![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List maternal immune/autoimmune disorders that can cause fetal/neonatal problems through passive transfer of antibodies across the placenta.
|
Hyperthyroidism (fetal hyperthyroidism)
SLE (Ro/La and fetal heart block) ITP (neonatal ITP) Myasthenia Gravis (neonatal myasthenia) Herpes gestationalis (IUFD) Anti-phopholipid antibody syndrome (IUFD) |
|
|
List ramifications of in utero DES exposure
|
Cervical insufficiency
Vaginal Adenosis Vaginal cancer T-shaped uterus Infertility |
|
|
What is a Robersonian translocation?
|
two long arms of acrocentric chromosomes (e.g. 14, 15, 16, 21) fuse (e.g. 14:21). the loss of the genetic info from the very short p arms is inconsequential, and the translocation is only an issue when it is passed on.
|
|
|
What is autonomic dysreflexia?
What can protect against it in labour? |
A spinal lesion (traumatic transection, MS, etc.) usually above T5-6 coupled with a noxious peripheral stimulus (e.g. bladder infection, cervical dilation, catheterization, labour contractions) causes sympathetic stimulation resulting in hypertension, arrhythmia, respiratory distress.
Epidural analgesia. |
|
|
What is the difference between cryoprecipitate and FFP?
|
FFP: all clotting factors (no platelets)
Cryo: concentrated for fibrinogen, factor VIII, XIII & VWF. Cryo will replace low fibrinogen more effectively but does not contain additional factors that FFP does. |
|
|
List possible indications for PGD.
|
Known heritable genetic disease in parents
Recurrent miscarriage Multiple repeat failed IVF cycles Late maternal age (From Williams Gyne) |
|
|
True or False: For appendicitis in pregnancy, the incidence of appendiceal rupture decreases with increasing gestational age.
|
False.
Increases - 8% 1T, 20% 3T (Williams OB) |
|
|
Cystic hygroma in the first trimester is most often associated with?
Cystic hygroma in the second trimester is most often associated with? |
Trisomies
Monosomy X (Turner syndrome) |
|
|
Define ARDS (according to Williams OB)
|
Studies:
Radiographic lung infiltrates PaO2:FiO2 < 200 no HF |
|
|
Pertaining to female sexual function, SSRIs cause the least problem/dysfunction with:
Desire Arousal Orgasm |
Orgasm
(SOGC guideline) |
|
|
In what situation is routine prenatal screening for toxoplasmosis recommended?
|
HIV+
|
|
|
What relatively comon cardiotropic/anti arrhythmic drug is contraindicated for treating fetal arrhythmias?
|
Amiodarone.
|
|
|
True or False:
a) gastric emptying time is delayed in pregnancy b) small & large bowel transit time is increased in pregnancy |
a) false
b) true (UTD & Williams OB) |
|
|
In what situation should Pap test screening be done in a women under the age of 21?
|
HIV+ status (ACOG)
|
|
|
Two things that cause dilation of ureters and collecting system in pregnancy
|
1) Progesterone (<14wks) - ureteral relaxation
2) External compression (gravid uterus) |
|
|
What is the most common cause of non-obstructive azospermia?
|
Klienfelter's syndrome (47XXY and variants)
|
|
|
A man has obstructive azospermia due to congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens but no pulmonary or gastrointestinal manifestations of CF - what is his likely genotype?
|
1 x major mutation (e.g. detlaF508)
1 x minor (potentially non-screened for) mutation. This insult is enough to cause absence of the vas but not obvious clinical cystic fibrosis. |
|
|
List three indications for hysterectomy for GTN
|
PSTT
Done having children Resistant to chemo, isolated uterine occurance |
|
|
List genetic conditions Ashkenazi Jewish people are more at risk of:
|
BRCA1
BRCA2 CF Tay-Sachs Canavan disease Gaucher disease Fanconi Anemia Familial dysautonomia Niemann-Pick disease Bloom syndrome Mucolipidosis |
|
|
With regards to Turner syndrome/monosomy X:
a) In what percentage of spontaneous abortions does it occur? b) In what percentage of conceptions does it occur? c) What is rate per live births? |
a) 10%
b) 1.5% c) 1/2500 |
|
|
Is the short or long arm of X chromosome linked to short stature?
