for SCD's
|
-applying SCD's can be delegated
-Nurse is responsible for assessing circulation in the extremities *Instruct NA to notify nurse if -complains of leg pain -discoloration develops in extremites |
|
|
When do you NOT apply apply TED hose for DVT?
|
-local conditon affecting the leg
Ie. any skin lesion, gangrenous condition or recent vein ligation b/c application compromises circulation |
|
|
Antiembolic exercises
|
-knee flexion involving alternately extedning and flexing the knee
-need to be done hourly while awake -help to prevent DVT |
|
|
Exercises that help prevent Thrombophlebitis ?
|
-ankle pump/ calf pumps
-foot circles -knee flexion |
|
|
Swelling (inflammation) of a vein caused by a
blood clot |
Thrombophlebitis
|
|
|
ISOMETRIC EXERCISE
|
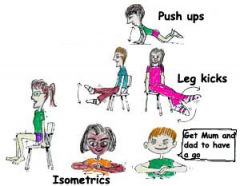
type of strength training in which the joint angle and muscle length do not change during contraction (compared to concentric or eccentric contractions, called dynamic/isotonic movements). Isometrics are done in static positions, rather than being dynamic through a range of motion. The joint and muscle are either worked against an immovable force (overcoming isometric) or are held in a static position while opposed by resistance (yielding isometric
|
|
|
DISUSE OSTEOPORSIS
|
form of osteoporosis which occurs characteristically in patients with immobilized limbs secondary to fracture or paralysis
-at risk for pathological fractures |
|
|
OSTEOPOROSIS
|
Osteoporosis is the thinning of bone tissue and loss of bone density over time.
Symptoms There are no symptoms in the early stages of the disease. Symptoms occurring late in the disease include: Bone pain or tenderness Fractures with little or no trauma Loss of height over time Low back pain due to fractures of the spinal bones Neck pain due to fractures of the spinal bones Stooped posture |
|
|
JOINT CONTRACTURE
|
-abnormal and possibly permanent condition characterized by fixation of teh joint
-Caused by Disuse, Atrophy and Shortening of the muscle fibers -may leave joint in a nonfunctional position -can begin to form after 8 hrs of immobility in older adults |
|
|
FOOTDROP
|
permanently fixed in a Plantar Flexion
-can Not dorsiflex the foot -Unable to lift toes off the ground -CVA & hemiplegia are at risk |
|
|
HEMIPLEGIA
|
condition in which half of a body is paralyzed. Hemiplegia is more severe than Hemiparesis, wherein one half of the body is weakened but not paralysed
|
|
|
Nursing Intervention for Musculoskeletal system:
|
-AROM/ PROM exercises (2 to 3 x's a day
-Monitor Ca intake -teach to perform ROM while bathing, eating, grooming and dressing -early ambulation -CPM (continuous passive motion)= moves an extremity to prescribed angle for a prescribed period, beneficial when the client must gradually increase the degree and duration of flexion and extension, used in orthopedic conditions after surgery -wt shifts in wheelchair q 15 mins |
|
|
PRESSURE ULCER
|
impairment of the skin as a result ofprolonged ischemia (decreased blood supply) in tissues
|
|
|
When does Ischemia develop?
|
-when the pressure on the skin is greater than the pressure inside the small peripheral blood vessels supplying blood to the skin
*older adult can develop skin breakdown w/in 3 hrs |
|
|
Where is edema assessed?
|
-sacral area
-calfs |
|
|
URINARY STAsIS
|
when urine sits in the bladder for a longer period of time allowing bacteria to multiply in the bladder
increases risk for UTI and renal calculi |
|
|
RENAL CALCULI
|
-calcium stones that lodge in the renal pelvis or pass through the ureters
*immobilized clients are at risk for calculi b/c of Hypercalcemia |
|
|
When does urinary output start to decline?
|
-about the 5th or 6th day after immobilization
-urine becomes concentrated, increases the risk for UTI and calculi |
|
|
Urinary tract is contaminated by what bacteria?
