![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Povidone-iodine |
What is the main solution in the laboratory activity "1,2,3,starch now"? |
A. StarchB. Povidone-IodineC. Iodine |
|
|
Purple |
What color will appear on bread doing iodine test? |
A. Yellow B. Purple C. Blue |
|
|
To determine the solubility materials in water & CCl4 |
What is the objective of Lab #2 "Water properties"? |
A. To determine the water property of NaCO3 B. To determine the presence of water molecule C. To determine the solubility materials in water & CCl4 |
|
|
Iodine test |
The following are qualitative analyses of Carbohydrates except: |
A. Iodine test B. Molisch's test C. Fehling's test |
|
|
CCl4 |
For part 2 in the laboratory activity "water properties", what solution will replace water trying to dissolve the solid materials? |
A. NaCO3 B. CCl4 C. Citric Acid |
|
|
The citric acid will be dissolve |
What happens when you mix the citric acid and water? |
A. The citric acid will be dissolve B. The citric acid will be undissolve C. No reaction at all. |
|
|
Gelatin |
The following substances are soluble in water except for: |
A. Sugar B. NaCO3 C. Gelatin |
|
|
Starch |
In what solute does the color turn to deep blue that indicates the presence of starch when the iodine test takes place? |
A. Glucose B. Starch C. Lactose |
|
|
Presence in color |
When you contact iodine testing a positive result refers to: |
A. Change in smell B. Presence in color C. Change in texture |
|
|
Potato & cooked rice |
Which among the following has a positive result in the iodine test? |
A. Potato B. Cooked rice C. Tomato |
|
|
Starch |
What substance can make the potato turns into violet? |
a. Iodine solution b. Salt C. Starch |
|
|
Protein |
It is an organic polymer made of many amino acids linked together in a specific way. |
A. Carbohydrates B. Protein C. Enzymes |
|
|
Glucose and lactose |
The _____ turned to elemental silver after adding Tollen's reagent. |
A. Glucose B. Lactose C. Both a and B |
|
|
Gelatin |
Which of the following is insoluble in water? |
A. Gelatin B. Citric Acid C. NaC03 |
|
|
Mortar and pestle |
All materials are used in "1,2,3, starch Now!" Except: |
A. Spoon B. Mortar and pestle C. Medicine dropper |
|
|
Iodine test |
A test that is used to detect the presence of starch in various samples. |
A. Sulfuric acid test B. Starch test C. Iodine test |
|
|
Sugar |
What substance is used and being observed when the water remained clear but the solute remained transparent at the bottom part? |
A. Salt B. Gelatin C. Sugar |
|
|
Tyrophan and Hopkins |
It is a combination of two substances being observed wherein the results of observation is into a clear color substance. |
A. Gelatin and Hopkins B. Tyrophan and Hopkins C. Albumin and Hopkins |
|
|
NACO3 |
What substance is being tested when the water was clear at the beginning and slowly change into cloudy, but there are still solutes that did not dissolve at the bottom |
A. Gelatin B. Sugar C. NACO3 |
|
|
Gelatin and Hopkins |
It is a combination of two substances being observed wherein the results of observation is into a watery structure and have a green color? |
A. Tyrosin and Hopkins B. Albumin and Hopkins C. Gelatin and Hopkins |
|
|
Baking Soda |
What is the commercial name for sodium bicarbonate? |
A. Citric Acid B. Baking Soda C. All purpose flour |
|
|
Dark blue |
What color will the product turn out if a starch product has iodine in it? |
A. Orange B. Yellow C. Dark Blue |
|
|
To transfer a liquid from one container to another |
What is the pipette use for? |
A. To scoop out powdered chemicals B. To transfer a liquid from one container to another C. To store chemicals. |
|
|
Starch |
All but one chemical is insoluble in water |
A. Glucose B. Lactose C. Starch |
|
|
Animal bones and cartilage |
Where does gelatin come from? |
A. Animal bones and cartilage B. Citric Acid C. Lemon Juice |
|
|
Aubergin |
What color does the sample give when it passes the positive test in starch? |