|
Short
|
|
|
What agent is known to cause phocomelia?
|
Thalidomide
(absence of a bone or limb segment) |
|
|
Name three conditions/drugs associated with newborn aplasia cutis (cutis aplasia)
|
Maternal Cocaine use
Methimazole/Carbimazole T13 Johanson-Blizzard syndrome Adams-Oliver syndrome Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome |
|
|
a) What is the rosette test?
b) What can it be used for? c) What is one advantage over a Kleihauer Betke? |
a) test for fetomaternal hemorrage. Maternal blood is mixed with anti-D Ab, washed, and mixed with cells expressing cDE antigens. Rosettes form if fetal Rh+ cells are present
b) fetomaternal hemorrage (occult) c) more sensitive, not quantitative |
|
|
List obstetric or gynecologic conditions that cause hyperthyroidism
|
Transient hyperthyroidism of early pregnancy
(Complete) molar pregnancy GTN Multifetal gestation Struma Ovarii |
|
|
Patient with invasive adenocarcinoma cervix on biopsy. Examination reveals extension to sidewall and imaging shows hydronephrosis left kidney. Aspiration of a subclavicular node is positive for malignant cells.
a) What is the stage? b) What is the management? |
a) Clinical stage IIIB
b) Chemoradiation |
|
|
According to SOGC guidelines, what six components are required prior to performing anti-incontinence surgery on a woman presenting with urinary incontinence if UDs are not ordered.
|
1) Focused history
2) Pelvic examination 3) Demonstration of mobility of the urethrovesical junction (i.e., the bladder neck) 4) Objective evidence of stress incontinence (including assessment for latent stress incontinence) 5) Postvoid residual urine volume measurement 6) Urinalysis and urine culture |
|
|
What two things can intermittent auscultation not assess for?
|
a) baseline variability
b) characterization of decels |
|
|
5 coags that go up in pregnancy
|
answer
|
|
|
3 features of warfarin embryopathy
3 features of warfarin fetopathy |
answer
|
|
|
5 features of complicated variable decel
|
answer
|
|
|
Regarding emergency contraception:
a) The copper IUD can be recommended up to how many days post-coitus? b) How many women will get pregnant if the copper IUD is inserted <=5 days post-coitus? |
a) 7 (SOGC says some trials show efficacy at 7d)
b) 1-2 |
|
|
a) Give six indications for uterine artery doppler sonography
b) When should it be done (gestational age)? c) What two things should be done if it is "positive", i.e. notching is seen? |
a)
Previous IUFD Previous severe pre-eclampsia < 34wks Previous abruption Previous FGR fetus Essential/chronic HTN Current gestional HTN/pre-eclampsia Pregestational diabetes w/ end organ complications Renal disease Low PAPP-A High bhCG or AFP (>2.0 MoM) b) 17-22wks GA c) Repeat at 24-26wks Maternal AFP and bhCG <=18wks if possible If positive, refer to MFM |
|
|
Define birth/Perinatal asphyxia in one sentence.
|
Hypoxemia with metabolic acidosis
|
|
|
a) Give three RFs for maternal development of post-partum thyroiditis
b) Total T4 increases, decreases, or stays the same, in pregnancy? |
a)
Positive anti-TPO Ab (even if normal thyroid fxn) Previous PP thyroiditis DMI (25%) Quiescent Grave's disease b) Increases (TBG increases, FT4 stays essentially the same) |
|
|
A fetus has this BPP in 20min:
3 body movements 2 x flexion/extension movements 20s of breathing continuously 1x1cm empty pocket of AF Normal NST What is the risk of perinatal mortality within 7 days without intervention? |
89/1000
(BPP 6/10 with abN fluid) |
|
|
List six ultrasound findings consistent with a diagnosis of congenital varicella/fetal varicella infection in a live fetus.
|
Limb hypoplasia/defects
Microcephaly (with microgyria) Porencephaly (cysts/cavities in cerebral hemisphere) FGR Hydrops Echogenic liver, intestinal, cardiac foci (calcifications) Ventriculomegaly Chorioretinitis Cerebral cortical atrophy Hydronephrosis Splitting hydrops: ascites, polyhydramnios, placentamegaly, skin edema, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion: gets half-marks. |
|
|
For a given fetus, risk of perinatal morbidity/mortality is highest with varicella infection of a naive women:
a) First trimester b) < 20wks GA c) > 20wks GA d) Term |
Term.