|
-Escherichia Coli
|
|
|
Peristalsis
|
wave-like contractions that move food along the digestive tract
|
|
|
Cathartics
|
substance that expels material from or cleanses the gastrointestinal tract
-causing bowel evacuation, usually of liquid feces |
|
|
Nursing Inverventions for Skin
|
-shift wt q 15 mins
-turn client q 1 to 2 hours -limit sitting in chair to < 2 hr -monitor nutritional intake |
|
|
Assess bladder by:
|
palpation
|
|
|
A full bladder feel?
|
Round
-can hold up to 2L |
|
|
Assessment for Elimination:
|
-I & O q 8 hrs
-bowel sounds q8 hrs -consistency of BM's -bladder distention |
|
|
Autonomic Dysreflexia
|
-means an over-activity of the Autonomic Nervous System. It can occur when an irritating stimulus is introduced to the body below the level of spinal cord injury, such as an overfull bladder.
-also known as hyperreflexia, is a state that is unique to patients after spinal cord injury at a T-5 level and above. **S/S hypertension, HA, pallor |
|
|
Aredia
|
drug,
-indicated for the treatment of moderate or severe hypercalcemia associated with malignancy, with or without bone metastases |
|
|
Where do you look to assess Urine, w/ a client who has a catheter?
|
Look in the Tube NOT the bag!!
|
|
|
Psychosocial changes associated w/ Immobility?
|
-depression
-alteration in self-concept & anxiety -behavioral changes-withdrawal, altered sleep/wake pattern(laying in bed all the time, not knowing if it's night or day), hostility, inappropriate laugher, and passivity -altered sensory perception -inaffective coping, resulting in confusion, disorientation -can lead to sensory alterations |
|
|
Depression:
|
exaggerated feelings of sadness, melancholy, jejection, worthlessness, emptiness and hopelessness out of proportion to reality
-results from worrying about present/future levels of health, finances, and family needs -worrying increases the clients depression, causing withdrawal |
|
|
Contraindications for ROM:
|
-Don't do if pt needs to conserve energy (cardiac pt)
-cardiac distress -respiratory distress -swollen, inflammed or injured joints **If in doubt, Ask MD |
|
|
When do you start ROM w/ a stroke pt?
|
-Start PROM immediately
|
|
|
Principles R/T ROM Exercises:
|
-joints exercised sequentially (neck to toes)
-move the body part to stretch the muscle, keep the joint flexible -support extremity above and below the joint -ROM of helpless/immobile should be done @ least BID, more often if tolerated or needed -Do Not grasp fingernails/toenails -work from proximal to distal(work from in to out) joints of extremity |
|
|
If pt has been OOB, what is the principle for applying TED hoses?
|
-have pt lie down and elevate legs 15 to 30 mins before applying
-prevents fluid from getting trapped |
|
|
Orthopnea
|
-client w/ respiratory d/o sometimes assumes a posture of leaning on the table in front of the chair in attempt to breath more easily
|
|
|
ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENTS:
|
-used when assessing metabolic functioning to evaluate muscle atrophy
-measures ht, wt & skinfold thickness -indicates losses in muscle tone and muscle mass |
|
|
Atelectatic area
|
-client's chest mvmt is often asymmetrical
|
|
|
Hazard of immoblity of cardio system, when a pt is laying down?
|
-lying down increases cardiac workload and results in an increased pulse rate
|
|
|
EMBOLUS
|
-dislodged venous thrombus
- blood clot that moves through the bloodstream until it lodges in a narrowed vessel and blocks circulation. 90% of all Pulmonary emboli begin in deep veins of lower extremities |
|
|
What is used to measure ROM?
|
-gonimeter
|
|
|
Braden Scale
|
score a patient/client's level of risk for developing pressure ulcers. It measures functional capabilities of the patient that contribute to either higher intensity and duration of pressure or lower tissue tolerance for pressure. Lower levels of functioning indicate higher levels of risk for pressure ulcer development.
