![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Binary fission is the process by which bacteria divide. A parent cell produces extra copies of the chromosome and ribosomes and produces the precursors for forming materials such as peptidoglycan and phophlipids. This produces an exact replicate known as a clone.
Chromosomal DNA attaches to membrane. Membrane increase in length. DNA is replicated and partitioned. New cell wall is synthesized. Daughter cells are formed. |
____ is the process by which bacteria ____. A parent cell produces extra copies of the ____ and ____ and produces the ____ for forming materials such as ____ and ____ . This produces an exact replicate known as a ____.
____ attaches to membrane. ____ increase in length. DNA is ____ and ____. New ____ is synthesized. ____ cells are formed. |
|
|
Conservation of Energy:
The amount of ATP in a cell is limited, and it must be replaced continually to maintain repair and growth. This is achieved by using the energy liberated during the oxidative stages of catabolism to synthesize ATP from ADP and phosphate. The synthesis of ATP linked to catabolism occurs by two distinct mechanisms: substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative, or respiratory-chain, phosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation is the major method of energy conservation under aerobic conditions in all nonphotosynthetic cells. |
Conservation of Energy:
The amount of ____ in a cell is ____ , and it must be replaced continually to maintain ____ and ____. This is achieved by using the energy ____ during the ____ of catabolism to synthesize ____ from ____ and ____. The synthesis of ____ linked to catabolism occurs by two distinct mechanisms: ____ phosphorylation and ____, or ____ phosphorylation. ____ is the major method of energy conservation under ____ conditions in all ____ cells. |
|
|
Diffusion is the net movement of molecules or ions from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
|
____ is the net movement of ____ or ____ from an area of ____ concentration to an area of ____ concentration.
|
|
|
Bacteria do not have directional movement, the ability to move directly from one place to another. They move instead in a random pattern known as run and tumble.
Run is movement in a straight line while tumbles are used to make directional corrections. |
Bacteria do not have ____, the ability to move ____. They move instead in a ____ known as ____.
____ is movement in a straight line while ____ are used to make directional ____. |
|
|
Endosymbiosis is the theory by which bacteria were ingested by eukaryotic cells and continue to function in eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria and chloroplasts had their origins from bacterial endosymbionts.
|
____ is the theory by which bacteria were ____ by ____ and continue to function in ____ cells. ____ and ____ had their origins from bacterial ____.
|
|
|
Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a permeable membrane (cell membrane). Water passes through the membrane in an attempt to equalize the concentration of solute (salts and/or sugars dissolved in the water), which cannot pass through the membrane, on both sides of the membrane.
|
____ is the diffusion of ____ through a permeable membrane (____). Water passes through the ____ in an attempt to ____ the ____ of solute (____ ), which ____ through the membrane, on ____ of the membrane.
|
|
|
Phagocytosis is the ingestion of bacteria and other particles by a cell, usually a white blood cell. Capsules found on pathogens help prevent the phagocytosis of the organism.
|
____ is the ingestion of ____ and other ____ by a cell, usually a ____. ____ found on pathogens help prevent the ____ of the organism.
|
|
|
Sporulation is the process bacteria undergo to form spores or endospores. The most clinically-significant sporeformers are Gram positive rods in the genera Bacillus and Clostridium.
|
____ is the process bacteria undergo to form ____ or ____ . The most clinically-significant ____ are Gram ____ rods in the genera ____ and ____.
|
|
|
Transcription is the process of making a complimentary copy of mRNA to DNA so "the code" or message is passed, or transcribed from DNA to mRNA. It takes place in the nucleus of a cell.
|
____ is the process of making a ____ of ____ to DNA so "the code" or ____ is passed, or ____ from ____ to mRNA. It takes place in the ____ of a cell.
|
|
|
Translation is the use of mRNA as a template in the synthesis of proteins where mRNA is used to produce a chain of amino acids. It takes place in the ribosomes of a cell.
|
____ is the use of ____ as a template in the synthesis of ____ where ____ is used to produce a ____. It takes place in the ____ of a cell.
|
|
|
Principal differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
|