(Highest risk of death (20-30%) if contracted around birth 5d before and 2 days after: neonatal varicella. Risk of congenital varicella developing is <=2%.) |
|
|
Which is incorrect regarding emergency contraception?
a) There are no absolute contraindications to the use of hormonal emergency contraception. b) Levonorgestrel 1.5mg PO once prevents >=60% of pregnancies if given <= 5days post-coitus c) If used <=24h, Levonorgestrel only (Plan B) is 95% effective in preventing pregnancy d) If Alesse is used for the Yuzpe method, 5 pills are given PO q12 x 2 e) Copper IUD, if used <=5 days post-coitus, 99/100 women will not get pregnant. |
b) Prevents >=60% of pregnancies if given <= 3days since intercourse. Hormonal contraception is most efficacious within 72h, though can be used up to 5d with less efficacy.
All from SOGC emergency contraception guideline. |
|
|
a) Explain the two cell theory of ovarian steroidogensis.
b) Preovulatory follicles (primary oocytes) are arrested at which phase of replication? c) Does Meiosis II begin before or after fertilization with sperm? d) Bonus: Call-Exner bodies are only seen pathologically in granulosa cell tumours. If not, where else? |
a) LH causes androgen (androstenedione) by theca cell, which diffuses into granulosa cell. FSH causes aromatization of androgen to estrogen.
b) Diplotene stage, Prophase I, Meiosis I c) Before. d) Granulosa cells of a developing follicle. |
|
|
Of the infectious causes of genital ulcers which are typically painful and which are typically painless (if not secondarily infected)?
|
Painful
HSV Chancroid Painless Syphilis LGV GI |
|
|
According to SOGC guidelines, with careful case selection:
a) what is the risk of perinatal mortality with vaginal delivery of a breech fetus? b) What is the risk of serious short-term neonatal morbidity? c) List five contraindications to recommending vaginal breech delivery besides general C/I to vaginal birth |
a) 2/1000
b) 2% c) Type of breech Fetal growth/EFW Attitude of fetal head d) Non-frank or complete breech presentation Cord presentation FGR or Macrosomia (<2500g; >4000g) Clinically inadequate maternal pelvis Fetal anomalies (e.g. hydrocephalus, SCT) In the guideline but not directly in the c/i section: Lack of U/S to define characteristics as above Lack of continuous monitoring in second stage Requirement for labour induction Ability to do emergent C/S Attendant skilled in neonatal resuscitation |
|
|
Patient undergoes staging procedure for suspected ovarian cancer (EOC). Washings are positive. One ovary shows capsular breech. LN are negative. There is a 1cm met on the infracolic omentum. CT scanning has not identified any other possible nodes/mets.
a) What is the stage? b) What is her approximate 5-year survival? She undergoes first line chemotherapy. c) What is the biochemical/cellular mechanism of action of the agents used for her chemotherapy d) List 3 life-threatening complications of this chemo. |
a) IIIB (<2cm extra-pelvic, intraabdominal met)
b) 40% c) Carboplatin - alkylating agent, causes crosslinks and adducts in DNA Paclitaxel - disrupts microtubule formation and function d) Neutropenia Thrombocytopenia Infusion/Hypersensitivity/Anaphylactic reaction Renal failure Entero-toxicity, malabsorption Electrolyte imbalance |
|
|
Give three non-antibiotic options to prevent recurrent UTI in post-menopausal women.
|
Vaginal estrogen
Cranberry products Acupuncture Probiotics - not enough current evidence to recommend No evidence for lifestyle modification, wt loss, increased fluids, etc. |
|
|
a) According to 2003 SOGC guidelines give two indications for surgical removal (hysterectomy) for completely asymptomatic fibroids
b) Can women on menopausal HT experience fibroid growth? c) What is the incidence (%) of leiomyosarcoma diagnosed during hysterectomy for symptomatic fibroids in women 40-50 yrs old? d) Give three risk factors on history that increases suspicion for leiomyoscarcoma. |
a)
Rapidly enlarging Enlarging post-menopause (concern for leiomyosarcoma) Uncontrollable hemorrhage b) Yes (guideline quotes RCTs) c) 1% d) age previous pelvic irradiation ethnicity (black) tamoxifen use |
|
|
Four factors which increase the risk for fluid absorption during hysteroscopic myomectomy
|
SOGC fibroid guideline:
Intrauterine pressure Size of the cavity Length of the procedure Vascularity of the myoma/endometrium Not using a fluid management system |
|
|
Give six absolute or relative contraindications to uterine fibroid embolization.
