![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
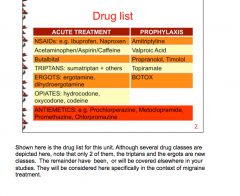
What drugs are used in the acute treatment of migraines?
Which for prophylaxis? |
|
|
|
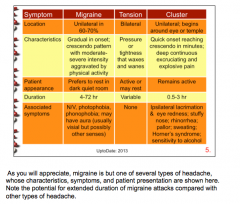
Where do most migraines occur (unilateral or bilateral)? How does the patient appear? How long do they last? |
|
|
|
What can tension headaches be treated with? Cluster headaches? |

|
|
|
What classes are used for prophylaxis of migraines?
Which class for mild (or menstrual) migraine? Which class for moderate-severe? |

|
|
|
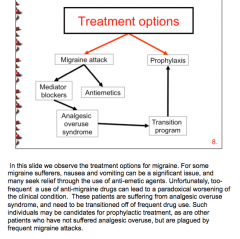
Draw out the treatment pathway for migraines. |
|
|
|
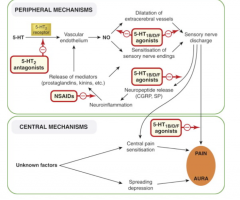
Draw out the migraine pathogenesis: |
|
|
|
What neurotransmitters are released by triggers? What do they produce? What do most effective current drugs act on? |
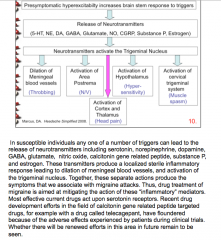
|
|
|
Where do NSAIDs and triptans act in the pathophysiology of migraines? |
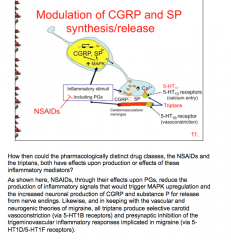
|
|
|
What are the five NSAID drugs most commonly used for migraine? |

|
|
|
What pregnancy category are the NSAIDs? Which require the greatest number of doses per day (and fewest)? |
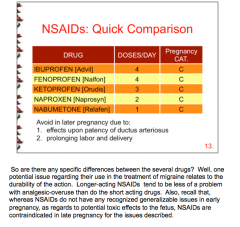
CONTRAINDICATED IN LATE PREGNANCY |
|
|
What are side effects of butalbital? Deficiency of what enzyme may be important with chronic high doses of acetaminophen? |
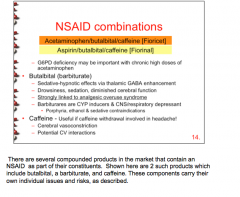
|
|
|
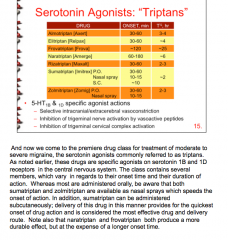
Almotriphan, elitriptan, fovatriptan, naratriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan, zolmitriptan
Agonists of what? Which are most rapid in onset? Shortest and longest half-lives? Which are nasal sprays? |
|
|
|
What are some side effects of triptans? Vasospasm of what arteries (thus contraindicated in what diseases)?
|

|
|
|
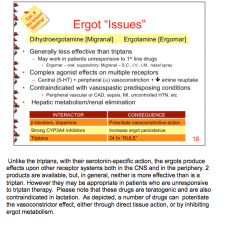
What do ergots cause contraction of? What have they been used to control? How is it useful in migraines?
What is acute and chronic ergotism characterized by? |

|
|
|
What are the two ERGOT drugs? Are they more or less effective than triptans? What is the mechanism? How metabolized and eliminated? Any CYP interaction? What is the 24 hour rule? Any problems during pregnancy or breast feeding? |
|
|
|
When does migraine most often occur in pregnancy? What drug should you use? What if it persists later into pregnancy? |

|
|
|
What is most frequently used to treat menstrual migraine?
|

|
|
|
Low dose combination OCs produce two fold increase of what? Should OCs be used in patients who have aura-associated migraines? |

