![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
PTH: increased Ca: increased P: decreased |
1⁰ hyperparathyroidism |
|
|
|
PTH: increasedCa: decreased or normalP: Markedly high |
2⁰ hyperparathyroidism |
|
|
|
PTH: increasedCa: decreasedP: increased |
Pseudohypoparathyroidism |
|
|
|
PTH: decreased to absentCa: decreased P: decreased |
1⁰ hypoparathyroidism |
|
|
|
PTH: decreasedCa: increased OR decreasedP: decreased |
2⁰ hypoparathyroidism |
|
|
|
What is the normal range of serum calcium? |
8.6 - 10.3 mg/dl |
|
|
|
What is the normal range of ionized calcium? |
1.16- 1.21 mmol/L |
|
|
|
What is the normal rage of phosphorous? |
2.8 - 4.5 mg/dL(adult) |
|
|
|
Increased anion gap is associated with.. |
Metabolic acidosis |
|
|
|
Salicylic acid or poison will cause.. |
Metabolic acidosis |
|
|
|
Increased pCO2 is a sign of.. |
Hyperventilation |
|
|
|
What is the process of collecting blood gas samples? |
, ensure patient is calm and breathing stable for 15 min (30 for artificial air), collect from artery or vein (< 2 min tourniquet), use heparin gel to centrifuge and separate, If collected in glass =2 hr stability, place in ice/eater slurry If plastic = test immediately |
|
|
|
What electrode used a buffer solution to calibrate? |
pH |
|
|
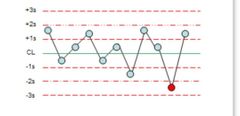
What is the violation? |
1:2s |
|
|
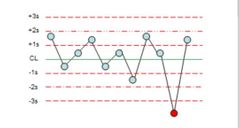
What is the violation? |
1:3s |
|
|
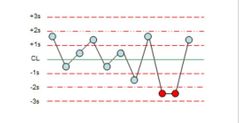
What is the violation? |
2:2s |
|
|
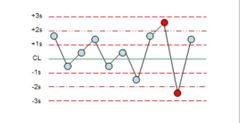
What is the violation? |
R4s |
|
|
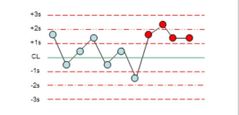
What is the violation? |
4:1s |
|
|
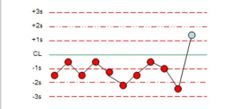
What is the violation? |
10x |
|
|
|
What is the equation for osmolality? |
2[Na]+([glucose]/18)+([Urea or BUN]/2.8) |
|
|
|
How do you convert mg/dl to mEq/L? |
((mg)(valence electrons)/(atomic weight))/ 0.1 |
|
|
|
How many valence electrons does sodium have? Atomic weight? |
V= 2 Mass = 22.9 |
|
|
|
How many valence electrons does chloride have? Atomic mass? |
V= 7 Mass= 35.45 |
|
|
|
What deficiencies can cause tetany? (Spasm) |
- low calcium (common) - low magnesium - low potassium - (alkalosis) |
|
|
|
What is likely if.. BUN : increased Creatinine: normal Ammonia: high |
?? |
|
|
|
In hyperchloremia states with normal Sodium, the patient will experience.. |
Metabolic Acidosis |
Chloride is = [H] |
|
|
In states of hypochloremia.. the patient will experience.. |
Metabolic Alkalosis |
Chloride = [H] |
|
|
In metabolic acidosis, the [HCO3]/apCO2 is.. |
<20 (acidosis = less bicarb!) |
|
|
|
In metabolic alkalosis, the [HCO3]/apCO2 is.. |
>20 ( more bicarb!) |
|
|
|
What is the normal range of osmolality in serum? |
285 - 295 mOsm/L |
|
|
|
What is the normal range of osmolality in a 24 hr urine? |
500 - 800 mOsm/L |
|
|
|
What does a urine osmolality of >1200 indicate? |
Dehydration (think of it as more solutes/particles) |
|
|
|
What does a urine osmolality of <50 indicate? |
Over hydration (think of it as LESS particles/diluted) |
|
|
|
What is the calculated osmolality if you want mg/dl? |