|
Absolute:
pregnancy desiring pregnancy unwilling to consider hysterectomy (may need emergently) active genitourinary infection active genitourinary malignancy reduced immune status severe vascular disease limiting access radiographic contrast media allergy impaired renal function Relative: Sub-mucosal and pedunculated fibroids previous internal iliac or uterine artery occlusion recent GnRH analogue administration |
|
|
Confirmation of:
I) antibiotic prophylaxis administration, and II) venous thromboembolism prophylaxis during obstetrical surgical safety checklist procedures occurs: a) During the briefly b) During the time-out c) During the briefing and time-out d) During the debriefing |
I - b) Time-out (under nursing duties)
II - a) Briefing (under nursing duties) new 2013 guideline |
|
|
Is there evidence from randomized controlled trials that suggests HRT in breast-cancer survivors increases the risk of breast cancer recurrence?
|
Yes
SOGC 2004 guideline - All studies discussed in guideline were observational (HABITS RCT was just starting). Per UTD 2013, HABITS was stopped early due to a 2x increased incidence of Br Ca recurrence in HRT users versus non-users. |
|
|
a) Give the three other gynecologic surgical procedures not including hysterectomy for which antibiotic prophylaxis is recommended.
b) Is it recommended at the time of HSG? c) Is it recommended at the time of UDs? d) Doubling the dose of prophylactic antibiotics can be considered for women with BMI >=25; >=30; or >=35? |
a)
Pelvic-Organ Prolapse surgery Stress Urinary incontinence (tape) Therapeutic abortion b) No - Only if dilated tubes are present c) No - Only if the incidence of UTI post-UDs is >10% d) >=35 (morbid obesity) |
|
|
List three modifications/interventions/treatments that can be recommended for improvement of urogenital atrophy in a post-menopausal woman.
|
Regular vaginal intercourse
Cranberry product (pure juice or pills) for UTI Vaginal moisturizers (Replens) Vaginal estrogen (premarin, ring, vagifem) |
|
|
Primary amenorrhea in a 15yo. Exam shows normal breast development, tanner stage I pubic and axillary hair, and a blind-ended vagina. Serum testosterone is in the normal male range.
a) What important surgical intervention is required, why, and when would you do it? b) At what biochemical/cellular level is the defect in this individual? c) What is the difference between a mosaic and a chimera? |
a) Gonadectomy, gonadoblastoma/dysgerminoma, after puberty
b) Androgen receptor c) Chimera - two zygotes fuse to create one individual with different genetic material Mosaic - same zygote, change to genetic material at the >=2 cell stage and propagation of two different cell lineages |
|
|
List six causes of female pseudohermaphroditism.
|
Maternal androgen ingestion
CAH (21-hydroxylase, 11b, 3b deficiency) Placental aromatase deficiency Theca lutein cysts/hyperreactio luteinalis Luteomas Sertoli-Leydig tumour Leydig cell tumour Adrenal androgen producing tumour |
|
|
28 yr old female with complex cystic-solid ovarian mass with vascular flow and excrescences.
a) Germ cell or epithelial ovarian cancer more likely? b) If bilateral and LDH+, CA125-, what would be your management? c) If unilateral and AFP+, CA125-, what would be your management? d) A patient receives first line chemotherapy for immature teratoma, give the three most concerning chemotherapy adverse effects? |
a) EOC - incidence is higher than GCT if >20-25yrs old (williams gyne & UTD)
b) Dysgerminoma - USO, staging including LN, chemo per stage c) YST - USO, no staging, chemo regardless d) BEP (bleomycin, etoposide, cisplatin) a) bleo - pulmonary fibrosis b) etop - secondary malignancies c) cis - nephro or neuro toxicity |
|
|
A women has been exposed to Rubella through a friends vaccinated child.
