![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PAGODA (related to Buddhism) |
-a Hindu or Buddhist temple or sacred building, typically a many-tiered tower, in India and East Asia |
|
|
AVALOKITESVARA (related to Buddhism) |
-"Lord who contemplates", is a bodhisattva who embodies the compassion of all Buddhas. -This bodhisattva is variably depicted and described and is portrayed in different cultures as either female or male |
|
|
VAIROCANA (related to Buddhism) |
-a celestial buddha who is often interpreted, in texts like the Flower Garland Sutra, as the Dharma Body of the historical Buddha (Siddhartha Gautama) |
|
|
AMIDA RAIGO (related to Buddhism) |
-an appearance of Amida Buddha on a purple cloud at the time of one's death. It has given rise to a type of Japanese painting (a raigō-zu) of a Buddha accompanied by bodhisattvas -Amida: a celestial buddha according to the scriptures of Mahāyāna Buddhism. Amida is the principal buddha in Pure Land Buddhism, a branch of East Asian Buddhism |
|
|
PURE LAND (WESTERN PARADISE) (related to Buddhism) |
-also referred to as Amidism, is a broad branch of Mahāyāna Buddhism and one of the most widely practiced traditions of Buddhism in East Asia. Pure Land is a tradition of Buddhist teachings that are focused on Amida Buddha. -three primary texts of the tradition, known as the "Three Pure Land Sutras", are the Infinite Life Sutra, the Amitabha Sutra, and the Contemplation Sutra -Pure Land oriented practices & concepts are found in basic Mahāyāna Buddhist cosmology, & are an important part of the Mahāyāna Buddhist traditions of China, Japan, Korea, Vietnam and Tibet. -The term "Pure Land Buddhism" is used to describe both the Pure Land soteriology of Mahāyāna Buddhism, which may be better understood as "Pure Land traditions" or "Pure Land teachings," and the separate Pure Land sects that developed in Japan |
|
|
APSARAS (related to Buddhism) |
-(in Hindu mythology) a celestial nymph, typically the consort of a gandharva or heavenly musician |
|
|
KUNDIKA (related to Buddhism) |

-distinctively shaped containers such as this example were traditionally used in Asia as water sprinklers for Buddhist purification rituals (cast in bronze) - (Goryeo dynasty (918–1392), Korea) |
|
|
KSHITIGARBHA (related to Buddhism) |

-a bodhisattva primarily revered in East Asian Buddhism and usually depicted as a Buddhist monk. His name may be translated as "Earth Treasury", "Earth Store", "Earth Matrix", or "Earth Womb" (left is example) |
|
|
HANDSCROLL (related to court arts) |
-a long narrow scroll for displaying a series of scenes in Chinese, Japanese, or Korean painting and calligraphy -the handscroll presents an artwork in the horizontal form and can be exceptionally long, usually measuring up to a few meters in length and around 25–40 cm in height |
|
|
HANGING SCROLL (related to court arts) |
-a painting or text on silk or paper that is either displayed on a wall (hanging scroll) & is rolled up when not in use -one of the many traditional ways to display and exhibit East Asian painting and calligraphy |
|
|
ARCHITECTURAL PAINTING (related to court arts) |
-accurate depiction of architectural forms with the aid of a ruler (technique of Chinese art) -In China, architectural painting was called "jiehua", and mainly seen as an inferior type of painting. Known masters of the genre include the 10th century painter Guo Zhongshu, and Wang Zhenpeng, who was active around 1300 |
|
|
MONUMENTAL LANDSCAPE PAINTING (related to court arts) |

-The classic Chinese perspective of three planes is evident - near, middle (represented by water and mist), and far. Unlike earlier examples of Chinese landscape art, the grandeur of nature is the main theme, rather than merely providing a backdrop. -Fan Kuan's Travelers Among Mountains and Streams, a large hanging scroll, is an example of this |
|
|
CALLIGRAPHY (related to court arts) |
-the design and execution of lettering with a broad tip instrument, brush, among other writing instruments. -a contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined as, "the art of giving form to signs in an expressive, harmonious, and skillful manner" -the art of writing beautifully -a script, often cursive, but sometimes angular, produced chiefly by brush, especially Chinese, Japanese, or Arabic writing of high aesthetic value |
|
|
THREE PERFECTIONS (related to court arts) |