- rating scale made up of six subscales scored from 1-4 (1 for low level of functioning and 4 for the highest level or no impairment). |
|
|
Dehydration increases the risk for:
|
-skin breakdown
-thrombus formation -respiratory infections -constipation |
|
|
Inadequate I & O increases risk for:
|
-renal system impairment (recurrent infections to renal failure)
|
|
|
Abrupt changes in personality have a physiological cause such as:
|
-surgery
-medication reaction -pulmonary embolus -acute infection |
|
|
Is acute confusion in older adult normal or not normal?
|
-Not Normal
|
|
|
Common reactions to immobilization include:
|
-boredom
-feelings of isolation -depression and -anger **listen carefully to family if they report emotional changes -family is a key resource for info about behavior changes |
|
|
Disuse Syndrome
|
-applies to immobile clients who are at risk for multisystem problems
-term that encompasses similar concepts and includes nursing diagnoses related to inactivity. Risks for disuse syndrome include impaired skin integrity, constipation, altered respiratory function, altered peripheral tissue perfusion, activity intolerance, impaired physical mobility, injury, altered sensory perception, powerlessness, and body image disturbance. |
|
|
What nursing interventions can a nurse delegate to a NA?
|
-encourage client to do leg exercises
-encourage use of incentive spirometer -encourage cough and deep breath -NA's may turn and position client -apply TED hose -Assist nurse w/ measurements of leg circumferences -ht -wt |
|
|
When a pt is immobilized, Vitamin B complex is needed for:
Vitamin C |
-skin integrity and wound healing
-necessary to replace protein stores |
|
|
Total Parenteral nutrition refers to:
|
-delivery of nutritional supplements through a central or peripheral intravenous catheter
|
|
|
Enteral Feedings include:
|
-delivery through a nasogastric, gastrostomy or jejunostomy tube of high-protein, high-calorie solutions w/ vitamins, minerals and electrolytes
|
|
|
Sedentary lifestyle
|
lack of physical exercise/activity
|
|
|
Completing a puzzle helps a child to develop:
|
-Fine motor skills
|
|
|
Reading helps a child to develop:
|
-cognitively
|
|
|
What types of pt's need assistance in position changes?
|
-impaired nervous, skeletal, or muscular system functioning
-increased weakness -increased fatigability |
|
|
TROCHANTER ROLL
|
-prevents external rotation of the hips when client is in a supine position
|
|
|
TRAPEZE BAR:
|
allows client to pull w/ upper extremities to raise the trunk off the bed
-assist in transfer from bed to wheelchair -perform upper arm exercises -increases independence' -maintains upper body strength -decreases the shearing action from sliding across or up and down in bed |
|
|
Hand splint wrist:
|
-maintains proper alignment of thumb (slight adduction) and the wrist (slight dorsiflexion)
-use only on client which the splint was made for |
|
|
Handrolls:
|
maintains the thumb in a slight adduction and in opposition to the fingers
|
|
|
Positioning pt's prevent:
|
-muscle discomfort
-pressure ulcers -damage to superficial nerves -blood vessels -contractures |
|
|
Fowlers position:
|
head of bed elevated at a 45 to 60% angle
|
|
|
INSTRUMENTAL ACTIVITES OF DAILY LIVING (IADL's):
|
skills such as shopping,
-preparing meals -banking -taking meds |
|
|
ADL's
|
relate to physical self care
-grooming -eating -toileting -transferring |
|
|
What is done prior to ambulating a client?
|
1. assess activity tolerance, strength, pain and coordination, balance
-Pulse/Resp 2. explain expectations-how far to walk, why activity is important, when walk will occur 3. check enviroment for obstacles 4. establish resting points 5. dangle before ambulating 6. document pt response to activity |
|
|
Delegating effective transfer tech to a NA?
|
-can be delegated expect clients who are being transferred for the 1st time after prolonged bed rest, extensive surgery, critical illness or spinal cord trauma = *Required supervision by Nurse
- |
|
|
HEMIPLEGIA
|
-one-sided paralysis
|
|
|
HEMIPARESIS:
|
-One sided weakness
|
|
|
Client mvmt Algorithms:
|
serves as assessment tools and guide safe client handling and mvmt
|
|
|
Crutches:
|
-elbow slightly flexed at 30 degree w/ wt in the palms of hands
-complications: crutch palsy -can damage axilla *upstairs: good leg goes up 1st *downstairs: bad leg goes down 1st |

