![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
132 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
True constituents of milk |
Milk fat, Casein, Lactose
|
|
|
Milk is excellent source of |
Calcium and phosphorus |
|
|
Milk is low in |
Iron, copper and iodine |
|
|
Best cow breed |
Jersey Indian- Sahiwal, Rathi, Gir, Red sindhi |
|
|
Best buffalo breed |
Murrah Mehsani Jaffarbadi |
|
|
Method for standardization of fat |
Pearson's square |
|
|
Test for effectiveness of pasteurization |
Phosphatase test |
|
|
Lactose properties |
1/6 sweet as sucrose 54% of the SNF content of milk |
|
|
Yellow colour of milk due to |
Carotene |
|
|
Green colour of whey due to |
Riboflavin |
|
|
TA of Milk |
Cow 0.13-0.14% Buffalo 0.14- 0.15% |
|
|
Fat and SNF of Standarized milk Recombined milk Tonned milk Double Toned milk
|
Standardized 4.5% Fat, 8.5% SNF Recombined 3% Fat Tonned 3% Fat , 8.5% SNF Double tonned 1.5% Fat , 9.0% SNF |
|
|
Pasteurization of milk is done at |
63°C/ 30 minutes 72°C /15 sec |
|
|
Cream milk fat % |
NLT 25% milk fat |
|
|
Cream |
It is a fat rich portion of milk obtained by gravity or mechanical method of separation. The fat content of cream varies widely in the range of 18 to 85% depending upon the method of separation. |
|
|
Cheese |
a product obtained by draining after the coagulation of milk and may contain coagulating agent sodium chloride and calcium chloride not exceeding 0.02% by weight. |
|
|
Butter |
NMT 1.5% by weight curd NMT 3.0% by weight NaCl NMT 80% by weight of milk fat |
|
|
Ice cream |
NLT 10% milk fat 3.5% protein 36% Total solid NMT 0.5% stabilizer NMT 0.5% emulsifier |
|
|
Unsweetened condensed milk |
UCM - NLT 8% milk fat, NLT 26% milk solid NMT 0.5% fat by wt. , NLT 20% Total milk solid |
|
|
Whole milk powder |
NMT 5% moisture NLT 26% fat NMT 1.2% TA |
|
|
Skim milk powder |
NMT 1.5% fat NMT 5% moisture NMT 1.5% TA |
|
|
Colour and flavour of Butter is due to |
Annatto, Diacetyl content =NMT 4ppm |
|
|
Sweetened condensed milk |
NLT 9% fat, NLT 31% Total solid, NLT 40% cane sugar |
|
|
Butteroil and it's fat% |
Refers to fat concentrate obtained mainly from butter or cream by removal of practically all the water and SNF 99.5- 99.8% |
|
|
Maximum solubility index for roller dried and spray dried |
RD 15 SD 2 |
|
|
Coagulated milk powder |
Dahi, shrikhand, paneer and chhanna |
|
|
Products of clarified butter fat industry |
Makkhan, ghee, lassi and ghee residue |
|
|
% milk fat and varieties of khoa |
NLT 20% milk fat Pindi, dhar, danedar |
|
|
Ghee |
Pure clarified fat derived solely from milk or from desi butterNLT 99-99.5% fatNMT 0.5% moisture |
|
|
Common adulterants of milk |
Urea Starch Sucrose Water Neutraliser Detergent |
|
|
Paneer |
NMT 70% moisture NLT 50%milk fat of dry matter |
|
|
Concentrated Whole milk product |
Khoa, mawa, rabri and kulfi |
|
|
Father of white Revolution |
Dr. V Kurien |
|
|
Number of milk producer cooperative Union Number of state cooperative milk marketing federation. |
170 15 |
|
|
Milk and milk product order |
In 1992 the milk and milk product order was promulgated under the essential commodities act 1995 to regulate milk and milk products production in the country. |
|
|
Gujarat Punjab Haryana Andhra Pradesh Rajasthan Karnataka Kerala Kolhapur. |
Gujarat- Amul Punjab- Verka Haryana- Vita Andhra Pradesh- Vijaya Rajasthan- Saras Karnataka- Nandini Kerala- Milma Kolhapur- Gokul |