-the gathering of poets, calligraphers and painter to create an artwork in ancient China. The resulting product would be a painting that would include the work of a calligrapher to write a poem -(left is an example of this) |
|
|
LITERATI (related to court arts) |
-scholar officials who serve the emperor/court, higher educated class focused on literature/the arts -civil service analysis (test like the SAT) allows individuals to move up in class |
|
|
EMAKIMONO (related to court arts) |
-(literally 'picture scroll'), often simply called emaki, is a horizontal, illustrated narrative form created during the 11th to 16th centuries in Japan. -Emaki-monocombines both text and pictures, and is drawn, painted, or stamped on a handscroll |
|
|
YAMATO-E (related to court arts) |

-a style of decorative painting in Japan during the 12th and early 13th centuries, characterized by strong color and flowing lines -(left is scene from The Tale of Genji by Tosa Mitsuoki, from the 17th century revival of the style) |
|
|
MONO NO AWARE (related to court arts) |
-literally "the pathos of things", and also translated as "an empathy toward things", or "a sensitivity to ephemera" -a Japanese term for the awareness of impermanence, or transience of things, and both a transient gentle sadness (or wistfulness) at their passing as well as a longer, deeper gentle sadness about this state being the reality of life |
|
|
CELADON (related to court arts) |
-a willow-green color -"paneling painted in celadon green" -a gray-green glaze used on pottery, especially that from China -pottery made with celadon glaze. |
|
|
SHOGUN (related to court arts) |
-a hereditary commander-in-chief in feudal Japan. -because of the military power concentrated in his hands and the consequent weakness of the nominal head of state (the mikado or emperor), the shogun was generally the real ruler of the country until feudalism was abolished in 1867 |
|
|
DAIMYO (related to court arts) |
-(in feudal Japan) one of the great lords who were vassals of the shogun -(vassal: a holder of land by feudal tenure on conditions of homage and allegiance [synonyms: serf/dependent/servant/slave/subject/thrall/villein]; a person or country in a subordinate position to another) |
|
|
SAMURAI (related to court arts) |
-a member of a powerful military caste in feudal Japan, especially a member of the class of military retainers of the daimyos |
|
|
SHOIN (related to court arts) |
-a type of audience hall in Japanese architecture that was developed during the Muromachi period -the term originally meant a study and a place for lectures on the sūtra within a temple, but later it came to mean just a drawing room or study |
|
|
CHANOYU (related to court arts) |
-a Japanese ceremony at which tea is prepared, served, and taken with an ancient and involved ritual -also called tea ceremony. -origin of chanoyu: Japanese, cha (tea) + no (particle) + yu (hot water) |
|
|
WABI-SABI (related to court arts) |
-a concept in traditional Japanese aesthetics constituting a world view centered on the acceptance of transience and imperfection -the aesthetic is sometimes described as one of beauty that is "imperfect, impermanent, and incomplete" -characteristics of the wabi-sabi aesthetic include asymmetry, roughness, simplicity, economy, austerity, modesty, intimacy, and appreciation of the ingenuous integrity of natural objects and processes -a concept derived from the Buddhist teaching of the three marks of existence, specifically impermanence, suffering, and emptiness or absence of self-nature |
|
|
WABI-CHA (related to court arts) |
-use of humble materials -a style of Japanese tea ceremony particularly associated with Sen no Rikyū -the term came into use in the Edo era, prior to which it was known as wabi-suki (suki meaning "artistic inclination," and "wabi" literally meaning 'forlorn') -evolved as part of a movement to appreciate local wares and simpler styles |
|
|
Seated Buddha Asuka Period second half of 6th century Korea soapstone |

Paekche Kingdom |
|
|
Pensive Bodhisattva (Maitreya) 7th century Hakuko Period Korea gilt bronze |

Silla Kingdom |
|
|
Horyuji (Temple of Exalted Law) original construction between 601-607 Asuka Period Japan |

-Pagoda at Horyuji is a burial mound reliquary of the buddha derived from the Great Stupa at Sanchi, India -meant to circumabulate, not enter -impression of weightlessness through cloud shaped gables -Kondo: "golden hall" holds the most important sculptures and images, circumambulation around central altar in red room |
|
|
Tori Busshi, Shaka triad 623 gilt bronze (inside Horyuji Temple) |

-inside Kondo -first work where the artist's name is known -this work was created to stave off illness and/or protect the after life of the sick Prince Shotoku |
|
|
Tamamushi Shrine c. 650 wood, metal, and lacquer paint (inside Horyuji Temple) |

-mini golden hall (Kondo) -decorated with wings of Tamamushi beetle -"exact" Kondo replica architecturally -originally portable altar, now permanently installed -Hungry Lioness Jataka on the side (3 parts) |
|
|
Fengxian Temple, Longmen grottoes c. 675 Tang Dynasty China |