|
|
|
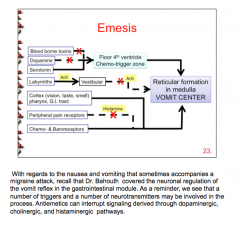
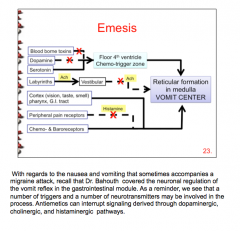
80% of migraines produce what symptom (think pain)? Are triptans effective for this? What drugs should you turn to? Why are opiates not a good idea? |

|
|
|
|
|
|
What antiemetic drugs can be used in the treatment of migraine? Name some adverse effects of each. Antiemetic effect. |
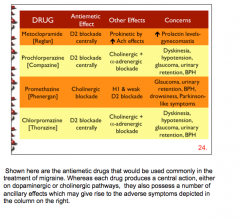
|
|

|

|
|
|
What ares of the brain do the major drug classes used in prophylaxis impact? |
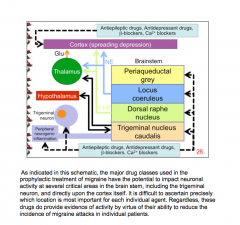
|
|
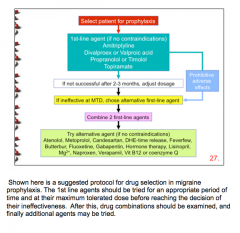
Review |
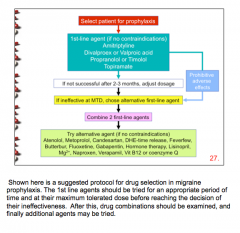
Review |
|

What is the action and adverse effects of each? Which are CatX? |

|
|
|
Can botox be used in migraines? Comparison with placebo? Mechanism? |
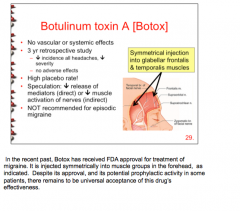
|
|
|
What are some symptoms of analgesic overuse syndrome? |

|
|
|
What is the mechanism of analgesic overuse syndrome? Reduced levels of what? Where does free radical damage occur? |
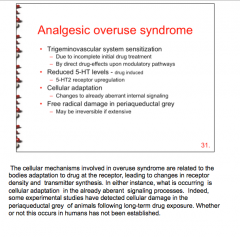
|
|
|
Which drug classes carry the highest risk of analgesic overuse syndrome? Lowest? |
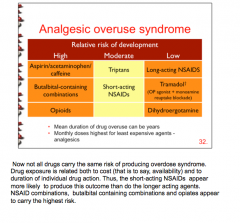
|
|
|
What is the three faceted approach? |

|
|

|

|
|
|
What should you give for mild-moderate migraine?
Amitripyline Ergotamine Naproxen Timolol |
Naproxen NSAIDs for MILD => MODERATE |
|
|
Which drug works exclusively on serotonin-1B and 1D receptors? |
Sumitriptan |
|
|
Taking ergotamine for attack some 12 hours ago. For additional interventions, which drug is contraindicated?
Oxycodone Elitriptan Metoclopramide Propranolol |
Elitriptan |
|
|
Pregnancy. What is contraindicated in first semester for migraine?
|
Ergotamines |
|
|
For women taking oral contraceptives, which of the following is at the greatest increased risk of ischemic stroke? |
Migraine with aura |
|
|
Which of the following drugs used in treatment of migraine controls nausea that come patients experience?
Butalbital Dihydroergotamine Promethazine Topiramate
Which receptor is blocked? |
Promethazine
Cholinergic block |
|
|
Which of the following is the most appropriate for prophylaxis in children? |
Propranolol = THE ONLY ONE PROVEN TO BE EFFECTIVE FOR MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS IN CHILDREN! |
|
|
Which of the following triptans would demonstrate the slowest onset of action? |
Frovatriptan
Won't give if migraine already in progress |
|
|
Which of the following would NOT be an a contraindication for the use of a triptan?
Diabetes Heart disease Uncontrolled HTN Cerebrovascular disease Pregnancy |
Pregnancy (only contraindicated with ergots) |
|
|
Which of the following drugs would be MOST likely to intreat with MAO inhibitors?
Dihydroergotamine Naproxen Oxycodone Sumatriptan |
Sumatriptan |