|
|
|
Cell Image
|

|
|
|
Eukaryotic cell membrane
|

|
|
|
Prokaryotic cell image
|

|
|
|
Components of a bacterial cell
|
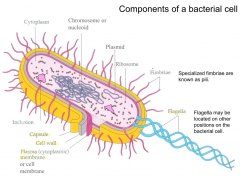
|
|
|
Gram positive/negative cell wall image
|

|
|
|
Run and tumble image
|

|
|
|
Sporulation Image
|

|
|
|
Cell arrangment and morphology image
|

|
|
|
Some bacteria can arrange themselves into patterns. Typical patterns include pairs (di), clusters (staph), or chains (strept).
|
Some bacteria can ____ themselves into ____ . Typical patterns include ____ (____), ____ (____), or ____ (____).
|
|
|
Bacillus is a long narrow cell which is often described as rod-shaped. They can be arranged in single, pairs, or in chains.
|
____ is a long narrow cell which is often described as ____. They can be arranged in ____, ____, or in ____.
|
|
|
Biofilm is a microbial community that usually forms as a slimy layer on a surface. Fimbriae help provide attachment and play a role in the formation of biofilms.
|
____ is a microbial community that usually forms as a ____ on a ____. ____ help provide ____ and play a role in the ____ of ____.
|
|
|
Chemotaxis is the process in which bacteria are stimulated to move by chemicals in the solution in which the bacteria live.
|
____ is the process in which bacteria are ____ to ____ by chemicals in the ____ in which the bacteria live.
|
|
|
Coccus is a spherical or ovoid shaped bacterium. They can be arranged in clusters (staph), chains (strept), or pairs (diplo)
|
____ is a spherical or ovoid shaped bacterium. They can be arranged in ____ (____), ____ (____), or ____ (____)
|
|
|
Most deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules are double-stranded helices, consisting of two long biopolymers made of simpler units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nucleobase (guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine), as well as a backbone made of alternating sugars (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups, with the nucleobases (G, A, T, C) attached to the sugars.
|
Most ____ (____) molecules are double-stranded helices, consisting of two long ____ made of simpler units called ____. Each ____ is composed of a ____ (____ , ____ , ____ , and ____ ), as well as a backbone made of ____ (____ ) and ____, with the ____ attached to the ____.
|
|
|
Spores have little or no metabolic or biochemical activity so they can be described as dormant. When the environmental conditions are favorable for growth, the spore will germinate to develop into a metabolically active vegetative cell.
|
____ have little or no metabolic or ____ activity so they can be described as ____. When the ____ are favorable for growth, the spore will ____ to develop into a ____ vegetative cell.
|
|
|
Electron transport chain is a series of compounds that transfer electrons from one compound to another, generating ATP by oxidative phosphorylation.
|
____ is a series of compounds that ____ from one compound to another, generating ATP by ____.
|
|
|
A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solutes than an isotonic solution and causes a cell to shrink as the water leaves a cell.
|
A ____ solution has a higher concentration of solutes than an isotonic solution and causes a cell to ____ as the water ____ a cell.
|
|
|
Glycocalyx is present as a capsule or slime layer in prokaryotic cells. It can be present in some eukaryotic cells that lack a cell wall. It helps strengthen the cell surface, helps cells attach together, and may contribute to cell-cell recognition. It is composed of carbohydrates covalently bonded to proteins and lipids in the plasma membrane.
|
____ is present as a capsule or slime layer in ____ cells. It can be present in some eukaryotic cells that ____. It helps strengthen the cell ____, helps cells ____, and may contribute to ____. It is composed of ____ covalently bonded to ____ and ____ in the plasma membrane.
|
|
|
The Gram stain was developed in 1884 by Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram. It is the most useful differential stain used in the laboratory.
|
The ____ was developed in 1884 by Danish bacteriologist ____. It is the most useful ____ stain used in the laboratory.
|
|
|
A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes than an isotonic solution and causes a cell to swell as the water enters a cell.
|