-derived from indian culture -site started by emperor, completed by empress (who was a beautiful lowly prostitute and devoiut buddhist, and she gave up personal belongings for budget of construction) -feminine styled buddha, rock-cut |
|
|
Vairocana Buddha c. 675 Tang Dynasty China (inside Fengxian Temple) |

-Vairocana Buddha: brings all parts of the universe together -empress led majority of construction, led to more feminine styled buddha -rock-cut |
|
|
Seokguram caves (Stone Buddha Temple) second half of 8th century United Silla Period Korea |

|
|
|
Shakyamuni/Vairocana Buddha second half of 8th century United Silla Period carved granite (inside Seokguram caves) |

|
|
|
Avalokitesvara/Gwaneum second half of 8th century United Silla Period carved granite (inside Seokguram caves) |

|
|
|
Todaiji (Eastern Great Temple) 8th century Nara period Japan |
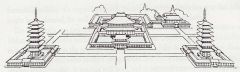
-single central axis oriented north/south -Buddhist temple complex, that was once one of the powerful Seven Great Temples, located in the city of Nara, Japan |
|
|
Daibutsuden c. 762 8th century Nara period Japan (inside Todaiji Temple) |

-temple of the Buddha -image eventually destroyed in fires, replica bronze statue made -massive space to allow for circumambulation of the Giant Buddha |
|
|
Vairocana Buddha (Dainichi) 752 8th century Nara period Japan bronze (inside Todaiji Temple) |

-replica bronze statue of original Giant Buddha after destruction in fires |
|
|
GuKaizhi, Admonitions of the Court Instructress 6th-8th century copy of a Six Dynasties period painting China ink and color on silk handscroll
|

-man writing in a woman's voice prescribing proper behavior for women in court -organized by writing/image/writing/etc... -composed of several panels -one image is of aesthetics letting people hide their true selves due to ease vs. difficulty |
|
|
ZhangXuan, Court Ladies Preparing Newly WovenSilk 8th century Tang Dynasty China ink and color on silk handscroll |

-despite depiction, it is unlikely this ever occurred outside of purely ceremonial acts by court ladies -women dressed in elegant robes of the latest fashion with ornamental forehead marks, and decorative combs in high set hair -Tang Dynasty "fat ladies" |
|
|
ZhangZeduan, Going Up the River in theSpringtime 11th-12th century Northern Song dynasty China ink and color on silk handscroll |

-describes the busy water and land carriage, flourishing markets in the capital of Northern Song dynasty on a spring day -lost inscription indicates the emperor’s love of this scroll -created at a time of economic crisis and civil rebellions at the end of the dynasty, the only subject of this scroll is prosperity and peace |
|
|
FanKuan, Travelers by Streams and Mountains c. 1000 Northern Song dynasty China hanging scroll |

-"shanshui": mountains and waters -"monumental landscape painting" -no one fixed viewing point/vanishing point |
|
|
Guo Xi, Early Spring 1072 Northern Song dynasty China hanging scroll ink on silk |

-"landscape as a gentlemenly occupation" -Gao Xi was a court painter -imperial metaphor (probably done for the birthday of the emperor, "rebirth") |
|
|
Ma Yuan, Viewing Plum Blossoms by Moonlight early 13th century Southern Song dynasty China fan mountedas album leaf ink and color on silk |

-a visual poem evoking a complex sense of time, place, and mood. |
|
|
Huaisu, Autobiography 777 Tang dynasty China ink on paper handscroll |

-got drunk as he wrote/drew characters -was part of literati |
|
|
Qiao Zhongchang, Illustration of the Second Ode to the Red Cliff 1123 Northern Song China handscroll ink onpaper |

-handscroll series similar to "Admonitions..." series -"I crouched on a tiger like boulder and climbed a dragon twisting tree" |
|
|
The Tale of Genji, Chapter 36 The Oak Tree 1 (Kashiwagi): Third Princess, Emperor Suzaku-in, Genji 1120-1150 Heian period Japan ink and colors on decorated paper |

-Genji= "shining one" -Genji's many loves (didn't believe in one love) -theme of Karmic destiny -young Genji had affair & baby with his father's (emperor) consort, the baby raised as son of the emperor |
|
|
The Tale of Genji, The Oak Tree 2: Yugiri, Kashiwagi 1120-1150 Heian period Japan ink and colors on decorated paper |

-Genji= "shining one"-Genji's many loves (didn't believe in one love) -theme of Karmic destiny-young Genji had affair & baby with his father's (emperor) consort, the baby raised as son of the emperor |
|
|
The Tale of Genji, The Oak Tree 3: Genji holding “his son” Kaoru 1120-1150 Heian period Japan ink and colors on decorated paper |

