![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Moore's Law |
Because of this, the cost of data communications and data storage is essentially zero. |
|
|
1. Abstract Reasoning 2. Systems Thinking 3. Collaboration 4. Ability to Experiment |
4 Skills Needed |
|
|
Abstract Reasoning |
Ability to make and manipulate models. |
|
|
Systems Thinking |
Ability to model the components of a system, to connect inputs and outputs among those components into a sensible whole that reflects the structure and dynamics of the phenomenon observed. |
|
|
Collaboration |
Activity of 2 or more people working together to achieve a common goal, result, or work product. |
|
|
Experimentation |
Making a reasoned analysis of an opportunity, envisioning potential solutions, evaluating those possibilities, and developing the most promising ones, consistent with the resources you have. |
|
|
System |
A group of components that interact to achieve some purpose. |
|
|
Information System (IS) |
A group of components that interact to produce information. |
|
|
1. Hardware 2. Software 3. Data 4. Procedures 5. People |
Five-Component Framework |
|
|
Management Information Systems (MIS) |
The management and use of information systems to help businesses achieve their strategies. |
|
|
Management (in MIS) |
To develop, maintain, and adapt. |
|
|
Information Technology (IT) |
The products, methods, inventions, and standards that are used for the purpose of producing information (hardware, software, and data). |
|
|
1. 10+ characters 2. does not contain your user name, real name, or company name 3. does not contain a complete dictionary term 4. is different from previous passwords used 5. contains both upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special characters |
A strong password has: |
|
|
Business Process |
A network of activities for accomplishing a business function. |
|
|
Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) |
An international standard for creating business process diagrams. |
|
|
Swimlane Format |
A graphical arrangement in which all of the activities for a given role are show in a single vertical or horizontal lane. |
|
|
Activities |
Specific tasks that need to be accomplished as part of the process |
|
|
Role |
A subset of the activities in a business process that is performed by actors. |
|
|
Actor |
A person, group, department or organization. |
|
|
1. Start 2. End 3. Activity (describes what you're going to do (also a square)) 4. Data Repository (do this, do that) 5. Questions to ask (what the system actually does) |
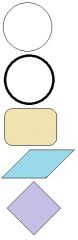
What do each of these mean in a BPMN? |
|
|
Repository |
A collection of data that is stored within the business process (computer databases, collections of files). |
|
|
Data Flows |
Represent movement of data from one activity to the next. |
|
|
Sequence Flows |
The next action to perform. |
|
|
Effective Business Process |
Enables the organization to accomplish its strategy. |
|
|
Efficiency |
The ratio of benefits to costs |
|
|
Actors: Hardware and people Instructions: Software and procedures Bridge: Data |
Who are the actors, instructions, and bridges in the 5-component model? |
|
|
Information |
The knowledge derived from data. |
|
|
Data |
Recorded facts or figures. |
|
|
1. Accurate 2. Timely 3. Relevant 4. Just barely sufficient 5. Worth its cost |
Critical Data Characteristics: |
|
|
Industry Structure > Competitive Strategy > Value Chains > Business Processes > Information Systems |
Planning Processes: |
|
|
Helps organizations determine the potential profitability of an industry.