|
|
Percentage and different forms of casein |
80%, alpha, beta gamma and kappa casein. |
|
|
Whey protein |
Beta- lactoglobulin (responsible for cooked and creamelized flavour), alpha- lactalbumin (synthesis of lactose) |
|
|
Commercial sterilisation |
It refers to the absence of any microorganisms capable of reproducing in foods under non- refrigerated conditions of storage and distribution instead of the absolute absence of every existing form of microbial life. |
|
|
Operation flood |
Commenced in 1970 to replicate the Anand pattern in 18 areas of milk production. |
|
|
First aseptically processed milk in metal cans was developed by |
Jonas Nielsen in 1913 (Denmark) |
|
|
Only approved method of RAW milk preservation apart from refrigeration is |
Lactoperoxidase system |
|
|
Thermization |
Heating milk to 57° - 68° Celsius for a period of 15 sec. which will inactivate psychrotrophic bacteria and thereby prevent enzyme production. |
|
|
Lactoperoxidase system |

|
|
|
Bactofugation |
It is a process in which a specially designed centrifuge called a Bactofuge is used to separate microorganism from milk. The optimal bactofugation temperature is 55 to 62 degree centigrade. |
|
|
Lactose in milk can be hydrolysed by |
Beta D- galactosidase, which breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose. |
|
|
Base material for sweetmeats like Rasogolla, Sandeash, etc. |
Chhanna |
|
|
Most popular sterilizing method for aseptic packaging is |
Hydrogen peroxide |
|
|
Specific gravity of milk serum and fat |
Milk serum 1.036 Fat 0.9 |
|
|
Fat percentage in low, medium and high fat cream should not be less than |
25, 40 and 60% respectively |
|
|
Step involved in preparation of cream for butter making |
Standardization of cream (38-41% fat) Pasteurization (80°C/16 sec) Cooling (~ 5°C) Ageing (5-8°C/6-12 hour) of cream |
|
|
Ghee |
The word ghee is evolved from sanskrit word 'ghrut'. Ghee is a common Indian name for clarified butter fat. Ghee may contain butylated hydroxyl anisole at concentration not exceeding 0.02%. |
|
|
Test that indicates the presence of dalda (hydrogenated vegetable fat) as an adulterant in ghee. |
Baudouin test Positive test indicates presence of dalda Vanaspati ghee contains 5% sesame oil. Pure ghee does not contain sesame oil. Fats and oils are treated with 5ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 2% furfural solution in alcohol. After 5-10 minutes rose-red colour appearance shows the presence of sesame oil in the given sample. |
|
|
Three grades of ghee based on free fatty acids |
Special max 1.4% FFA General max 2.5% FFA Standard max 3.0% FFA |
|
|
Melting range of ghee |
28 to 44° C |
|
|
Fat percent in desi Butter |
76% |
|
|
Butyro-refractometer reading of ghee |
40 - 45 at 40°C |
|
|
Saponification number of ghee |
NLT 220 |
|
|
Iodine value of ghee |
26-38 |
|
|
The Polenske value of cow ghee |
2 -3 And it is higher than buffalo ghee 1-1.5 |
|
|
Anhydrous milk fat |
It is a milk fat based dairy product in its purest form it is the fatty products derived exclusively from milk and products obtained from milk by means of process which results in almost total removal of water and milk solids not fat. |
|
|
Chhanna |
Fat: min 50% It is heat and acid- coagulated milk product also known as India's traditional soft, cottage cheese. |
|
|
Chhanna making process |