-Genji= "shining one"-Genji's many loves (didn't believe in one love) -theme of Karmic destiny-young Genji had affair & baby with his father's (emperor) consort, the baby raised as son of the emperor |
|
|
The Tale of Genji, Chapter 38 The Bell Cricket 1 (Suzumushi): Third Princess Nyosan 1120-1150 Heian period Japan ink and colors on decorated paper |

-Genji= "shining one"-Genji's many loves (didn't believe in one love) -theme of Karmic destiny-young Genji had affair & baby with his father's (emperor) consort, the baby raised as son of the emperor |
|
|
The Tale of Genji, The Bell Cricket 2: Genji meeting Emperor Reizei-in 1120-1150 Heian period Japan ink and colors on decorated paper |

-Genji= "shining one"-Genji's many loves (didn't believe in one love) -theme of Karmic destiny-young Genji had affair & baby with his father's (emperor) consort, the baby raised as son of the emperor |
|
|
The Tale of Genji, Chapter 40 The Rites (Minori): Genji meeting the dying Lady Murasaki 1120-1150 Heian period Japan ink and colors on decorated paper |

-Genji= "shining one"-Genji's many loves (didn't believe in one love) -theme of Karmic destiny-young Genji had affair & baby with his father's (emperor) consort, the baby raised as son of the emperor |
|
|
Animal Caricatures (Chōjū-jinbutsu-giga) 12th-13th centuries Heian period Japan ink on paper handscroll |

-famous set of four picture scrolls, or emakimono -anthropomorphic rabbits and monkeys bathing and getting ready for a ceremony, a monkey thief runs from animals with sticks and knocks over a frog from the lively ceremony. Further on, the rabbits and monkeys are playing and wrestling while another group of animals participate in a funeral and frog prays to Buddha as the scroll closes |
|
|
Byodoin, Hodo (Phoenix Hall) c. 1053 Heian period Japan |

-originally a monastery -the original statue was lost and replaced in 1053 with a large wooden statue of Amida, a national treasure of the Empire carved by the Japanese artisan Jocho -an artistic reproduction of Amida's Western Pure Land -it's called Phoenix Hall in reference to the 2 phoenixes stretching their wings upon the temple roof |
|
|
Byodoin, Jocho, Amida Buddha and apsaras c. 1053 Heian period Japan |

-destroyed and rebuilt
|
|
|
Byodoin,Jocho, apsaras c. 1053 Heian period Japan |

|
|
|
Gyeongcheonsa pagoda 1348 Goryeo dynasty Korea marble |

-this massive ten-story pagoda is the first one known to be made from marble -base and the main body are elaborately decorated with carvings of Buddhas, bodhisattvas, and floral designs, |
|
|
Kim Wumun, Water Moon Avalokitesvara, Suwol Gwaneum 1310 Goryeo dynasty Korea hanging scroll ink,colors, and gold on silk |

-some areas also painted on back to darken/deepen the tones/colors |
|
|
Celadon kundika c. 13th century Goryeo dynasty Korea stoneware with celadon glaze |

-named for the green glaze -water dropper |
|
|
Kshitigarbha and the Ten Kings of Hell 13th-14th centuries Goryeo dynasty Korea hanging scroll ink, colors, andgold on silk |

-buddha of the underworld -holds wish-granting jewel -4 directional kings in 4 corners to protect -10 kings of hell dressed in official's robes surrounding dog/creature |
|
|
Ginkakuji (“Silver Pavilion”) 15th century Muromachi period retirement villa of Ashikaga Yoshimasa, Japan |

-windows covered in paper -assymetrical shoin architecture -chapel for avalokitesvara |
|
|
Ginkakuji (“Silver Pavilion”), Dojinsai, Kogudo 15th century Muromachi period retirement villa of Ashikaga Yoshimasa, Japan |

-Dojinsai= tea room -host poetry, theater, and tea ceremonies -chanoya= "hot water for tea" -art of preparing and serving matcha |
|
|
Sen no Rikyu, Taian tearoom at Myokian Temple 1582 Momoyama period Kyoto, Japan |

-Sen no Rikyu famous for austerity/wabi-cha and use of calligraphy -course unrefined plaster for walls and use of humble materials -infamous/famous entrance: boulders placed below small sliding crawl-sized door raised from the ground |
|
|
Attributed to Chojiro, Tea bowl named “Oguro” late 16thcentury Momoyama period Japan Raku ware, earthenware with lead glaze |

-Oguro= "big black" -raku: carved and fired, rustic and unrefined |

