![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cladding |
|
|
|
Building Envelope |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Secondary requirements of Building Envelope (6) |
|
|
|
Curtain wall system |
|
|
|
3 conditions in order for water to penetrate cladding system |
|
|
|
Five forces which move water |
|
|
|
PEC rain screens |
|
|
|
PERSIST stands for |
|
|
|
PERSIST wall |
|
|
|
IGU |
|
|
|
COMMON IGU coatings and gasses |
|
|
|
Tint and treatments |
|
|
|
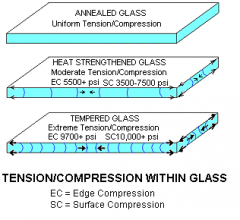
Annealed glass |
|
|
|
Glass types in terms of force |
|
|
|
Conventional stucco |
|
|
|
EIFS- |
|
|
|
**Single layer barrier system (Low performance) |
|
|
|
** Cavity or PEC (high performance) |
|
|
|
Roofing intro |
|
|
|
The role of a roofing system (3) |
|
|
|
Low slope characteristics |
|
|
|
Built up roof |
|
|
|
Membrane roof |
|
|
|
2 Roof categories |
|
|
|
2 Low slope roofs |
|
|
|
Built up products |
|
|
|
Ways built up can be applied |
|
|
|
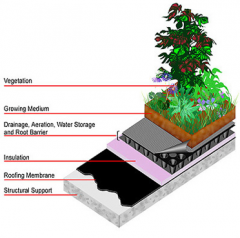
Green Roof |
|
|
|
Low slope characteristics |
|
|
|
Installation position |
|
|
|
Perlite |
|
|
|
Polyisocyanurate |
|
|
|
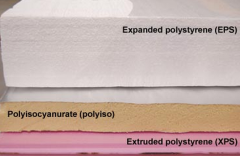
Expanded polstyrene |
|
|
|
Extruded polystyrene |
|
|
|
Expanded and Extruded Polystyrene |
|
|
|
Inverted patio roofs have the membrane on the Top or Bottom ? |
Bottom |
|
|
Steep Roof Characteristics |
Problem: Ice damming , poor ventilation |
|
|
Preventing Ice Dams |
|
|
|
4 Fundamental changes to buildings in last 50 years |
|

