![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The Law of Demand
|
as the price of a good or service rises, the quantity demanded by buyers will fall.
Two effects explain this: Substitution Effect Income Effect |
|
|
Substitution Effect
|
If the price of a product rises, buyers will buy less and purchase a substitution instead.
|
|
|
Income Effect
|
A rise in the price of a product is like a decrease in your income. If you continue to purchase the same amount, you will have less money to buy other products.
|
|
|
The Law of Supply
|
As the price of a good or service rises, the quantity supplied by sellers will rise.
|
|
|
The Law of Diminishing Returns
|
With some incomes held fixed, the returns to an input will diminish as more of it is added.
|
|
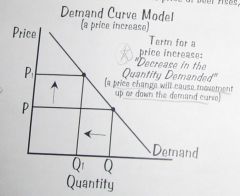
Demand Curve Model:a price increase
|
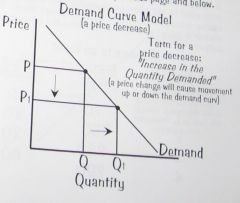
Demand Curve Model: a price decrease
|
|
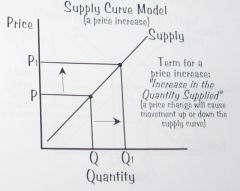
Supply Curve Model: an increase in the quantity supplied
|
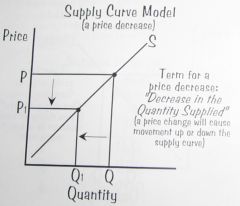
Supply Curve Model: a dedrease in the quantity supplied.
|
|
|
Equilibrium occurs at the price in which the quantity demanded by buyers is equal to the quantity supplied by sellers.
|
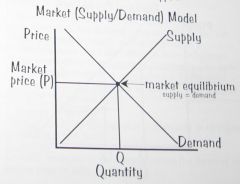
Equilibrium
|
|
|
If there is an increase in demand caused by a factor other than price, the demand curve will shift to the right.
|
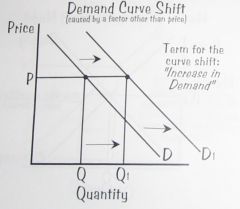
Increase in Demand
|
|
|
If there is a decrease in demand caused by a factor other than price, the demand curve will shift to the left.
|
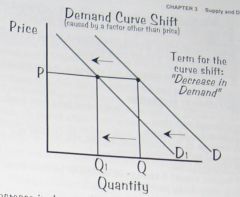
Decrease in Demand
|
|
|
Nonprice determinant that shifts the demand curve (of 10):
1 Product Innovation |
Demand increases because of improvements or changes in the design of a product.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinant that shifts the demand curve (of 10):
2 Income |
Demand increases or decreases because the incomes of buyers rise or fall.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinant that shifts the demand curve (of 10):
3 Advertising |
Sellers influence customers to buy the product.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinant that shifts the demand curve (of 10):
4 Fads |
Brief popularity of a product causes demand to increase significantly for a short time period.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinant that shifts the demand curve (of 10):
5 Quality |
A product defect or discovery that it could be harmful or unsafe changes demand.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinant that shifts the demand curve (of 10):
6 Trends or Preferences |
Unlike a fad, an increase in demand for a product continues over time.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinant that shifts the demand curve (of 10):
7 Number of Buyers |
A change in the numbers of buyers will change the demand for a good or service.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinant that shifts the demand curve (of 10):
8 Expectations |
If buyers expect a change in design or performance, they may delay purchases.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinant that shifts the demand curve (of 10):
9 Weather |
A snowy winter increases demand for snowblowers.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinant that shifts the demand curve (of 10):
10 Other Products |
Substitutes are products that are used in place of other products.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinant that shifts the demand curve (of 10):
11 Legislation |
A new law prohibiting, legalizing, or mandating a product will change demand.
|
|
|
If there is an increase in supply caused by a factor other than price, the supply curve will shift to the right.
|
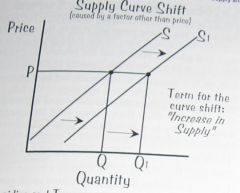
Increase in Supply
|
|
|
If there is a decrease in supply caused by a factor other than price, the supply curve will shift to the left.