It is a process involving destabilisation of casein particle by acidification of milk with dilute acid at relatively higher temperature. |
|
|
Khoa making process |
Fat : min 30% It is conventionally prepared by heating, evaporating and dessication of milk in an open kettle at atmospheric pressure accompanied by continuous stirring until dove lai consistency is achieved. |
|
|
Shrikhand |
It is a popular fermented, sweetened, indigenous dairy product having semi solid consistency. It has typical sweetish-sour taste. It is a fermented milk product which is very close to flavoured quarg of Germany. |
|
|
In fruit shrikhand milk fat and protein... |
Milk fat on dry basis NLT 7% Prior protein on dry basis NLT 9% |
|
|
Kefir |
It is characterized by foamy, effervescent milk product. It is fermented milk product which involves mixed lactic acid and alcoholic type of fermentation. Self carbonated beverage |
|
|
Kumiss |
It is a mare's milk acid - alcohol fermented product similar to kefir and is very popular in Russia and Central Asia. |
|
|
Yoghurt |
It is a coagulated milk product obtained by lactic acid fermentation through the action of S. thermophilus and Lb. bulgaricus. Similar to Indian dahi Egyptian Leben Armenian maztoon |
|
|
Cheese |
It may contain max of 3000ppm sorbic acid or its Na, K, Ca salts calculated as sorbic acid, and or 12.5 ppm of nisin, either singly or in combination. Natamycin may be used for surface treatment only. |
|
|
Sweetened condensed milk |
They are the milk products which can be obtained by the partial removal of water from milk with the addition of sugar or by any other process which leads to a product of the same composition and characteristics. It may sometimes contained at the refined lactose, calcium chloride, citric acid and sodium citrate, sodium salt of orthophosphoric acid and polyphosphoric acid not exceeding 0.3 % by weight of the finished product. |
|
|
Evaporated milk |
It is sterilized, concentrated, homogenised to milk. The product can be kept without refrigeration and has a long shelf life. |
|
|
Casein present in the milk is found in the form of |
Calcium caseinate-phosphate complex |
|
|
Platform test |

|
|
|
Clot on boiling test and alcohol test |

|
|
|
How many parts by weight of 30 % cream and 4% milk must be mixed to milk testing 5% fat? |
One part of 30% cream and 25 parts of 4% milk must be mixed |
|
|
Rind rot is being observed in |
Cheese |
|
|
Type of cheese |

|
|
|
Eyes are the characteristic of |

Swiss cheese |
|
|
Microorganisms involved in yoghurt formation |
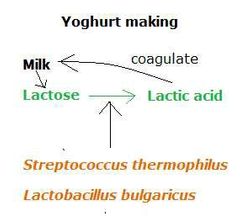
|
|
|
Energy value of milk |
Cow milk 75 C/ 100 g Buffalo milk 100 C/ 100 g |
|
|
Which amino acid is absent in milk? |
Methionine |
|
|
Milk fat is |
Oil in water type emulsion |
|
|
Casein is present in milk in |
Colloidal form |
|
|
Which casein is calcium insensitive casein? |
Kuppa casein |
|
|
Site of rennin action |
Kuppa casein |
|
|
Serum protein consists of |
Alpha lactalbumin |
|
|
First milk that cow produces after calving |
Colostrum |
|
|
Dye reduction test (MBR) is carried out to |
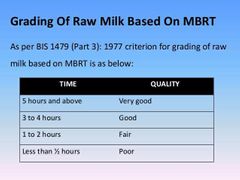
The methylene blue reduction test is based on the fact that the color imparted to milk by the addition of a dye such as methylene blue will disappear more or less quickly. The removal of the oxygen from milk and the formation of reducing substances during bacterial metabolism causes the color to disappear.