a) She has known immunity and is 32 weeks pregnant, what is the risk of congenital rubella syndrome (CRS)? b) She is unsure of her immune status and 32 weeks GA, what should be done? c) The same women is 8 weeks. Her Rubella IgM is positive but IgG titre is low (not protective). What is the risk of her fetus developing CRS? What can you do to confirm the diagnosis? How would you counsel her? |
a) None
Known immunity > 12 weeks, CRS never been reported b) Serologic testing can be done, but no cases of CRS have been reported after 20wks even with primary infection (>20 weeks FGR is the only recognized sequelae of fetal infection, which may be nearly 100% at term) c) 90%. Repeat IgG titres 4-5 weeks later (exposure, if acute illness repeat 2-3 weeks later). Or maternal rubella culture. High-risk of CRS. MFM referral. Options: i) observation/follow-up U/S (note that CRS is difficult to identify on U/S) ii) termination (empiric) iii) Amnio for viral PCR |
|
|
Umbilical cord abnormality found more commonly in breech presentation fetuses
|
Short cord.
|
|
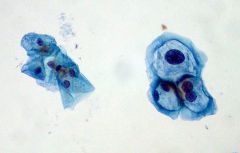
List three features of this type of cell.
|
Koilocyte
1) Nuclear enlargement (two to three times normal size) 2) Irregularity of the nuclear membrane contour 3) A darker than normal staining pattern in the nucleus, known as Hyperchromasia 4) A clear area around the nucleus, known as a perinuclear halo. |
|
|
What pharmacologic therapy for OAB has the highest level of evidence for safety in the elderly or cognitively impaired?
|
Tolterodine
|
|
|
If hormonal contraceptive is missed, during which week(s) is ovulation escape most likely?
|
First, Third
|
|
|
a) Give five maternal risk factors for macrosomia and two fetal causes associated with macrosomia
b) Has induction of labour for suspected fetal macrosomia been shown to improve outcomes (e.g. reduce risk for shoulder dystocia?) |
Maternal
Obesity DM Post-term pregnancy Multiparity LMA Previous macrosomic infant Constitutional Racial/ethnic Fetal causes Male sex Beckwith-Wiedemann Pallister-Killian Sotos Perlman Simpson-Golabi-Behmel Costello Weaver b) No |
|
|
Four broad factors that can cause labour dystocia.
|
1) Uterine contractions (expulsive forces)
2) Fetus - macrosomic, presentation, position 3) Bony pelvis - type, ?contracted? 4) Maternal soft tissue of reproductive tract |
|
|
Define arrest of descent.
|
No descent for > 1 hour.
|
|
|
After how many hours of adequate contractions with no cervical dilation, as measured by montevideo units, should arrest of dilatation be diagnosed?
a) 1hr b) 2hr c) 3hr d) 4hr |
d) Four hours (per Williams OB recommendations)
|
|
|
a) How are montevideo units calculated?
b) What is the minimum uterine pressure required to cause cervical dilation in normal labour? |
a) Sum: Peak pressure during contraction - uterine baseline pressure, for each contraction, in a 10 min period. At least 180 is the goal.
b) 15mmHg |
|
|
Define: engagement.
|
Leading edge of fetus is at the level of the ischial spines.
|
|
|
a) Define precipitous labour.
b) List 6 adverse maternal and/or neonatal outcomes of precipitous labour. |
a) Onset of labour to expulsion of fetus <= 3 hours.
b) PPH Abruption Cervical or vaginal/perineal lacerations Uterine rupture Brachial plexus injury Low Apgars Meconium Drop newborn (Williams OB AbN labour chapter) |
|
|
List 5 risk factors/associations with fetal face presentation.
|
Polyhydramnios
Contracted maternal pelvis Prematurity Parity Nuchal cord (prevents neck flexion) Abnormal fetus Anencephaly |
|
|
What is the incidence of OP position at *delivery*?
a) 1% b) 5% c) 15% d) 25% |
b) 5%
(Williams OB) |
|
|
What is the incidence of shoulder dystocia when the birthweight is >= 4500g?
a) 1% b) 5% c) 20% d) 50% |
c = 20%
(Williams OB) |
|
|
Which is false regards McRobert's maneuver for shoulder dystocia?
a) describes lying woman on back and flexing thights at the hips b) increases pelvic dimensions to permit delivery c) straightens sacrum inline with lumbar vertebrae d) rotates symphysis pubis and disimpacts fetal shoulder to permit delivery. |
B = it does NOT increase or open up pelvis. it is felt that the mechanism to help reduce shoulder dystocia is rotating the symphysis pubis results in the anterior shoulder being disimpacted.