A. Yellow Ochre B. Terracotta C. Aubergin |
|
|
NaC03 |
Which among the following dissolves easily when mixed with CCl4? |
A. Sugar B. NaCO3 C. Salt |
|
|
4 drops of Hopkins + 3 H2SO4 |
Which of the following chemicals caused the gelatin to burn? |
A. 4 drops of Hopkins + 3 H2SO4 B. 1 drop of Nitric Acid + NH404 C. 3 drops of Nitric Acid + 1 drop of Hopkins |
|
|
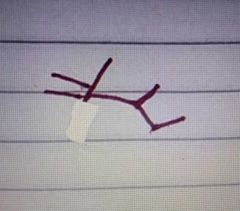
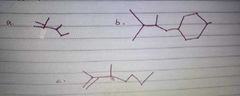
Which among the following is the chemical structure of serine |
|
|
|
Gummies |
Which of the following has the presence of starch? |
A. Gummies B. Mango C. Candy |
|
|
Brown |
What color can be seen when a thing has the presence of starch? |
A. Brown B. Pink C. Rainbow |
|
|
NaCo3 |
Which compound is the most soluble? |
A. Sugar B. Gelatin C. NaCO3 |
|
|
False |
You can measure the amount of starch present in the cooked rice. |
A. True B. False C. None of the above |
|
|
False |
Upon dilution to the CCl4 the citric acid completely and immediately dissolve |
A. True B. False C. A & B |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
are most abundant organic compounds found in living organisms and are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates |
act as the primary source to provide energy for functioning of living organisms |
|
|
|
hydrates of carbon |
These are called carbohydrates because they can be considered as |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Generally defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones or the compounds which produces such products on hydrolysis |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates |
are called saccharides |
|
|
|
Reducing sugars |
-Carbohydrates that can reduce Tollen’s, Benedict’s or Fehling’s reagents are called______ -sugar with free aldehyde or ketone grou -All monosaccharides and most of the disaccharides -Some examples are Maltose and Lactose. |
|
|
|
non-reducing sugars |
-Carbohydrates that cannot reduce Tollen’s, Benedict’s or Fehling’s reagents are called -example is sucrose |
|
|
|
Molisch’s test |
Molisch's regeant is 10% alcoholic solution of α-naphthol. This is a common chemical test to detect the presence of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates undergo dehydration by sulphuric acid to form furfural (furfuraldehyde) that reacts with α-naphthol to form a violet coloured product. |
|
|
|
Fehling's test |
This is an important test to detect the presence of reducing sugars. Fehling’s solution A is copper sulphate solution and Fehling’s solution B is potassium sodium tartrate. On heating, carbohydrate reduces deep blue solution of copper (II) ions to red precipitate of insoluble copper oxide. |

|
|
|
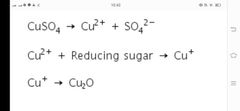
Benedict's test |
distinguishes reducing sugar from non-reducing sugar. Benedict’s reagent contains blue copper (II) ions (Cu2+, cupric ions) that are reduced to copper (I) ions (Cu+, cuprous ions) by carbohydrates. These ions form precipitate as red coloured cuprous (copper (I) oxide. |
|
|
|
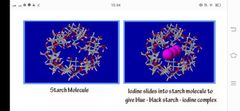
Iodine test |
is used to detect the presence of starch. Iodine is not much soluble in water so iodine solution is prepared by dissolving iodine in water in presence of potassium iodide. Iodine dissolved in an aqueous solution of potassium iodide reacts with starch to form a starch/iodine complex which gives characteristics blue black colour to the reaction mixture. |
|
|
|
Elemental Silver |
What element did the Glucose and Lactose transform into after undergoing the Tollen's Test? |
A. Water Element B. Liquid Mercury C. Elemental Silver |
|
|
Tollen's test |
Tollen’s reagent is ammoniacal silver nitrate solution. On reacting with carbohydrate elemental silver is precipitating out of the solution, occasionally onto the inner surface of the reaction vessel. This produces silver mirror on the inner wall of the reaction vessel. |

|