To determine the extent of bacterial contamination and growth in milk |
|
|
Lactometer |
Find adulteration of milk by water Find the specific gravity of milk |
|
|
Recknagel phenomenon |
Increase in specific gravity of milk with time |
|
|
Freezing point of cow milk is |
-0.54 to -0.59 |
|
|
Colour of skim milk |
Bluish |
|
|
Fat and SNF content of milk |
Cow milk Fat 3-4% SNF 9% Buffalo milk Fat 6% SNF 9% |
|
|
Chemical that is used to preserve milk the milk samples taken for the platform test |
Mercuric chloride |
|
|
Alcohol-alizarin test |
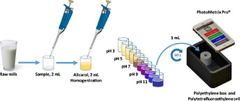
Determine the heat stability and pH of milk |
|
|
The most striking difference between normal milk and colostrum is |
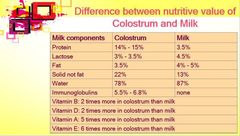
Casein and lactose content |
|
|
Colostrum has |
Brownish yellow colour and salty taste |
|
|
Sterilized milk can be stored at least for |
One week |
|
|
Viscolizer is a type of |
Homogeniser It produces a greater cream volume on the held bottled milk than normal milk of the same fat content, and therefore deceives the purchaser. |
|
|
Curd tension can be measured by |
Hill curd tension test |
|
|
Filled milk |
Water, skim milk and fat from vegetable sources are mixed together. |
|
|
Fat % in Table cream Whipping cream Plastic cream |
Table 20 - 25% Whipping 40% Plastic 60% |
|
|
Aim of neutralisation (partial reduction of acidity) of cream is |
To avoid excessive fat Loss in butter milk To prevent the production of an undesirable of flavour To improve the keeping quality of milk |
|
|
If you want to make butter from cream, and want to store for longer period, then the acidity of cream should be reduced to______% before churning |
0.06 |
|
|
Chemicals used to neutralise cream |
NaOH |
|
|
Max amount of common salt in butter is |
3% |
|
|
Ripened cream butter is made from |
Cream inoculated with culture |
|
|
In butter making the term working means |
Kneading of butter |
|
|
Name the phase transformation method |
Churning Oil-in-water type emulsion is changed to water-in-oil emulsion type |
|
|
Vacreation |
This refers to pasteurization of milk /cream under reduced pressure by direct steam. This process removes feed and other volatile flavors from cream, and to pasteurize it for butter making. |
|
|
Minimum milk fat content of softy Ice cream |
10% |
|
|
Soft, semi hard and hard cheese are classified on the basis of |
Moisture content |
|
|
Cheese that is made from skim milk |
Cottage |
|
|
Curing temp of cheese |
16°C |
|
|
Green cheese |

cheese before ripening |
|
|
Salt balance theory |
Given by Sommer and Hart It is based on the ratio of Ca and Mg to citrate and phosphate |
|
|
Purpose of salting in butter manufacturing |
To improve keeping quality To enhance taste To increase overrun |
|
|
Salting in the manufacture of cheese is done with the objective |
To check the undesirable fermentation and regards formation of lactic acid |
|
|
Function of stabilizer in Ice cream is |
Prevent formation of ice crystals |
|
|
Sunlight flavour of milk is attributed to |
The photolysis of amino acids |
|
|
The difference in casein precipitated by acid and rennin is that |
Rennin casein can't be closed second time |
|
|
Most variable component of milk |
Fat followed by protein |
|
|
When milk is heated it's acidity decreases at first owing to |
Release of Carbon dioxide |
|
|
Moisture and fat % of cheese |
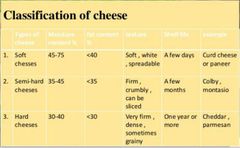
|
|
|
National Dairy Development board (NDDB) was created in |
1965 at Anand |
|
|
Frozen dessert specification |
Fat : max 2.5% Protein : min 5.5% |
|
|
Regional office of NDDB for Northern region Western region Eastern region Southern region |
Northern : Delhi Western : Mumbai Eastern : Kolkata Southern : Bangalore |
|
|
Natural antioxidant present in butter fat is |
Lecithin |
|
|
Effects of heating milk |
The amount of colloidal phosphate increases The amount of Ca²+ decreases Lactose isomerizes and partly degrades to utilise lactose and organic acids |
|
|
Heat stability of mik is proportional to |
The amount of urea |
|
|
Vacreation |
Rapid heating of cream by injecting stream |