|
|
|
What are five phases of wound healing as outlined in TeLinde's operative gynecology?
|
1) Inflammation
2) Epithelialization 3) Fibroplasia 4) Wound contraction 5) Scar maturation |
|
|
When is the optimal time to perform tertiary wound closure (delayed primary closure)?
|
3-6 days after the wound was made
|
|
|
Describe technique for doing a Smead-Jones closure.
|
Interrupted sutures
Far-Far-Near-Near Mass Closure Vertical mattress Layers: Subq fat, rectus fascia, rectus muscle, peritoneum |
|
|
a) Currently, where does catgut come from?
b) How is it degraded by the body? |
a) Sheep or Cow intestine
b) Enzymatically - proteolysis by enzymes elaborated by WBC infiltrating the wound. Results in increased inflammation, immune activation from foreign proteins. |
|
|
How are synthetic sutures like vicryl and monocryl degraded or broken down?
|
Hydrolysis.
Less inflammatory. |
|
|
a) Define late onset PPH.
b) List causes of late onset PPH |
a) Post partum: >24h, < 12 weeks
b) Metritis Eschar bleed Subinvolution of placental site Retained products Blood clots von Willebrand's Disease |
|
|
How much blood flows to the uterus/intervillous space at term?
|
600 ml / minute
|
|
|
List 8 risk factors for/causes of abruption.
|
Trauma
Cocaine use Smoking HTN Polyhydramnios Circumvellate placenta PPROM PROM Age (>35yrs) Previous abruption Chorioamnionitis Uterine anomaly (e.g. fibroids) Parity (controverial) |
|
|
What cause of abruption is most associated with fetomaternal hemorrhage?
|
Trauma
|
|
|
a) The placenta delivers and then a gush of blood that was contained by the placenta and membranes occurs. What type of placental delivery was this?
b) What is the other type of placental delivery? |
a) Schultze.
b) Duncan. |
|
|
List three adverse outcomes from the use of uterine compression sutures.
|
Uterine ischemic necrosis
Focal ischemia and myometrial weakening --> predisposes to future uterine rupture Abnormal placentation |
|
|
When can women be offered an invasive prenatal diagnostic procedure without at least having multiple marker screening first? (4)
|
1) Ultrasound findings
2) IVF+ICSI pregnancy 3) Hx of aneuploid child 4) Either parent known carrier of a chromosomal disorder |
|
|
Give two methods to screen for open neural tube defect?
|
Ultrasound (18-22wks)
MS-AFP (16-20wks) |
|
|
a) Cause of increased nuchal translucency in Turner's syndrome.
b) Cause of increased nuchal translucency in Down's syndrome. |
a) Lymphatic duct dysplasia leading to subq fluid accumulation.
b) Altered dermal collagen - more hydrophilic and leads to subq edema. |
|
|
What maternal obstetrical/pregnancy risk is common for T13 pregnancies?
|
Pre-eclampsia (50%)
|
|
|
If an RV fistula is not obviously secondary to obstetric injury, what is a critical component of management?
|
Biopsy to rule out malignancy.
|
|
|
5 principles of vesico-vaginal fistula repair
|
Preoperative assessement
Timely repair Tension free Multilayer Surrounding viable tissue Post-operative bladder cath |
|
|
What is the Latzko technique for vesicovaginal fistula repair?
|
Apposition of anterior and posterior proximal vaginal walls
Fistula tract not removed Shortens vagina |
|
|
If a women with an infected urethral diverticulum is diagnosed, what swabs should be done?
|
GC
|
|
|
Five "R's" of Radiation biology
|
Repair
Resortment Repopulation Reoxygenation Regulation (molecular) |
|
|
List actions that can be taken for "intrauterine resuscitation" for an atypical/abnormal FHR
|
Reposition (lateral, all fours)
Oxygen D/C syntocin/uterotonic Vaginal exam (relieve pressure on cord) IV fluid bolus Amnioinfusion reduce anxiety (catcheolamines) Uterine relaxant (nitro) |
|
|
What pH is usually greater, post-delivery umbilical artery or vein?
|
Vein
|

