![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Alopecia
|
Abnormal Hair loss
|
|
|
|
Trichology
|
Scientific study of hair and its diseases and care
|
|
|
|
Alopecia Areata
|
Autoimmune disorder that causes the affected hair follicles to be mistakenly attacked by a person's own immune system.
|
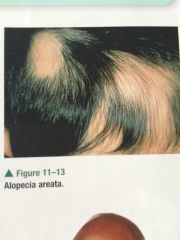
|
|
|
Alopecia totalis
|
Total loss of scalp hair
|
|
|
|
Alopecia Universalis
|
Complete loss of body hair
|
|
|
|
Amino Acids
|
Units that are joined together end to end like pop beads by strong, chemical peptide bonds to form the polypeptide chains that comprise proteins.
|
|
|
|
Anagen Phase
|
AKA: Growth phase
Phase during which new hair is produced. |
Growth Phase
|
|
|
Androgenic Alopecia
|
AKA: Androgenetic Alopecia
Hair loss characterized by miniaturization of terminal hair that is converted to vellus hair; on men. |
|
|
|
Canities
|
Gray Hair
|
|
|
|
Carbuncle
|
Inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue caused by staphylococci; similar to a furuncle but larger.
|
|
|
|
Catagen Phase
|
Brief transition period between the growth and resting phases of a hair follicle. It signals the end of the growth phase.
|
|
|
|
COHNS
|
Carbon
Oxygen Hydrogen Nitrogen Sulfur |
|
|
|
Cortex
|
Middle layer of the hair; a fibrous protein core formed by elongated cells containing melanin pigment.
|
|
|
|
Disulfide bond
|
Strong chemical side bond that joins the sulfur atoms of two neighboring cysteine amino acids to create one cystine. Strongest bond.
|
|
|
|
Hair root
|
The part of the hair located below the surface of the epidermis.
|
|
|
|
Hair shaft
|
The portion of hair that projects above the epidermis.
|
|
|
|
Hair stream
|
Hair flowing in the same direction.
|
|
|
|
Hair texture
|
Thickness or diameter of the individual hair strand
|
|
|
|
Helix
|
Spiral shape of a coiled protein created by polypeptide chains that intertwine with each other
|
|
|
|
Hydrogen bond
|
Weak, physical bond.
Broken with water or heat. |
|
|
|
Hydrophilic
|
Easily absorb moisture
|
|
|
|
Hydrophobic
|
Naturally resistant to being penetrated by moisture.
|
|
|
|
Hypertrichosis
|
AKA: hirsuties
Growth of terminal hair in areas of the body that normally grow only vellus hair. |
|
|
|
Cowlick
|
Tuft of hair that stands straight up
|
|
|
|
Fragilitas crinium
|
Technical word for brittle hair
|
|
|
|
Furuncle
|
Boil in the scalp
|
|
|
|
Hair bulb
|
Lowest part of a hair strand. Forms the lower part of the hair root.
|
|
|
|
Helix
|
Spiral shape of a coiled protein created by polypeptide chains that intertwine with each other
|
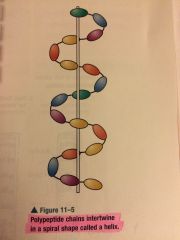
|
|
|
Hair density
|
The number of individual hair strands on 1 square inch of scalp.
|
|
|
|
Hair Elasticity
|
Ability of the hair to stretch and return to its original length without breaking.
Test when wet. |
|
|
|
Hair follicle
|
The tube-like depression or pocket in the skin or scalp that contains the hair root.
|
|
|
|
Hair porosity
|
Ability of the hair to absorb moisture.
|
|
|
|
Keratinization
|
Process by which newly formed cells in the hair bulb mature, fill with Keratin, move upward, lose their nucleus, and die.
|
|
|
|
Polypeptide chain
|
A long chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
|
|
|
|
Postpartum alopecia
|
Temporary hair loss after giving birth.
|
|
|
|
Proteins
|
Long, coiled complex polypeptides made of amino acids
|
|
|
|
Ringed hair
|
Variety of vanities characterized by alternating band of gray and pigmented hair throughout the length of the hair strand.
|
|
|
|
Salt bond
|
Weak, physical bond
Dissolved with acid or alkaline products |
|
|
|
Scutula
|
Dry, sulfur-yellow, cup like crust on the scalp in times favosa or tinea favus
|
|
|
|
Side bonds
|
Bonds that cross link the polypeptide chains together and are responsible for the extreme strength and elasticity of human hair
|
|
|
|
Telogen phasr
|
Resting phase
Final phase in the hair cycle, last until hair is shed. |
|
|
|
Terminal hair
|
Long, coarse, pigmented hair found on the scalp, legs arms, and bodies of males and females
|
|
|
|
Tinea
|
Ringworm
|
|
|
|
Lanthionine bond
|
The bonds created when disulfide bonds are broken by hydroxide chemical hair relaxers after the relaxer is rinsed from the hair
|
|
|
|
Tinea favosa
|
AKA: tinea favus
Fungal infection characterized by dry, sulfur yellow, cup like crust on the scalp called scutula |
|
|
|
Trichoptilosis
|
Split ends
|
|
|
|
Trichorrhexis nodosa
|
Knotted hair
|
|
|
|
Vellus hair
|
Lanugo hair, short, fine, unpigmented hair.
|
|
|
|
Wave pattern
|
The shape of the hair strands
|
|
|
|
Whorl
|
Hair that forms in a circular pattern on the crown of the head
|
|
|
|
Malassezia
|
Naturally occurring fungus that is present on all human skin. Responsible for dandruff when is out of control.
|
|
|
|
Medulla
|
Innermost layer of the hair that is composed of round cells; often absent in fine and naturally blond hair.
|
|
|
|
Monilethrix
|
Beaded hair
|
|
|
|
Pediculosis capitis
|
Infestation of the hair and scalp of head lice.
|
|
|
|
Peptide bond
|
AKA: end bond
Chemical bond that joins amino acids to each other, end to end, to form a polypeptide chain. |
|
|
|
Pityriasis
|
Dandruff
|
|
|
|
Pityriasis capitis simplex
|
Classic dandruff
Scalp irritation, large flakes, and itchy scalp. |
|
|
|
Pityriasis steatoides
|
Severe case of dandruff.
Accumulation of greasy or waxy scales, mixed with sebum, that stick to the scalp in crusts. |
|