|
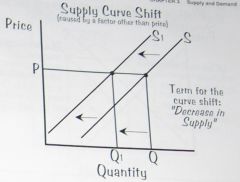
Decrease in supply.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinants that shift the supply curve:
Prices of other products. |
Assume a seller uses its resources to produce two products; if one product rises in price, the supplier will produce more of it and less of the other product.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinants that shift the supply curve:
Technology |
Using computers, software, and robots, producers are able to produce more output in the same amount of time or at a lower cost per unit.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinants that shift the supply curve:
Number of Sellers |
Higher trade barriers such as tariffs or import taxes will reduce the number of foreign sellers in the market. Lower trade barriers will shift the supply curves to the right
|
|
|
Nonprice determinants that shift the supply curve:
Input or Resource Prices |
A rise in the price of inputs paid such as wages paid to labor will shift the supply curve to the left.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinants that shift the supply curve:
Subsidies and Taxes |
Government subsidies or payments to producers lower the costs of production shifting the production curve to the left.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinants that shift the supply curve:
Government Regulations |
The deregulation of the airlines enabled new airlines to enter the market shifting the supply curve to the right.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinants that shift the supply curve:
Expectations |
Producers such as farmers may anticipate that corn prices will soon fall so they sell their stored inventories today causing the supply curve to shift to the right.
|
|
|
Nonprice determinants that shift the supply curve:
Weather |
A drought, unusual coldness, or perfect conditions will shift the supply curves of food products.
|
|
|
What is the effect on the cream cheese market if bagel prices fall?
|
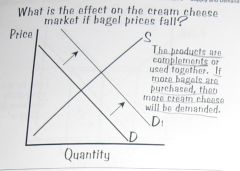
The products are Compliments.
|
|
|
What is the effect on the market for prescription drugs as the baby boomers age?
|
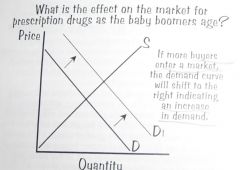
More buyers enter market.
|
|
|
What is the effect on the market for prescription drugs as the baby boomers age?
|
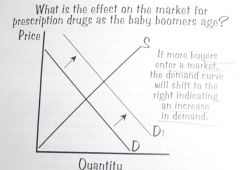
More buyers enter market.
|
|
|
What is the effect on the market for milk if the price is set above equilibrium?
|
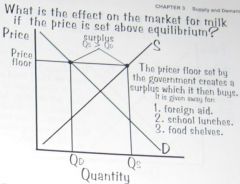
Price floor. A price floor will create a surplus of a good or service.
|
|
|
What is the effect on the market for soybeans if corn prices rise?
|
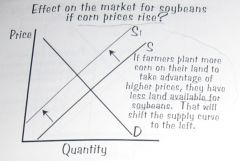
.
|
|
|
What is the effect on the market for organic food if more farms produce it?
|
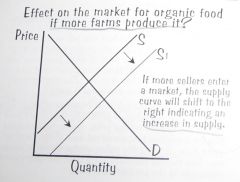
.
|
|
|
What is the effect on the market for donuts if bagle prices rise?
|
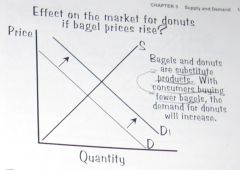
Substitute Products.
|
|
|
What is the effect on the market for organic food if more farms produce it?
|
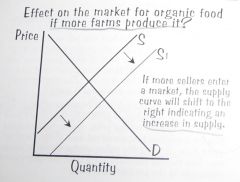
.
|
|
|
Price Ceiling: When the price of an object is set below market equilibrium, it is called a price ceiling. This means that the product cannot be sold above the celilng price.
|
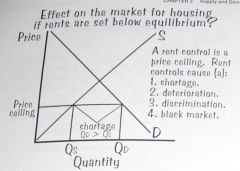
A Price ceiling will cause a shortage of a good or service.
|
|
|
Externalities
|
Costs and benefits that are not internalized.
|
|
|
Pollution is a negative externality.
|
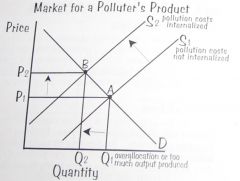
This is why the government must intervene to ensure that the pollution costs are internalized.
|
|
|
Direct Controls
|
Government regulators set maximum levels for pollution.
|
|
|
Public Goods.
|
Public goods are provided by the government because it is in societies best interest.
Two types: Pure Public Goods and Near Public Goods. |
|
|
Pure Public Goods
|
Pure public goods must be provided by the government because of the free-rider problem. If you do not pay for it, you cannot be excluded from consuming it.
Examples: national defense, clean air. |
|
|
Near Public Goods.
|
Near public goods are not pure because the private sector or market can supply them. However some people would be excluded because they could not afford to pay for them. It is considered in society's best interest that everyone should have access to these goods.
Examples: Education, public health measures, infrastructure. |

