![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is economics
|
It is a social science that describes the factors that determine the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.
|
|
|
What is the main economic problem
|
Scarcity (nepriteklius)
|
|
|
Indicate and define resources in economics
|
Land, labor and capital.
|
|
|
Differences of micro and macroeconomics
|
Microeconomics refers to more individual or company specific studies in economics while Macroeconomics refers to big picture study of economics, so looking at concepts like industry, country or global economic factors.
|
|
|
What is demand
|
It is the willingness and ability of buyers to purchase different quantities of a good at different prices during a specific time period.
|
|
|
Why demand might increase (rightward shift in the demand curve)
|
Income increases (for normal goods); Income decreases (for inferior goods); Changes in preferences; The price of substitute increases; The price of complement decreases; The number of buyers increases; Price increase expectations.
|
|
|
Why demand might decrease (leftward shift in the demand curve)
|
Income decreases (for normal goods); Income increases (for inferior goods); Changes in preferences; The price of substitute; The price of complement increases; The number of buyers decreases; Price decrease expectations.
|
|
|
Why does quantity demanded go down as price goes up
|
Because people tend to buy more when price goes down and buy less when price goes up.
|
|
|
What is supply
|
It is the willingness and ability of sellers to produce and offer to sell different quantities of a good at a different prices during a specific time period.
|
|
|
Why supply might increase (rightward shift in the supply curve)
|
The price of relevant resources decreases; The advance in technology; The price of substitute decreases; The price of complement in production increases; The number of sellers increases; Price decrease expectations; The taxes decrease.
|
|
|
Why supply might decrease (leftward shift in the supply curve)
|
The supply of relevant resources increases; Technology gets old; The price of substitute increases; The price of complement decreases; The number of sellers decreases; Price increase expectations; The taxes increase.
|
|
|
Movement and shift of the demand curve
|
Demand curve shifts to the rights as demand increases. It shows how the quantity of a good demanded by consumers depends on its price. It is downward sloping. Holding other things equal, consumers will want to purchase more of a good as its price goes down.
|
|
|
Movement and shift of the supply curve
|
Supply curve shifts to the right as supply increases. It shows how the quantity of a good offered for sale changes as the price of the good changes. It is upward sloping. The higher the price, the more firms are able and willing to produce and sell.
|
|
|
What is equilibrium price
|
It is a price that equates the quantity supplies to the quantity demanded.
|
|
|
What is market mechanism
|
It is a tendency in free market for price to change until the market clears.
|
|
|
What is surplus
|
It is a situation in which the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded.
|
|
|
What is shortage
|
It is a situation in which the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied.
|
|
|
How is equilibrium price determined
|
It is a point where supply and demand curves intersect.
|
|
|
What happens if market price is higher than the equilibrium price
|
The surplus occurs. Goods are storaged thus producers are forced to decrease prices. The quantity demanded increases, the quantity supplied decreases and price moves to equilibrium price.
|
|
|
What happens if market price is lower than the equilibrium price
|
The shortage occurs. Consumers are not able to find the products they need thus they are willing to increase prices. The quantity demanded decreases, the quantity supplied increases and price moves to equilibrium price.
|
|
|
Who initiates new prices
|
When there is surplus, producers initiate new prices, when there is shortage, consumers initiate new prices.
|
|
|
What is elasticity
|
It is a measurement of how responsive one economic variable is to another.
|
|
|
What is the measurement unit of elasticity
|
It does not have a measurement unit.
|
|
|
How do you calculate price elasticity of demand
|
Percentage change in quantity demanded divided by percentage change in price. Percentage change of average of two quantities demanded divided by percentage change of average of two prices.
|
|
|
How do you calculate price elasticity of supply
|
Percentage change in quantity supplied divided by percentage change in price. Percentage change of average of two quantities supplied divided by percentage change of average of two prices.
|
|
|
What might be the values of elasticity
|
Perfectly elastic (E = infinity), relatively elastic (E>1), unit elastic (E=1), relatively inelastic (0
|
|
|
Represent values of elasticity of demand graphically |
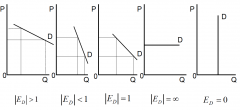
|
|
|
Represent values of elasticity of supply graphically
|
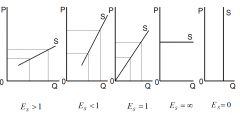
|
|
|
Examples of perfectly elastic demand
|
A small percentage change in price causes an extremely large percentage change in the quantity demanded. For ex: the demand of electricity of Tesla.
|
|
|
Examples of relatively elastic demand
|
The quantity demanded changes proportionately more than price changes.
|
|
|
Examples of unit elastic demand
|
The quantity demanded changes proportionately to price changes.
|
|
|
Examples of relatively inelastic demand
|
The quantity demanded changes proportionately less than price changes.
|
|
|
Examples of perfectly inelastic demand
|
The quantity demanded does not change as price changes.
|
|
|
Examples of perfectly elastic supply
|
The quantity supplied does not change as price changes.
|
|
|
Examples of relatively elastic supply
|
The quantity supplied changes proportionately more than price changes.
|
|
|
Examples of unit elastic supply
|
The quantity supplied changes proportionately to price changes.
|
|
|
Examples of relatively inelastic supply
|
The quantity supplied changes proportionately less than price changes.
|
|
|
Examples of perfectly inelastic supply
|
The price does not change as the quantity supplied changes.
|
|
|
What are time periods in economics
|
Moment (instant); short period of time (short-run); long period of time (long-run).
|
|
|
If a firm’s goal is to maximize income, what should you do increase or decrease prices
|
It depends on elasticity of demand. When demand is elastic, total revenue increases when the price decreases. When the demand is inelastic, total revenue increases when the price increases. When the demand is unit elastic, total revenue doesn’t change when price changes.
|
|
|
What is income elasticity of demand
|
It is a measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in income.
|
|
|
How does demand depend on normal good
|
For normal goods the income elasticity of demand is positive, meaning that the quantity demanded for normal necessities will increase with income, but at a slower rate than luxury goods. For ex: car market.
|
|
|
How does demand depend on inferior good
|
For inferior goods the income elasticity of demand is negative, meaning that the quantity demanded for inferior goods falls as incomes rise. For ex: tobacco.
|
|
|
What is cross elasticity of demand
|
It is a measure of the responsiveness in quantity demanded of one good to changes in the price of another good. It indicates whether the goods are substitutes or complements.
|
|
|
Positive cross elasticity of demand
|
If the elasticity coefficient is positive, the goods are substitutes meaning that the increase in one product’s price will increase consumption of another product.
|
|
|
Negative cross elasticity of demand
|
If the elasticity coefficient is negative, the goods are complements meaning that increase in one product’s price will decrease consumption of another product.
|