2[Na]+ [Glucose]/18 +[Urea]/2.8 |
|
|
|
What is the calculated osmolality if you want mg/dl and youre given BUN instead of urea? |
2[Na]+ [Glucose]/18 + ([BUN] /2 )/2.8 |
BUN = 2X Urea |
|
|
How do you calculate the osmol gap? |
(Measured mOsm/kg)-(Calculated mOsm/kg) |
|
|
|
What does an elevated osmol gap indicate? |
Presence of volatile substances, such as alcohols (ex: ethanol is 80 mOsm/kg, which would drastically increase the measured) |
|
|
|
What is the major blood buffer? |
Hemoglobin |
|
|
|
What is the immediate buffer for blood? |
Bicarbonate |
|
|
|
Formula for TCO2 |
CO2(dissolved) + [HCO3] + [H2CO3] |
|
|
|
Formula for [HCO3] |
TCO2 - (0.0301)(pCO2) |
a = Brunson’s constant = 0.0301 |
|
|
Which direction would the oxygen dissociation curve shift if.. Low pH |
Right shift (more pCO2) |
Co2 +H2O <-> H2CO3 <-> H + HCO3 More H = .... |
|
|
Which direction would the oxygen dissociation curve shift if..High pH |
Left shift |
Co2 +H2O <-> H2CO3 <-> H + HCO3Less H = .... |
|
|
What are the results of a right shift on an oxygen dissociation curve? pCo2 = pH= Temp = 2,3-DPG = O2 affinity = |
pCo2 = increasedpH= decreasedTemp = increased 2,3-DPG = increased O2 affinity = decreased |
"Tense in the tissues" |
|
|
What are the results of a left shift on an oxygen dissociation curve?pCo2 =pH= Temp = 2,3-DPG =O2 affinity = |
pCo2 = decreasedpH= increasesTemp = decreased 2,3-DPG = decreasedO2 affinity = increased |
|
|
|
Normal range of pCO2 |
35-45 mmHg |
|
|
|
Normal range of HCO3 |
22-26 mEq/L |
|
|
|
Normal range of pO2 |
75 - 100 mmHg |
|
|
|
Aldosterone is produced in... |
The Zona Glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex |
|
|
|
Cortisol is produced in the .. |
Zona Fasciculata of the adrenal cortex |
|
|
|
17 hydroxysteroid is a test to determine levels of... |
CORTSOL! (Also called 17 hydroxycorticosteroid) |
|
|
|
17 hydroxysteroid is a test to determine levels of... |
CORTSOL! (Also called 17 hydroxycorticosteroid) |
|
|
|
17 ketosteroid is used to measure... |
Testosterone and adrenal steroid hormone |
|
|
|
When arecortisol blood tests drawn? |
Morning. At its peak! |
|
|
|
What electrolyte deficiencies can cause tetany? |
Potassium and calcium |
|
|
|
Cause of osteoporosis |
Decreased calcitriol response (due to aging) |
|
|
|
Cause of osteomalacia |
Decreased vitamin D |
|
|
|
Cause of otitis fibrosa |
Elevated PTH (1⁰ hyperparathyroidism and chronic renal disease) |
|
|
|
Cause of paget's disease |
Increased osteoclast/osteoblast activity causing bone remodeling |
|
|
|
What are the unique lab results of someone with paget's disease? |
PTH, ca. And P normal.. but Alkaline Phosphatase elevated |
|
|
|
What anticoagulants can NOT be used for magnesium tests? |
EDTA. citrate, and oxalate since they chelate magnesium |
|
|
|
What deficiencies cause tetany? |
Magnesium and calcium |
|
|
|
What relationship does magnesium and calcium have? |
Direct [x]=[x] In serum |
|
|
|
What relationship does phosphorus and calcium have? |
INVERSE!!! |
|
|
|
What two elements make up bone matrix's hydroxyapatite? |
Phosphorus and calcium |
|