Competitive forces: -Competition from vendors and substitutes -Competition from new competitors -Competition from existing rivals
Bargaining Power forces: -Bargaining power of suppliers -Bargaining power of customers |
5 Forces Model (Porter) |
|
|
1. Cost 2. Differentiation 3. Industry-Wide 4. Focus |
Competitive Strategy's 4 Components |
|
|
TRUE |
True or False: To be effective, the organization's goals, objectives, culture, and activities must be consistent with the organization's strategy. |
|
|
Value |
The amount of money that a customer is willing to pay for a resource, product, or service. |
|
|
Margin |
The difference between the value that an activity generates and the cost of the activity. |
|
|
Value Chain |
A network of value-creating activities (5 primary, 4 support), each stage adds costs and value to the product. |
|
|
Primary Activities |
Business functions that relate directly to the production of the organization's products or services. |
|
|
Support Activities |
Business functions that assist and facilitate the primary activities. |
|
|
Linkages |
Interactions across value activities. |
|
|
Product Implementations: 1. Create new product or service 2. Enhance product or service 3. Differentiate product or service Process Implementations: 4. Lock in customers and buyers 5. Lock in suppliers 6. Raise barriers to market entry 7. Establish alliances 8. Reduce costs |
8 Principles of Competitive Advantage |
|
|
Switching Costs |
Making it difficult or expensive for customers to switch to another product. |
|
|
Hardware |
Electronic components and related gadgetry that input, process, output, and store data according to instructions encoded in computer programs or software. |
|
|
Keyboard, mouse, document scanners, bar-code scanners, microphones, cameras, tablet PCs, handwriting, magnetic ink readers, scanners. |
Types of Input Hardware: |
|
|
Central Processing Unit (CPU) |
Sometimes called the "brain" of the computer, selects instructions, processes them, performs arithmetic and logical comparisons, and stores results of operations in memory (processing unit). |
|
|
Main Memory |
RAM |
|
|
Video displays, printers, audio speakers, overhead projectors, flatbed plotters. |
Types of Output Hardware: |
|
|
Storage Hardware |
Saves data and programs; magnetic disks are common |
|
|
Universal Serial Bus (USB) |
Simplify the connections of peripheral gear to computers for both manufacturers and users. |
|
|
Binary Digits (bits) |
A zero or one; used for computer data because they are easy to represent physically. |
|
|
Bytes |
8-bit chunks. |
|
|
Data Channel (bus) |
How instructions move from main memory into the CPU. |
|
|
Cache |
A small amount of very fast memory in the CPU. |
|
|
Operating System (OS) |
A program that controls the computer's resources. |
|
|
Memory Swapping |
If there is not enough main memory, it will remove something and replace it with the newly requested program or data. |
|
|
32: less capable, cheaper, up to 4GB of memory
64: more main memory, 4+GB memory, expensive |
32-bit vs. 64-bit |
|
|
Volatile |
Contents are lost when the power shuts off (cache and main memory). |
|
|
Nonvolatile |
Contents are not lost when power is shut off (magnetic and optical disks). |
|
|
Client |
Computers used for word processing, spreadsheets, database access, have software that enables network connection. |
|
|
Servers |
Provide service; can process email, web sites, large/shared databases; fast and usually have multiple CPUs, lots of main memory 4+GB, very large disks 1+TB; limited or no video displays, no keyboards. |
|
|
Server Farm |
Servers organized into a collection of servers. |
|
|
Metro-Style Applications |
Touch-screen oriented and provide context-sensitive pop-up menus. |
|
|
Virtualization |
Process by which one computer hosts the appearance of many computers. |
|
|
Host Operating System |
Runs one or more operating systems as applications (physical computer and operating system) |
|
|
Virtual Machines (VM) |
Hosted operating systems. |
|
|
PC Virtualization |
A personal computer with several different operating systems. |
|
|
Server Virtualization |
A server computer hosts one+ othe rserver computers |
|
|
Desktop Virtualization |
A server hosts many versions of desktop operating systems (each desktop has complete user environment and appears as a PC) |
|
|
License |
The right to use a program but not purchase it. |
|
|
Site License |
A flat fee that authorizes the company to install the product on all company computers. |
|
|
Application Software |
Software that runs on top of the operating system and performs particular services and functions. |
|
|
Horizontal-Market Application |
Software that provides capabilities common across all organizations and industries (word processors, graphics programs; off the shelf) |
|
|
Vertical-Market Application |
Software that serves the need of a specific industry (can be altered or customized; customer billing program) |
|
|
One-of-a-Kind Application |
Software developed for a specific, unique need (IRS) |
|
|
Desktop Program |
A program that does not need to connect to any servers and only runs on your computer (Adobe Photoshop). |
|
|
Client-Server Applications |
Applications that process code on both the client and server. |
|
|
Thick-Client Application |
Application program that must be preinstalled on the client. |
|
|
Thin-Client Application |
Application program that runs within a browser and does not need to be preinstalled. |
|
|
Off-the-Shelf Software |
Types of horizontal applications |
|
|
Off-the-shelf with alterations software |
Can be horizontal and/or vertical applications |
|
|
Custome-Developed Software |
Like one-of-a-kind applications |
|
|
Firmware |
Computer software that is installed into devices such as printers, print servers, and various types of communication devices. |
|
|
GNU/GPL |
Open source agreement created by Stallman |
|
|
Source Code |
Computer code written by humans and that is understandable by humans. |
|
|
Machine Code |
Source code compiled that is processed by a computer. |
|
|
Closed Source |
Source code is highly protected and only available to certain people. |

