![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the characteristics of mixed µ/δ agonists?
|
peptides that bind to both receptors are highly potent
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of mixed µ agonist/δ antagonists?
|
The δ antagonist action appears to suppress tolerance, physical dependence, and related side effects of µ agoninsts
- potential for the "perfect" opioid analgesic |
|
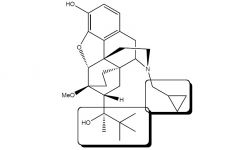
|
Buprenorphine
- µ & k partial agonist; δantagonist - pain relief; little tolerance, addiction, or resp. depression - extensive first pass 3-O-glucuronidation negates oral usage, can be taken sublingually - mixed with maloxone, cannot be ground up to be abused (method used w/ other drugs) |
|
|
In practical terms, how does a partial µ agonist such as Buprenorphine differ from a full agonist (morphine)?
|
The partial agonist may require less of the drug to reach EC50 (→more potent),
but there is a ceiling effect as a partial agonist cannot reach full effect |
|

|
Thebaine
- precursor for Buprenorphine and Etorphine |
|

|
Etorphine (Immobilon/M99)
~1000 more potent than morphine - only used for veterinary |
|
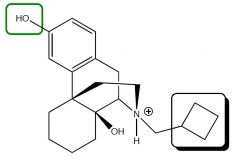
|
Butorphanol Tartrate
k agonist, µ antagonist - 5 times more potent than morphine - causes slight dysphoria, ↑ pulmonary arterial pressure and vascular resistance - less respiratory distress |
|
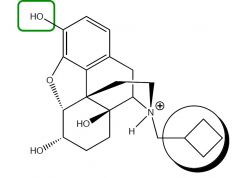
|
Nalbuphine
k agonist, µ antagonist - produces withdrawal symptoms in addicts - does not have adverse cardiovascular properties of pentazocine or butorphenol |
|
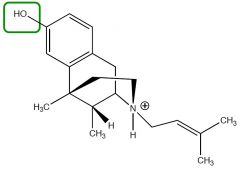
|
Pentazocine HCL and Lactate
k agonist, weak µ antagonist - 1/6 the potency of morphine - dysphoria - ↑ blood pressure |
|

|
Dezocine
µ & δ partial agonist, little effect on k - ceiling effect on respiratory depression - can be reversed with naloxone |
|

|
Diphenoxylate HCL w/Atropine Sulfate
→ Diphenoxin HCL with Atropine Sulfate weak µ agonist, reduces GI activity esterases hydrolyze the ester → 5x more potent limited CNS penetration |
|

|
Loperamide HCL
targets intestine µ receptors substrate for efflux transporter P-gp (limits amount in CNS) non-Rx |
|
|
Where does Buprenorphine come from?
|
semisynthetic from Thebaine
|
|
|
Metabolism due to free 3-OH occurs to what three molecules discussed?
|
Buprenorphine
Butorphenol Nalbuphine Pentazocine |