A ____ solution has a lower concentration of solutes than an isotonic solution and causes a cell to ____ as the water ____ a cell.
|
|
|
An isotonic solution is a solution in which, after immersion of a cell, osmotic pressure is equal across the cell's membrane.
|
An ____ solution is a solution in which, after immersion of a cell, osmotic pressure is ____ across the cell's ____.
|
|
|
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a molecule consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide, forming the outer membrane of Gram negative cell walls.
|
____ (____) is a molecule consisting of a ____ and a ____ , forming the outer membrane of ____ cell walls.
|
|
|
The most common morphology seen in bacteria include bacilli (rod), cocci (spherical), spirochetes (corkscrew), and vibrio (comma).
Morphology is the form and structure of an organism or of a part of an organism. |
The most common ____ seen in bacteria include ____ (____), ____ (____), ____ (____), and ____ (____).
____ is the ____ and ____ of an organism or of a part of an organism. |
|
|
An organelle is a membrane-enclosed structure within eukaryotic cells including:
nucleus endoplasmic reticulum golgi complex lysosomes vacuoles mitochondria |
An ____ is a membrane-enclosed structure within ____ cells including:
____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ |
|
|
Peptidoglycan is the structural molecule of bacterial cell walls consisting of molecules N-acetylglucosamine, N-acetylmuramic acid, tetrapeptide side chain, and peptide side chain. It is the main component of the Gram positive cell wall and forms an insoluble precipitant with crystal violet and Gram iodine.
|
____ is the structural molecule of ____ consisting of molecules ____, ____, ____, and ____. It is the main component of the ____ cell wall and forms an insoluble precipitant with ____ and ____.
|
|
|
Phospholipid is a complex lipid composed of glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group.
|
____ is a complex lipid composed of ____, ____, and a ____.
|
|
|
Polyhydroxybutyrate is produced by microorganisms apparently in response to conditions of physiological stress; mainly conditions in which nutrients are limited. The polymer is primarily a product of carbon assimilation (from glucose or starch) and is employed by microorganisms as a form of energy storage molecule to be metabolized when other common energy sources are not available.
|
____ is produced by microorganisms apparently in response to conditions of ____; mainly conditions in which ____ are ____. The polymer is primarily a product of ____ (from glucose or starch) and is employed by microorganisms as a form of ____ molecule to be metabolized when other common energy sources are ____ .
|
|
|
Polysaccharide is a carbohydrate consisting of 8 or more monosaccharides joined through dehydration synthesis.
|
____ is a carbohydrate consisting of 8 or more ____ joined through ____.
|
|
|
A protein is a large molecule containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (and sulfur); some proteins have a helical structure and others are pleated sheets.
|
A ____ is a large molecule containing carbon, ____ , oxygen, and ____ (and sulfur); some ____ have a ____ structure and others are ____.
|
|
|
Ribonucleic acid is the class of nucleic acids that comprises messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA.
|
____ is the class of nucleic acids that comprises ____, ____, ____.
|
|
|
Solute is a substance dissolved in another substance.
|
____ is a substance ____ in another substance.
|
|
|
Spirochete is a corkscrew-shaped bacterium with axial filaments.
|
____ is a corkscrew-shaped bacterium with ____.
|
|
|
Svedburg unit, a unit of sedimentation, measures size, weight, and shape. The S units cannot be added with arithmetic values.
|
____, a unit of ____ , measures size, weight, and shape. The ____ cannot be ____ with arithmetic values.
|
|
|
A tetrad is a group of four cocci.
|
A ____ is a group of four cocci.
|
|
|
Vibrio is a curved or comma-shaped bacterium.
|
____ is a curved or comma-shaped bacterium.
|
|
|
Many medical terms are composed of word parts. By combining the word parts, words can be formed.
prefixes - start the word stem - word base suffix - word ending |
Many medical terms are composed of ____. By combining the ____, ____ can be formed.
____- word start ____ - word base ____ - word ending |

